ผลของการฝึกกล้ามเนื้อหน้าท้องที่มีต่อความแข็งแรงของกล้ามเนื้อหายใจออกในนักศึกษาเพศชายระดับมหาวิทยาลัยที่สูบบุหรี่เป็นประจำ
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
อัตราการสูบบุหรี่ในกลุ่มวัยรุ่นมีแนวโน้มเพิ่มขึ้นอย่างต่อเนื่อง มีงานวิจัยที่พบว่า ผู้ที่สูบบุหรี่เป็นประจำ จะมีค่าความแข็งแรงของกล้ามเนื้อหายใจออกที่ต่ำกว่าผู้ที่ไม่สูบบุหรี่ ซึ่งอาจส่งผลกระทบต่อสมรรถภาพปอด งานวิจัยที่ผ่านมาบ่งชี้ว่า การฝึกความแข็งแรงของกล้ามเนื้อหน้าท้อง สามารถช่วยเพิ่มความแข็งแรงของกล้ามเนื้อหายใจได้ ดังนั้นการฝึกความแข็งแรงของกล้ามเนื้อหน้าท้องน่าจะเป็นทางเลือกหนึ่งในการป้องกันผลกระทบดังกล่าวในวัยรุ่นที่สูบบุหรี่เป็นประจำ
วัตถุประสงค์การวิจัย : เพื่อศึกษาผลของการฝึกกล้ามเนื้อหน้าท้องต่อความแข็งแรงของกล้ามเนื้อหายใจออกและสมรรถภาพปอด ในนักศึกษาระดับมหาวิทยาลัยเพศชาย
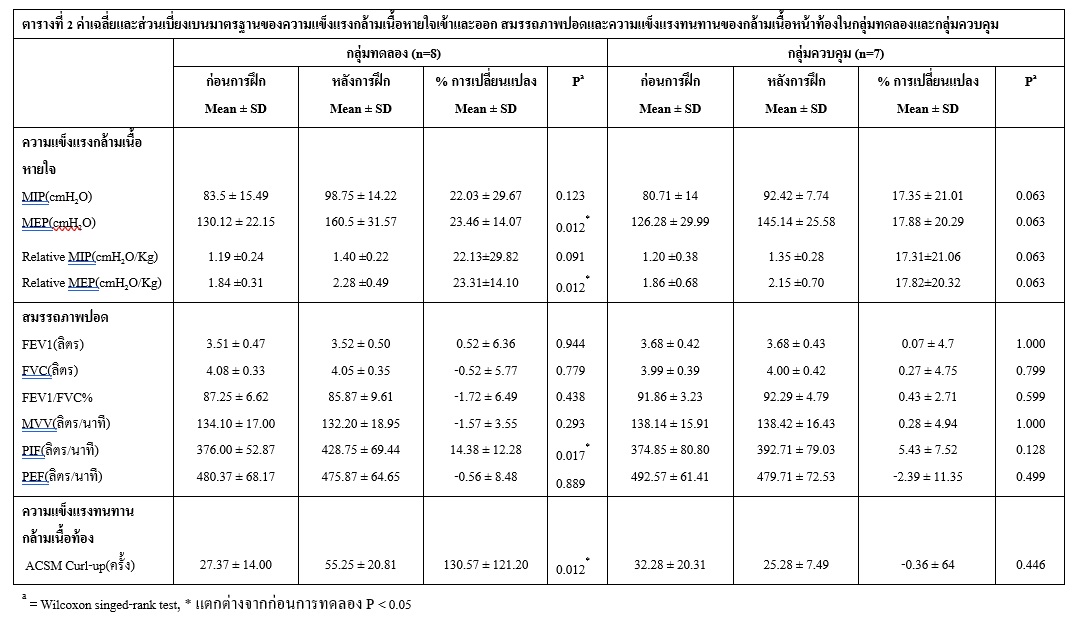
วิธีการวิจัย : นักศึกษาระดับมหาวิทยาลัยเพศชาย อายุ 18-22 ปี สุขภาพดี สูบบุหรี่เป็นประจำ จำนวน 15 คน แบ่งด้วยการสุ่มแบบอิสระเป็น 2 กลุ่ม กลุ่มทดลอง 8 คน กลุ่มควบคุม 7 คน โดยกลุ่มทดลองเข้ารับการฝึกกล้ามเนื้อหน้าท้อง 2 วันต่อสัปดาห์ ระยะเวลาทั้งหมด 8 สัปดาห์ ขณะที่กลุ่มควบคุมไม่ได้รับการฝึกใด ทั้งนี้ ก่อนและหลังการทดลองผู้เข้าร่วมการทดลองทุกคนได้รับการทดสอบ ความแข็งแรงกล้ามเนื้อหายใจเข้าและออก สมรรถภาพปอด และความแข็งแรงทนทานของกล้ามเนื้อหน้าท้อง
ผลการวิจัย : ภายหลังการฝึกกลุ่มทดลองมีค่าแรงดันสูงสุดขณะหายใจออก (MEP) เพิ่มขึ้น เปรียบเทียบกับก่อนการทดลอง อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ 0.05 ขณะที่กลุ่มควบคุมไม่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงค่าแรงดันสูงสุดขณะหายใจเข้า (MIP) และค่าสมรรถภาพปอดของทั้งสองกลุ่มไม่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงทั้งก่อนและหลังการทดลอง อย่างไรก็ตาม เปอร์เซ็นต์ความแข็งแรงและทนทานของกล้ามเนื้อหน้าท้องของกลุ่มทดลองมีค่าเพิ่มขึ้นและแตกต่างจากกลุ่มควบคุมอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ 0.05
สรุปผลการวิจัย : การฝึกกล้ามเนื้อหน้าท้องสามารถเพิ่มความแข็งแรงกล้ามเนื้อหายใจออกได้ไม่แตกต่างกับควบคุม แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม ความแข็งแรงกล้ามเนื้อหายใจออก ความแข็งแรงและทนทานของกล้ามเนื้อหน้าท้อง และสมรรถภาพปอดมีแนวโน้มเพิ่มขึ้นดีกว่าภายหลังการฝึก
Article Details
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Aliverti, A. (2016). The respiratory muscles during exercise. Breathe (Sheffield, England), 12(2), 165-168.
