A Thai guideline summary in management of pediatric septic shock
Thai pediatric septic shock guideline
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54205/ccc.v32.266195Keywords:
Pediatric, Septic shock, Thai guideline, ManagementAbstract
Sepsis-associated organ dysfunction, particularly septic shock, is a prevalent critical illness characterized by increased morbidity and mortality, particularly in children. Recognizing the imperative to enhance outcomes, a septic shock guideline tailored for pediatric patients was formulated. This guideline strives to establish an evidence-based framework for the effective management of septic shock and sepsis-associated organ dysfunction in Thai children. Key components encompass the prompt identification and stabilization of patients, meticulous titration of fluids and vasoactive agents, initiation of empirical antimicrobial therapy, judicious infectious source control, respiratory support, administration of sedation and analgesia, blood and blood product transfusion, correction of electrolyte imbalances, management of metabolic derangements, renal replacement therapy, and the implementation of multimodal monitoring. The objective is to optimize management, achieving therapeutic goals while continuously reassessing the patient's condition. Additionally, this guideline demonstrates adaptability by tailoring its suggestions to the resources available in Thailand’s medical facilities. Recognizing the diverse capabilities of healthcare institutions, the guideline endeavors to ensure its implementation is practical and feasible.
Downloads
References
Fitzgerald JC, Weiss SL, Kissoon N. 2016 Update for the Rogers' Textbook of pediatric intensive care: Recognition and initial management of shock. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2016;17(11):1073-9.
Balamuth F, Weiss SL, Neuman MI, Scott H, Brady PW, Paul R, et al. Pediatric severe sepsis in U.S. children's hospitals. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014;15(9):798-805.
Samransamruajkit R, Wong JJ, Smathakane C, Anantasit N, Sunkonkit K, Ong J, et al. Pediatric severe sepsis and shock in three asian countries: A retrospective study of outcomes in nine PICUs. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2021;22(8):713-21.
Weiss SL, Peters MJ, Alhazzani W, Agus MSD, Flori HR, Inwald DP, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign international guidelines for the management of septic shock and sepsis-associated organ dysfunction in children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2020;21(2):e52-e106.
Miranda M, Nadel S. Pediatric sepsis: A summary of current definitions and management recommendations. Curr Pediatr Rep. 2023;11(2):29-39.
Goldstein B, Giroir B, Randolph A, International Consensus Conference on Pediatric S. International pediatric sepsis consensus conference: definitions for sepsis and organ dysfunction in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2005;6(1):2-8.
Davis AL, Carcillo JA, Aneja RK, Deymann AJ, Lin JC, Nguyen TC, et al. American college of critical care medicine clinical practice parameters for hemodynamic support of pediatric and neonatal septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(6):1061-93.
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(3):304-77.
Dien Bard J, McElvania TeKippe E. Diagnosis of bloodstream infections in children. J Clin Microbiol. 2016;54(6):1418-24.
Buttery JP. Blood cultures in newborns and children: Optimising an everyday test. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2002;87(1):F25-8.
de Jong E, van Oers JA, Beishuizen A, Vos P, Vermeijden WJ, Haas LE, et al. Efficacy and safety of procalcitonin guidance in reducing the duration of antibiotic treatment in critically ill patients: a randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16(7):819-27.
Chuang YY, Huang YC, Lin TY. Toxic shock syndrome in children: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Paediatr Drugs. 2005;7(1):11-25.
Wilkins AL, Steer AC, Smeesters PR, Curtis N. Toxic shock syndrome - the seven Rs of management and treatment. J Infect. 2017;74 Suppl 1:S147-S152.
Topjian AA, Raymond TT, Atkins D, Chan M, Duff JP, Joyner BL, Jr., et al. Part 4: Pediatric basic and advanced life support: 2020 American heart association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2020;142(16_suppl_2):S469-S535.
