Factors Related to Quality of Life Among Persons with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Wenzhou, China: A Cross Sectional Study
คำสำคัญ:
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, quality of life, lower urinary tract symptoms, social support, sleep disturbance, depressionบทคัดย่อ
The aim of this research was to describe quality of life (QOL) and examine its relationship with the severity of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), sleep disturbance, depression, and social support among the persons with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) in Wenzhou, China. A simple random sampling technique was used to recruit 100 individuals with BPH, who came to follow up on their health at the Urological Clinic outpatient department of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University in Wenzhou, China. Research instruments included the demographic data questionnaire, the International Prostate Symptoms Score, the Verran and Snyder-Halpern Sleep Scale, the Geriatric Depression Scale-15, the Social Support Rating Scale, and the revised version of the Quality of Life Scale for BPH Patients, with Cronbach’s alpha values of 89, 92, 79, 88, and 94, respectively. Data was analyzed by descriptive statistics and Pearson’s correlation.
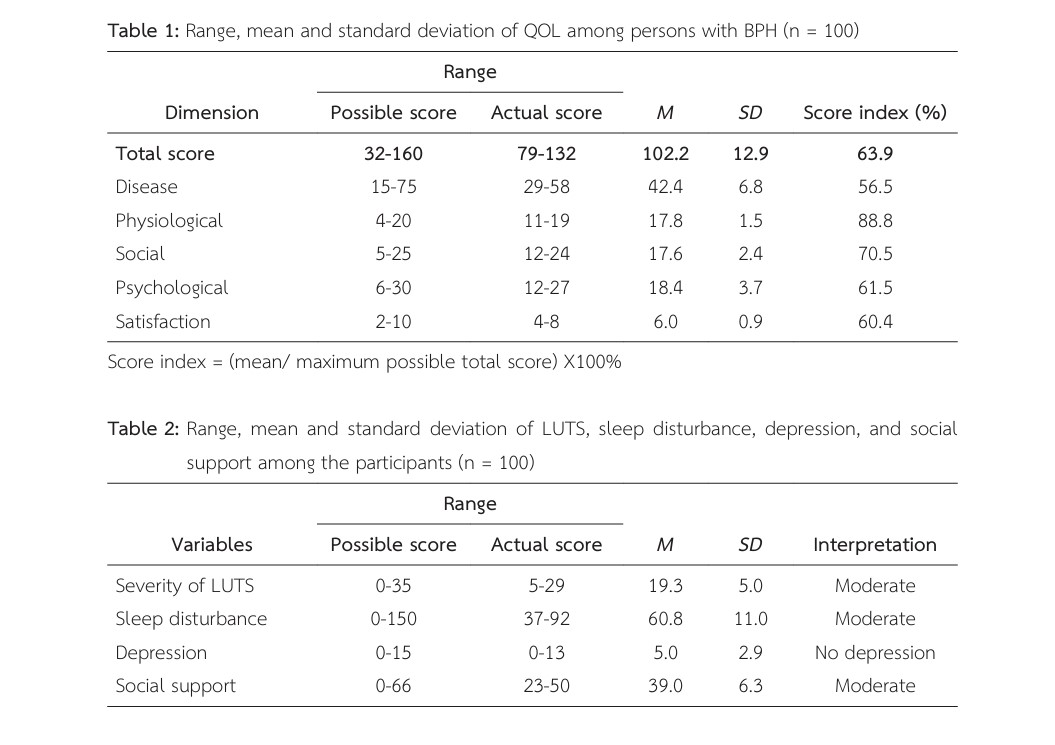
The results of this study showed that the mean score of QOL of BPH persons was 102.2 (SD = 12.9) out of 160. There was a significant positive relationship between social support and QOL among persons with BPH (r = .485, p < .001). Severity of LUTS (r = -.736, p < .001), sleep disturbance (r = -.553, p < .001), and depression (r = -.670, p < .001) had a negative relationship with QOL among them.
The findings in this study could make nurses and other health care providers have a better understanding towards the QOL of BPH persons in Wenzhou, China. Moreover, the results are useful for the development of effective interventions to reduce depression, sleep disturbances, LUTS, and increase social support, then improve the QOL of BPH persons.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Alcaraz, A., Carballido-Rodríguez, J., Unda-Urzaiz, M., Medina-López, R., Ruiz-Cerdá, J. L., Rodríguez- Rubio, F., & Manasanch, J. (2016). Quality of life in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms associated with BPH: Change over time in real-life practice according to treatment--the QUALIPROST study. International Urology and Nephrology, 48(5), 645-656.
Baek, Y., Jung, K., Kim, H., & Lee, S. (2020). Association between fatigue, pain, digestive problems, and sleep disturbances and individuals’ health-related QOL: A nationwide survey in South Korea. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 18(1), 159.
Bai, J., & Cheng, C. (2022). Anxiety, depression, chronic pain, and QOL among older adults in rural China: An observational, cross-sectional, multi-center study. Journal of Community Health Nursing, 39(3), 202-212.
