Predictors Of Medication Adherence Among Older Adults With Uncontrolled Hypertension
คำสำคัญ:
hypertension, medication adherence, medication self-efficacy, medication literacy, social supportบทคัดย่อ
This predictive correlational study aimed to examine medication adherence and its influencing factors among Chinese older adults with uncontrolled hypertension. Using simple random sampling, 137 patients aged 60 years and above were recruited from the Department of Cardiology at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University. Data were collected through validated instruments, including the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8), the Chinese Medication Literacy Scale (C-MLSHP), the Medication Self-Efficacy Scale (MASES-R), and the Multidimensional Social Support Scale (MSPSS). Descriptive statistics and multiple linear regression analyses were conducted.
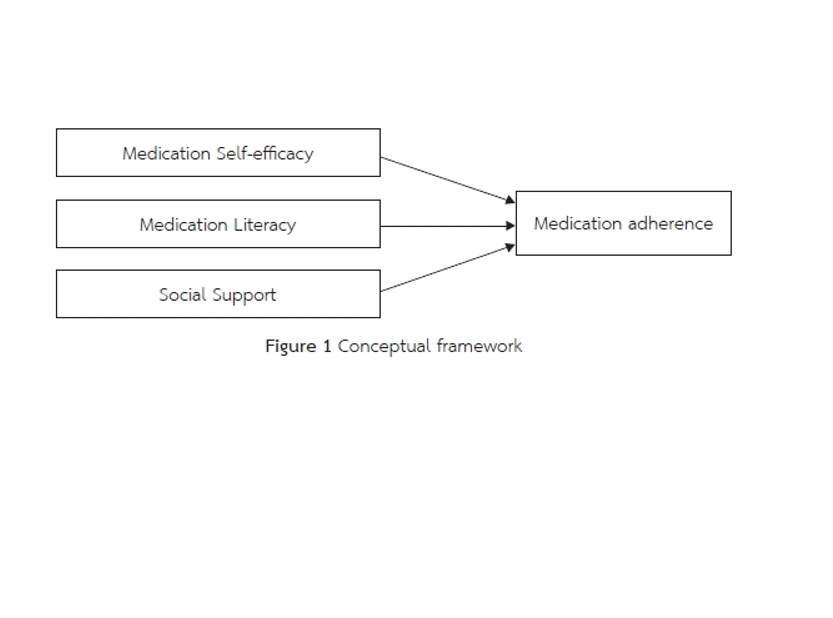
The results indicated a low mean medication adherence score (M = 5.59, SD = 0.98). Medication self-efficacy, medication literacy, and social support combinedly explained 30.8% of the variance in medication adherence (Adjusted R² = 0.308, F(3,133) = 21.185, p < .001). Medication self-efficacy emerged as the strongest predictor (β = 0.431, p < .001), followed by medication literacy (β = 0.240, p < .05). However, social support did not has a significant effect on medication adherence (β = 0.015, p > 0.05).
These findings underscore the critical role of medication self-efficacy and literacy in promoting medication adherence among older adults with uncontrolled hypertension and highlight the need for targeted nursing interventions aimed at enhancing these factors to improve health outcomes.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Abegaz, T. M., Shehab, A., Gebreyohannes, E. A., Bhagavathula, A. S., & Elnour, A. A. (2017). Nonadherence to antihypertensive drugs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine, 96(4), e5641.
Al-Ramahi, R. (2015). Adherence to medications and associated factors: A cross-sectional study among Palestinian hypertensive patients. Journal of Epidemiology and Global Health, 5(2), 125-132.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Benetos, A., Petrovic, M., & Strandberg, T. J. C. r. (2019). Hypertension management in older and frail older patients. Circulation Research, 124(7), 1045-1060.
Burnier, M., & Egan, B. M. (2019). Adherence in hypertension: A review of prevalence, risk factors, impact, and management. Circulation Research, 124(7), 1124-1140.
Creavin, S. T., Wisniewski, S., Noel-Storr, A. H., Trevelyan, C. M., Hampton, T., Rayment, D., Thom, V. M., Nash, K. J., Elhamoui, H., Milligan, R., Patel, A. S., Tsivos, D. V., Wing, T., Phillips, E., Kellman, S. M., Shackleton, H. L., Singleton, G. F., Neale, B. E., Watton, M. E., & Cullum, S. (2016). Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the detection of dementia in clinically unevaluated people aged 65 and over in community and primary care populations. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2016(1), CD011145. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011145.pub2
Cross, A. J., Elliott, R. A., Petrie, K., Kuruvilla, L., & George, J. (2020). Interventions for improving medication-taking ability and adherence in older adults prescribed multiple medications. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 5(5), CD012419. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD012419.pub2
DiMatteo, M. R., Haskard, K. B., & Williams, S. L. J. M. c. (2007). Health beliefs, disease severity, and patient adherence: A meta-analysis. Medical Care, 45(6), 521-528.
Fernandez, S., Chaplin, W., Schoenthaler, A. M., & Ogedegbe, G. J. J. o. b. m. (2008). Revision and validation of the medication adherence self-efficacy scale (MASES) in hypertensive African Americans. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 31, 453-462.