Rowan KM, Angus DC, Bailey M, Barnato AE, Bellomo R, Canter RR, et al. Early, Goal-directed therapy for septic shock - a patient-level meta-analysis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(23):2223-2234.
Carioca FL, de Souza FM, de Souza TB, Rubio AJ, Brandão MB, Nogueira RJN, et al. Point-of-care ultrasonography to predict fluid responsiveness in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Paediatr Anaesth. 2023;33(1):24-37.
Walker SB, Winters JM, Schauer JM, Murphy P, Fawcett A, Sanchez-Pinto LN. Performance of tools and measures to predict fluid responsiveness in pediatric shock and critical illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2024;25(1):24-36.
Weiss SL, Keele L, Balamuth F, Vendetti N, Ross R, Fitzgerald JC, Gerber JS. Crystalloid fluid choice and clinical outcomes in pediatric sepsis: A matched retrospective cohort study. J Pediatr. 2017;182:304-10 e10.
Emrath ET, Fortenberry JD, Travers C, McCracken CE, Hebbar KB. Resuscitation with balanced fluids is associated with improved survival in pediatric severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(7):1177-83.
Fernandez-Sarmiento J, Salazar-Pelaez LM, Acevedo L, Nino-Serna LF, Florez S, Alarcon-Forero L, et al. Endothelial and glycocalyx biomarkers in children with sepsis after one bolus of unbalanced or balanced crystalloids. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2023;24(3):213-21.
Sankar J, Muralidharan J, Lalitha AV, Rameshkumar R, Pathak M, Das RR, et al. Multiple electrolytes solution versus saline as bolus fluid for resuscitation in pediatric septic shock: A multicenter randomized clinical trial. Crit Care Med. 2023.
Joannidis M, Druml W, Forni LG, Groeneveld ABJ, Honore PM, Hoste E, et al. Prevention of acute kidney injury and protection of renal function in the intensive care unit: update 2017: Expert opinion of the working group on prevention, AKI section, European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(6):730-49.
Ranjit S, Aram G, Kissoon N, Ali MK, Natraj R, Shresti S, et al. Multimodal monitoring for hemodynamic categorization and management of pediatric septic shock: a pilot observational study. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014;15(1):e17-26.
Ventura MAC, Sheih HH, Bousso A, Goes PF, Fernandez IDCFO, de Souza DC, et al. Double-blind prospective randomized controlled trial of dopamine versus epinephrine as first-line vasoactive drugs in pediatric septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2015; 43(11): 2292-302.
Ramaswamy KN, Singhi S, Jayashree M, Bansal A, Nallasamy K. Double-blind randomized clinical trial comparing dopamine and epinephrine in pediatric fluid-refractory hypotensive septic shock. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2016;17(11):e502-e512.
Rodriguez-Nunez A, OUlego-Erroz I, Gil-Anton J, Perez-Cabllero C, Lopez-Herce J, Gaboli M, et al. Continuous terlipressin infusion as rescue treatment in a case series of children with refractory septic shock Ann Pharmacother. 2010; 44(10): 1545 – 53.
Otero Luna AV, Johnson R, Funaro M, Canarie FM , Pierce WR. Methylene blue for refractory shock in children: A systematic review and survey practice analysis. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2020;21(6):e378-e386.
Zhang Z, Chen K. Vasoactive agents for the treatment of sepsis. Ann Transl Med. 2016;4(17):333.
Emeriaud G, Lopez-Fernandez YM, Iyer NP, Bembea MM, Agulnik A, Barbaro RP, et al. Executive summary of the second international guidelines for the diagnosis and management of pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (PALICC-2). Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2023;24(2):143-68.
Conway JA, Kharayat P, Sanders RC, Jr., Nett S, Weiss SL, Edwards LR, et al. Ketamine use for tracheal intubation in critically ill children is associated with a lower occurrence of adverse hemodynamic events. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(6):e489-e97.