Bostanci, Ö., Mayda, H., Yılmaz, C., Kabadayı, M., Yılmaz, A. K., & Özdal, M. (2019). Inspiratory muscle training improves pulmonary functions and respiratory muscle strength in healthy male smokers. Respiratory Physiology and Neurobiology, 264, 28-32.
Cohen J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. New York, NY: Routledge Academic. Ferguson, B. (2014). ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription 9th Ed. 2014. The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association, 58(3), 328-328.
Gold, D. R., Wang, X., Wypij, D., Speizer, F. E., Ware, J. H., & Dockery, D. W. (1996). Effects of cigarette smoking on lung function in adolescent boys and girls. New England Journal of Medicine, 335 (13), 931-937.
Inoue-Choi M., Liao L.M., Reyes-Guzman C., Hartge P., Caporaso N., Freedman N.D. Association of Long-term, Low-Intensity Smoking With All-Cause and Cause- Specific Mortality in the National Institutes of Health-AARP Diet and Health Study. JAMA Internal Medicine. 2017;177(1):87-95.
Inthachai, T., Demekul, K., Phonsatsadee, N., Puttitommagool, P., & Boonyachart, N. (2019). Effects of physical activity and smoking on cardio-ankle vascular index, respiratory muscle strength, and exercise performance in early normal weight adulthood: a cross-sectional study. Journal of Exercise and Rehabilitation, 15(6), 804-810.
Ishida, H., Fujisawa, M., Yokoyama, R., Suehiro, T., & Watanabe, S. (2017). Electromyographic activities of the abdominal muscles during 30% and 75% of maximum expiratory pressure. Journal of Bodywork and Movment Therapies, 21(4), 794-797.
Ito, K., Nonaka, K., Ogaya, S., Ogi, A., Matsunaka, C., & Horie, J. (2016). Surface electromyography activity of the rectus abdominis, internal oblique, and external oblique muscles during forced expiration in healthy adults. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology, 28, 76-81.
Laveneziana P., Albuquerque A., Aliverti A., Babb T., Barreiro E., Dres M., Dubé B.P., Fauroux B., Gea J., Guenette J.A., Hudson A. L., Kabitz H.J., Laghi F., Langer D., Luo Y.M., Neder J. A., O’Donnell D., Polkey M.I., Rabinovich R.A., Rossi A., Series F., Similowski T., Spengler C.M., Vogiatzis I, Verges S.(2019). ERS statement on respiratory muscle testing at rest and during exercise. European Respiratory Journal . 53, 01214-2018
Maeo, S., Takahashi, T., Takai, Y., & Kanehisa, H. (2013). Trunk muscle activities during abdominal bracing: comparison among muscles and exercises. Journal of Sports Scince and Medicine, 12(3), 467-474.
Magni, C., Chellini, E., Lavorini, F., Fontana, G. A., & Widdicombe, J. (2011). Voluntary and reflex cough: similarities and differences. Pulmonary Pharmacology Therapeutics, 24(3), 308-311.
Miller, M. R., Hankinson, J., Brusasco, V., Burgos, F., Casaburi, R., Coates, A., Wanger, J. (2005). Standardisation of spirometry. European Respiratory Journal, 26(2), 319-338. Oliva-Lozano, J. M., & Muyor, J. M. (2020).
Core Muscle Activity During Physical Fitness Exercises: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(12), 4306.
Park, J. H., Kang, S.-W., Lee, S. C., Choi, W. A., & Kim, D. H. (2010). How respiratory muscle strength correlates with cough capacity in patients with respiratory muscle weakness. Yonsei Medical Journal, 51(3), 392-397.
Rexhepi, A., & Brestovci, B. (2008). Influence Of Smoking And Physical Activity On Pulmonary Function. Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine, 11.
Rodriguez, N.I.,Alarcon, S.M.,Gutierrez,G.C., Hermosilla, R.P., Contreras, G.T., Baez, R.C. (2014). Efecto del entrenamiento de músculos abdominales sobre la función respiratoria en adolescentes sanos: Estudio piloto. Revista chilena de enfermedades respiratorias., 30, 203-211.
Willett, G. M., Hyde, J. E., Uhrlaub, M. B., Wendel, C. L., & Karst, G. M. (2001). Relative activity of abdominal muscles during commonly prescribed strengthening exercises. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Reserch, 15(4), 480-485.