Barry, M. J., Fowler, F. J., Jr, O’Leary, M. P., Bruskewitz, R. C., Holtgrewe, H. L., Mebust, W. K., & Cockett, A. T. (1992). The American urological association symptom index for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The measurement committee of the American urological Association. The Journal of Urology, 148(5), 1549-1564.
Cao, Y., Qi, W., Shen, K., & Han, H. (2017). Effect of social support on self-management and QOL in elderly patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Chinese Modern Doctors, 55(11), 128-131.
Choi, W. S., Heo, N. J., Lee, Y. J., & Son, H. (2017). Factors that influence lower urinary tract symptom related quality of life in a healthy population. World Journal of Urology, 35(11), 1783-1789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-017-2052-2
Choi, W. S., & Son, H. (2019). The change of IPSS 7 (nocturia) score has the maximum influence on the change of QOL score in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms. World Journal of Urology, 37(4), 719–725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2410-8
Daely, S., Nuraini, T., Gayatri, D., & Pujasari, H. (2021). Impacts of age and marital status on the elderly’s QOL in an elderly social institution. Journal of Public Health Research, 11(2). doi.org/10.4081/jphr.2021.2731
Dan, T. (2013). The use of the simplified geriatric depression scale (GDS-15) in Chinese elderly people. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 21(3), 402-405.
Dan, W. (2017). Negative emotions and social support in patients with severe prostatic hyperplasia and the effect of targeted intervention. China Journal Health Psychology, 25(11), 1661-1665.
Daoxiu, Z., Min, L., Jianli, S., Can, L., & Pei, T. (2021). Current status and influencing factors of quality of life in elderly patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Chinese Journal of Modern Nursing, 4851-4855.
Dodd, M. J., Miaskowski, C., & Paul, S. M. (2001). Symptom clusters and their effect on the functional status of patients with cancer. Oncology Nursing Forum, 28(3), 465-470.
Egan, K. B. (2016). The epidemiology of benign prostatic hyperplasia associated with lower urinary tract symptoms: Prevalence and incident Rates. The Urologic Clinics of North America, 43(3), 289-297.
Fan, Y. (2022). To investigate the correlation between health behavior, self-care agency and QOL in elderly patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. International Journal of Nursing, 1188-1191.
Guo, Y., Shi, J., Hu, M., & Sun, Z. (2009). Construction and validation of a short-form quality-of-life scale for Chinese patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 7, 24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-7-24
Hickey, K. T., Bakken, S., Byrne, M. W., Bailey, D. C. E., Demiris, G., Docherty, S. L., Dorsey, S. G., Guthrie, B. J., Heitkemper, M. M., Jacelon, C. S., Kelechi, T. J., Moore, S. M., Redeker, N. S., Renn, C. L., Resnick, B., Starkweather, A., Thompson, H., Ward, T. M., McCloskey, D. J., Austin, J. K., & Patricia A Grady, P. A.(2019). Precision health: Advancing symptom and self-management science. Nursing Outlook, 67(4), 462-475.
Jianchun, L., Xiaoning, H., Tao, B., Zhenzhong, Z., & Tana, L. Z. (2014). Analysis on the status quo of self-care ability of empty-nesters and its social support system. Chinese Health Economics, 7(7), 68-71.
Kaplan, S. A. (2012). Major depression drives severity of American Urological Association symptom index. Journal of Urology, 187(3), 969-970. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2011.11.041
Li, Z., Ge, J., Feng, J., Jiang, R., Zhou, Q., Xu, X., & Liu, C. (2021). Less social support for patients with COVID-19: Comparison with the experience of nurses. Front Psychiatry, 12, 554435.
Lin, S. L., & Tsai, S. L. (2003). The reliability and validity of Chinese version of Verran and Snyder-Halpern sleep scale. Vancouver General Hospital Nursing, 20(1), 105-106.
Liu, C. L. S. (2020). Analysis of risk factors affecting self-care ability of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Electronic Journal of Practical Clinical Nursing, 18, 1-15.
Ma, L., Zhao, X., Liu, H., Zhu, H., Yang, W., Qian, Y., & Li, Y. (2015). Antidepression medication improves quality of life in elderly patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and depression. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 8(3), 4031-4037.
Martínez-Mesa, J., González-Chica, D. A., Bastos, J. L., Bonamigo, R. R., & Duquia, R. P. (2014). Sample size: How many participants do I need in my research? Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia, 89(4), 609-615. https://doi.org/10.1590/abd1806-4841.20143705
Martínez-Mesa, J., Menezes, A. M., Howe, L. D., Wehrmeister, F. C., Muniz, L. C., González-Chica, D. A., & Barros, F. C. (2014). Lifecourse relationship between maternal smoking during pregnancy, birth weight, contemporaneous anthropometric measurements and bone mass at 18 years old. The 1993 Pelotas Birth Cohort. Early Human Development, 90(12), 901-906.
Mei, J. (1999). To evaluate the reliability and validity of the geriatric depression scale and the general health questionnaire short form. Chinese Journal of Psychiatry, 1, 40-42.
Meng, W. H. T., & Zengkui, Y. (2014). Research progress of self-esteem and social status in elderly patients with chronic diseases. Southwest Defense Medicine, 5(5), 574-576.