Albert SG, Ariyan S, Rather A. The effect of etomidate on adrenal function in critical illness: A systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37(6):901-10.
Peerapornratana S, Manrique-Caballero CL, Gomez H, Kellum JA. Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 2019;96(5):1083-99.
Girardot T, Schneider A, Rimmelé T. Blood purification techniques for sepsis and septic AKI. Semin Nephrol. 2019;39(5):505-14.
Alobaidi R, Morgan C, Basu RK, Stenson E, Featherstone R, Majumdar SR, Bagshaw SM. Association between fluid balance and outcomes in critically ill children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatrics. 2018;172(3):257-68.
Leititis JU, Brandis M. Critical care in uraemic children. Pediatr Nephrol. 1992;6(1):88-95.
Sagy M, Silver P. Continuous flow peritoneal dialysis as a method to treat severe anasarca in children with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 1999;27(11):2532-2536.
Latour-Pérez J, Palencia-Herrejón E, Gómez-Tello V, Baeza-Román A, García-García MA, Sánchez-Artola B. Intensity of continuous renal replacement therapies in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2011;39(3):373-83.
Becker S, Lang H, Vollmer Barbosa C, Tian Z, Melk A, Schmidt BMW. Efficacy of CytoSorb®: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2023;27(1):215.
Wang G, He Y, Guo Q, Zhao Y, He J, Chen Y, et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy with the adsorptive oXiris filter may be associated with the lower 28-day mortality in sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2023;27(1):275.
Siripanadorn T, Samransamruajkit R. The role of blood purification by ha330 as adjunctive treatment in children with septic shock. Blood Purif. 2023;52(6):549-55.
Chen JJ, Lai PC, Lee TH, Huang YT. Blood purification for adult patients with severe infection or sepsis/septic shock: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Care Med. 2023.
Saetang P, Samransamruajkit R, Singjam K, Deekajorndech T. Polymyxin B. Hemoperfusion in pediatric septic shock: Single-center observational case series. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2022;23(8):e386-e91.
Borthwick EM, Hill CJ, Rabindranath KS, Maxwell AP, McAuley DF, Blackwood B. High-volume haemofiltration for sepsis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;1(1):Cd008075.
Borthwick EM, Hill CJ, Rabindranath KS, Maxwell AP, McAuley DF, Blackwood B. High-volume haemofiltration for sepsis in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;1(1):Cd008075.
Li P, Qu LP, Qi D, Shen B, Wang YM, Xu JR, et al. High-dose versus low-dose haemofiltration for the treatment of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2017;7(10):e014171.
John JC, Taha S, Bunchman TE. Basics of continuous renal replacement therapy in pediatrics. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2019;38(4):455-61.
Vinsonneau C, Allain-Launay E, Blayau C, Darmon M, du Cheyron D, Gaillot T, et al. Renal replacement therapy in adult and pediatric intensive care. Annals of Intensive Care. 2015;5(1):58.
Ullian ME. The role of corticosteroids in the regulation of vascular tone. Cardiovascular Research. 1999;41(1):55-64.
Venkatesh B, Cohen J. Hydrocortisone in vasodilatory shock. Crit Care Clin. 2019;35(2):263-75.
Annane D, Pastores SM, Rochwerg B, Arlt W, Balk RA, Beishuizen A, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency (CIRCI) in critically ill patients (Part I): Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM) 2017. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(12):1751-63.
Annane D, Bellissant E, Bollaert PE, Briegel J, Keh D, Kupfer Y. Corticosteroids for treating sepsis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2015(12):Cd002243.
Gibbison B, López-López JA, Higgins JP, Miller T, Angelini GD, Lightman SL, Annane D. Corticosteroids in septic shock: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2017;21(1):78.
Rochwerg B, Oczkowski SJ, Siemieniuk RAC, Agoritsas T, Belley-Cote E, D'Aragon F, et al. Corticosteroids in sepsis: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(9):1411-20.
