The success of non-ABO-identical convalescent plasma transfusion in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) related acute respiratory distress syndrome (CARDS): a case-report
Convalescent plasma for COVID-19
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54205/ccc.v30.254752Keywords:
Convalescent plasma, Coronavirus disease 2019, Acute respiratory distress syndrome, Incompatible ABO-Blood Group, ThailandAbstract
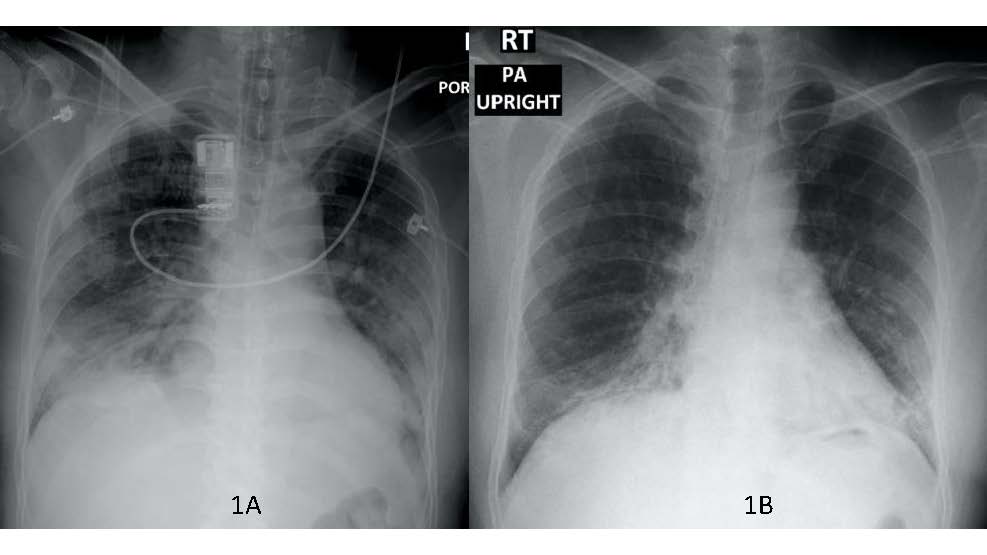
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is pandemic with substantial fatality without specific treatment. Convalescent plasma is used to treat infectious diseases including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection, because of the effect of direct neutralizing and suppression of viremia, and immunomodulation effect. Although several anti-cytokine agents were suggested to improve outcomes of the patient, the unavailability of drugs will be a major problem for accessing. We reported the experience of convalescent plasma transfusion for COVID-19 related acute respiratory distress syndrome (CARDS), who refractory to standard treatment and clinically improvement after convalescent plasma transfusion, despite unidentical blood group.
Downloads
References
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020; 395(10223):497-506.
Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA. 2020; 323(18):1824-36.
Di Minno G, Mannucci PM, Ironside JW, Perno CF, Gürtler L, Aledort L. Convalescent plasma for administration of passive antibodies against viral agents. Haematologica. 2020; 105(12):2710-5.
Brown BL, McCullough J. Treatment for emerging viruses: Convalescent plasma and COVID-19. Transfus Apher Sci. 2020; 59(3):102790.
Shen C, Wang Z, Zhao F, Yang Y, Li J, Yuan J, et al. Treatment of 5 Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 With Convalescent Plasma. JAMA. 2020; 323(16):1582-9.
Rojas M, Rodriguez Y, Monsalve DM, Acosta-Ampudia Y, Camacho B, Gallo JE, et al. Convalescent plasma in Covid-19: Possible mechanisms of action. Autoimmun Rev. 2020; 19(7):102554.
Estcourt LJ, Turgeon AF, McQuilten ZK, McVerry BJ, Al-Beidh F, Annane D, et al. Effect of Convalescent Plasma on Organ Support-Free Days in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama. 2021; 326(17):1690-702.
Bégin P, Callum J, Jamula E, Cook R, Heddle NM, Tinmouth A, et al. Convalescent plasma for hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an open-label, randomized controlled trial. Nat Med. 2021; 27(11):2012-24.
Group RC. Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2021; 397(10289):2049-59.
Simonovich VA, Burgos Pratx LD, Scibona P, Beruto MV, Vallone MG, Vázquez C, et al. A Randomized Trial of Convalescent Plasma in Covid-19 Severe Pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384(7):619-29.
Lang-Meli J, Fuchs J, Mathé P, Ho H-e, Kern L, Jaki L, et al. Case Series: Convalescent Plasma Therapy for Patients with COVID-19 and Primary Antibody Deficiency. Journal of Clinical Immunology. 2021.
WHO recommends against the use of convalescent plasma to treat COVID-19 [press release]. 2021.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 The Thai Society of Critical Care Medicine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