Michel, M. C., Schumacher, H., Mehlburger, L., & de la Rosette, J. (2020). Factors associated with nocturia-related QOL in men with lower urinary tract symptoms and treated with tamsulosin oral controlled absorption system in a non-interventional study. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 11, 816.
Mutalip, M. H. A., Rahim, F. A. A., Haris, H. M., Yoep, N., Mahmud, A. F., Salleh, R., & Ahmad, N. A. (2020). QOL and its associated factors among older persons in Malaysia. Geriatrics & Gerontology International, 92-97. doi:10.1111/ggi.13961
Ning, L. (2020). To explore the sleep status and influencing factors of hospitalized elderly residents based on symptom management theory. China: Shandong University.
Oelke, M., Adler, E., Marschall-Kehrel, D., Herrmann, T. R., & Berges, R. (2014). Nocturia: State of the art and critical analysis of current assessment and treatment strategies. World Journal of Urology, 32(5), 1109-1117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1396-0
Oelke, M., Wiese, B., & Berges, R. (2014). Nocturia and its impact on health-related quality of life and health care seeking behaviour in German community-dwelling men aged 50 years or older. World Journal of Urology, 32(5), 1155-1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1374-6
Pan, Y., Sun, M., Ma, Q., & Kun, L. (2020) Relationship between QOL and self-care ability in elderly patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 10, 2215-2218.
Park, S., Ryu, J. M., & Lee, M. (2020). QOL in older adults with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Healthcare (Basel), 8(2). 158. doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8020158
Pei, L., Liu, X. X., Du, H. D., Li, W., & Caiyun, L. (2019). Effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction therapy on anxiety, depression and QOL in elderly patients with prostatic hyperplasia. Nursing Research, 19, 3436-3439
Rom, M., Schatzl, G., Swietek, N., Rücklinger, E., & Kratzik, C. (2012). Lower urinary tract symptoms and depression. BJU International, 110(11), E918–E921. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11552.x
Sheikh, J. I., & Yesavage, J. A. (1986). Geriatric depression scale (GDS): Recent evidence and development of a shorter version. Clinical Gerontologist, 5, 165-173.
Shi, J., Sun, Z., Cai, T., & Yang, L. (2004). Development and validation of a quality-of-life scale for Chinese patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU International, 94(6), 837-844. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2004.05043.x
Silva, L., Lopes, V. J., & Merces, N. (2021). Symptom management theory applied to nursing care: Scoping review. Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem, 74(3), e20201004.
Snyder-Halpern, R., & Verran, J. A. (1987). Instrumentation to describe subjective sleep characteristics in healthy subjects. The Research in Nursing & Health, 10(3), 155-163. doi:10.1002/nur.4770100307
Sujuan, M. B. R. Z., Hua-Lu, Y., & Xiao-Qin, Z. (2015). Influencing factors of symptom management self-efficacy in maintenance hemodialysis patients. China Nursing Management, 15(9), 1063-1067.
Thorndike, R. M. (1978). Correlational procedures for research. New York: Gardner Press. Wang, D., & Foo, K. T. (2010). Staging of benign prostate hyperplasia is helpful in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostate hyperplasia. Annals of the Academy of Medicine of Singapore, 39(10), 798-802.
Wein, A. (2020). The standardization of terminology in lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardization subcommittee of the international continence society. Urology, 145, 310-311. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2020.04.064
Wong, C. K., Choi, E. P., Chan, S. W., Tsu, J. H., Fan, C. W., Chu, P. S., & Lam, C. K. (2017). Use of the international prostate symptom score (IPSS) in Chinese male patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Aging Male, 20. doi:10.1080/13685538.2017.1362380
Xiao, S. (1994). Theoretical basis and research application of social support rating scale. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 2, 98-100.
Xiong, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, X., Qin, F., & Yuan, J. (2020). The prevalence and associated factors of lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia in aging males. The Aging Male, 23(5), 1432–1439. https://doi.org/10.1080/13685538.2020.1781806
Yang, L. L., & Yongxue, H. X. (2015). Investigation on chronic diseases among cadres over 60 years old in Chengdu. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 35(15), 4341-4343.
Yang, Z. J. G. (2017). Quality of life and its influencing factors in elderly patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Chinese Journal of Andrology, 5, 34-39.
Yanli, L., Juan, L., & Lu, H. (2017). Effect of mifepristone combined with Guizhi Fuling capsule on serum CA125, CA199 and sex hormone levels in patients with endometriosis. World Clinical Drug, 38(7), 475-482.
Yanqin, Z. S. W., & Yanqi, G. (2014). QOL in patients with prostatic hyperplasia in Hebi, Henan Province. China Journal of Andrology, 28(5),47-49.
Zhang, D. X., Min, L., Sheng, J. L., Can, L., & Pei, T. (2021). Analysis of QOL and influencing factors in elderly patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Chinese Journal of Modern Nursing, 35, 4851-4855.
Zhiguo, T. L. C., Yanbin, Z, & Can, W. (2015). QOL and its related factors in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. China Journal Clinical (Electronic Edition), 9(13), 2623-2626.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.