Zhou X, Hu C, Yao L, Fan Z, Sun L, Wang Y, Xu Z. Effect of adjunctive corticosteroids on clinical outcomes in adult patients with septic shock - a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and trial sequential analysis. J Crit Care. 2018;48:296-306.
Fang F, Zhang Y, Tang J, Lunsford LD, Li T, Tang R, et al. Association of corticosteroid treatment with outcomes in adult patients with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(2):213-23.
Annane D, Bellissant E, Bollaert PE, Briegel J, Keh D, Kupfer Y, et al. Corticosteroids for treating sepsis in children and adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;12(12):Cd002243.
Lyu QQ, Chen QH, Zheng RQ, Yu JQ, Gu XH. Effect of Low-Dose Hydrocortisone therapy in adult patients with septic shock: A meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Intensive Care Med. 2020;35(10):971-83.
Nichols B, Kubis S, Hewlett J, Yehya N, Srinivasan V. Hydrocortisone therapy in catecholamine-resistant pediatric septic shock: A pragmatic analysis of clinician practice and association with outcomes. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017;18(9):e406-e14.
Lacroix J, Hébert PC, Hutchison JS, Hume HA, Tucci M, Ducruet T, et al. Transfusion strategies for patients in pediatric intensive care units. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(16):1609-19.
Nellis ME, Karam O, Valentine SL, Bateman ST, Remy KE, Lacroix J, et al. Executive summary of recommendations and expert consensus for plasma and platelet transfusion practice in critically ill children: From the Transfusion and Anemia EXpertise Initiative-Control/Avoidance of Bleeding (TAXI-CAB). Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2022;23(1):34-51.
Agus MS, Wypij D, Hirshberg EL, Srinivasan V, Faustino EV, Luckett PM, et al. Tight glycemic control in critically ill children. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(8):729-41.
Chen L, Li T, Fang F, Zhang Y, Faramand A. Tight glycemic control in critically ill pediatric patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2018;22(1):57.
Dias CR, Leite HP, Nogueira PC, Brunow de Carvalho W. Ionized hypocalcemia is an early event and is associated with organ dysfunction in children admitted to the intensive care unit. J Crit Care. 2013;28(5):810-5.
Zayed Y, Alzghoul BN, Banifadel M, Venigandla H, Hyde R, Sutchu S, et al. Vitamin C, Thiamine, and hydrocortisone in the treatment of sepsis: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Intensive Care Med 2022;37:327-36.
Wang K, Yin L, Song Y, Zhang M, Lu Y, Wang S. The Use of Hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid and thiamine in patients with sepsis and septic shock - A systematic review. J Pharm Pract. 2023;36:933-40.
Wald EL, Sanchez-Pinto LN, Smith CM, Moran T, Badke CM, Barhight MF, Malakooti MR. Hydrocortisone-ascorbic acid-thiamine use associated with lower mortality in pediatric septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201(7):863-7.
Weiss SL, Blowey B, Keele L, Ganetzky R, Murali CN, Fitzgerald JC, et al. Matched retrospective cohort study of thiamine to treat persistent hyperlactatemia in pediatric septic shock. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2019;20(9):e452-e6.
Schlapbach LJ, Gibbons K, Ridolfi R, Harley A, Cree M, Long D, et al. Resuscitation in pediatric sepsis using metabolic resuscitation-a randomized controlled pilot study in the pediatric intensive care unit (RESPOND PICU): Study Protocol and Analysis Plan. Front Pediatr. 2021;9:663435.
Alejandria MM, Lansang MA, Dans LF, Mantaring JB, 3rd. Intravenous immunoglobulin for treating sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(9):CD001090.
Lappin E, Ferguson AJ. Gram-positive toxic shock syndromes. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009;9(5):281-90.
Group IC, Brocklehurst P, Farrell B, King A, Juszczak E, Darlow B, et al. Treatment of neonatal sepsis with intravenous immune globulin. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(13):1201-11.
Adeva-Andany MM, Fernandez-Fernandez C, Mourino-Bayolo D, Castro-Quintela E, Dominguez-Montero A. Sodium bicarbonate therapy in patients with metabolic acidosis. Scientific World J. 2014;2014:627673.
Rimmer E, Houston BL, Kumar A, Abou-Setta AM, Friesen C, Marshall JC, et al. The efficacy and safety of plasma exchange in patients with sepsis and septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2014;18(6):699.
Chong M, Lopez-Magallon AJ, Saenz L, Sharma MS, Althouse AD, Morell VO, et al. Use of Therapeutic plasma exchange during extracorporeal life support in critically ill cardiac children with thrombocytopenia-associated multi-organ failure. Front Pediatr. 2017;5:254.
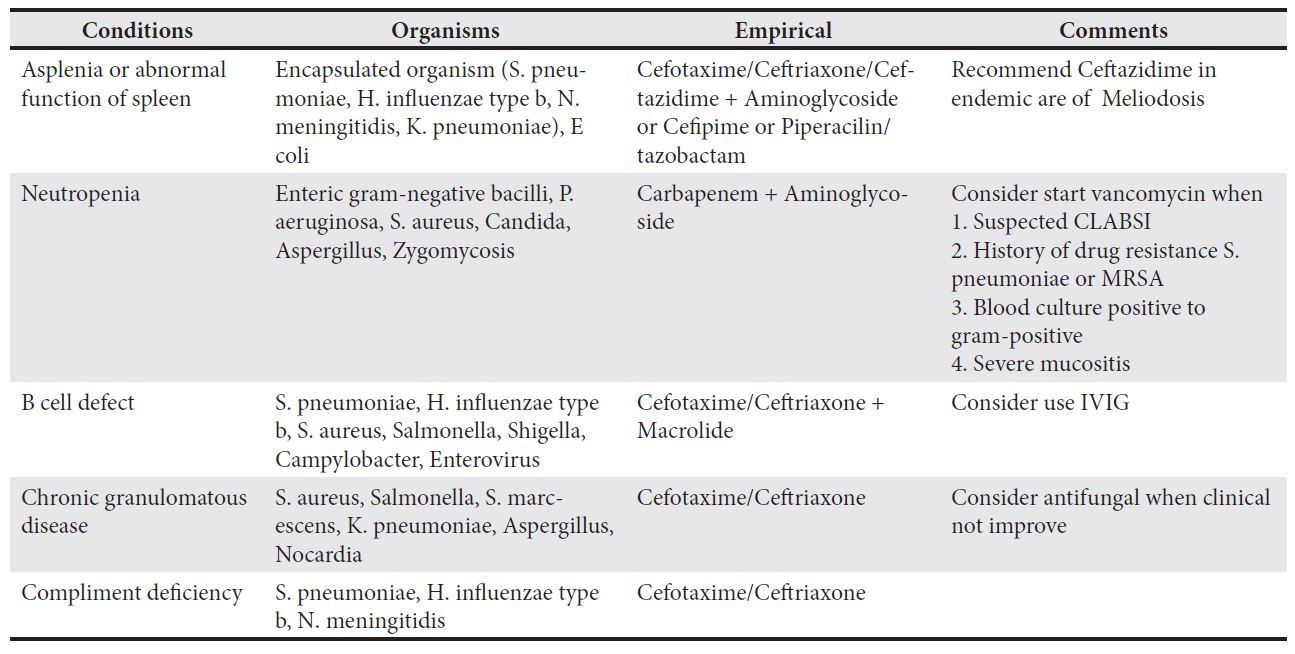
Mau LB, Bain V. Antimicrobial therapy in pediatric sepsis: What is the best strategy? Front Pediatr. 2022;10:830276.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Thai Society of Critical Care Medicine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