Folstein, M. F., Folstein, S. E., & McHugh, P. R. J. J. o. p. r. (1975). “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12(3), 189-198.
Gao, M. Y., Yang, M., Kuang, W. H., & Qiu, P. Y. (2015). Factors and validity analysis of mini-mental state examination in Chinese elderly people. Beijing da xue xue bao. Yi xue ban= Journal of Peking University. Health Sciences, 47(3), 443-449.
Gao, Z., Chen, S., Huang, X., Ye, J., Liu, J., Huang, Z., Chen, J., Li, L., Liu, Y., & Lin, S. (2022). Risk prediction model for uncontrolled hypertension in Chinese community. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 8, 808071. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.808071
Hamrahian, S. M. (2020). Medication non-adherence: A major cause of resistant hypertension. Current Cardiology Reports, 22(11), 133.
Hawkins, M. A., Gathright, E. C., Gunstad, J., Dolansky, M. A., Redle, J. D., Josephson, R., Moore, S. M., & Hughes, J. W. (2014). The MoCA and MMSE as screeners for cognitive impairment in a heart failure population: A study with comprehensive neuropsychological testing. Heart & Lung, 43(5), 462-468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrtlng.2014.05.011
Horne, R., Chapman, S. C., Parham, R., Freemantle, N., Forbes, A., & Cooper, V. J. P. o. (2013). Understanding patients’ adherence-related beliefs about medicines prescribed for long-term conditions: a meta-analytic review of the Necessity-Concerns Framework. PloS one, 8(12), e80633.
Huang, L., Jiang, Q., & Ren, W. (1996). Correlation between coping styles, social support and psychosomatic symptoms in cancer patients. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 4, 160–161.
Kokubo, Y., & Iwashima, Y. J. H. (2015). Higher blood pressure as a risk factor for diseases other than stroke and ischemic heart disease. Hypertension, 66(2), 254-259.
Krousel-Wood, M., Joyce, C., Holt, E., Muntner, P., Webber, L. S., Morisky, D. E., Frohlich, E. D., & Re, R. N. (2011). Predictors of decline in medication adherence: Results from the cohort study of medication adherence among older adults. Hypertension, 58(5), 804-810.
Laerkner, E., Egerod, I., & Hansen, H. P. (2015). Nurses’ experiences of caring for critically ill, non-sedated, mechanically ventilated patients in the Intensive Care Unit: A qualitative study. Intensive and Critical Care Nursing, 31(4), 196-204.
Locke, E. A. J. P. p. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. Personnel Psychology, 50(3), 801.
Ma, L. Y., Chen, W. W., Gao, R. L., Liu, L. S., Zhu, M. L., Wang, Y. J., Wu, Z. S., Li, H. J., Gu, D. F., Yang, Y. J., Zheng, Z., & Hu, S. S. (2020). China cardiovascular diseases report 2018: An updated summary. Journal of Geriatric Cardiology: JGC, 17(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2020.01.001
Martos – Méndez, M. J. (2015). Self-efficacy and adherence to treatment: The mediating effects of social support. Journal of Behavior, Health & Social Issues, 7 (2), 19-29.
Mills, K. T., Stefanescu, A., & He, J. (2020). The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nature reviews. Nephrology, 16(4), 223–237. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-019-0244-2
Morisky, D., Ang, A., Krousel-Wood, M., & Ward, H. (2008). Predictive validity of a medication adherence measure in an outpatient setting. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 10(5), 348-354.
Neiva Pantuzza, L. L., Nascimento, E. D., Crepalde-Ribeiro, K., Botelho, S. F., Parreiras Martins, M. A., Camila de Souza Groia Veloso, R., Gonzaga do Nascimento, M. M., Vieira, L. B., & Moreira Reis, A. M. (2022). Medication literacy: A conceptual model. Research in Social & Administrative Pharmacy : RSAP, 18(4), 2675–2682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2021.06.003
Patnode, C. D., Perdue, L. A., Rossom, R. C., Rushkin, M. C., Redmond, N., Thomas, R. G., & Lin, J. S. (2020). Screening for cognitive impairment in older adults: Updated evidence report and systematic review for the US preventive services task force. JAMA, 323(8), 764-785. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.22258
Remm, S., Halcomb, E., Hatcher, D., Frost, S. A., & Peters, K. J. J. o. c. n. (2023). Understanding relationships between general self‐efficacy and the healthy ageing of older people: An Integrative re Journal of Clinical Nursing, 32(9-10), 1587-1598.
Ruppar, T. M., Conn, V. S., & Russell, C. L. (2008). Medication adherence interventions for older adults: Literature review. Research and Theory for Nursing Practice, 22(2), 114–147.
Scheurer, D., Choudhry, N., Swanton, K. A., Matlin, O., & Shrank, W. J. T. A. j. o. m. c. (2012). Association between different types of social support and medication adherence. The American Journal of Managed Care, 18(12), e461-467.
Schoenthaler, A., Ogedegbe, G., Allegrante, J. P. J. H. E., & Behavior. (2009). Self-efficacy mediates the relationship between depressive symptoms and medication adherence among hypertensive African Americans. Health Education & Behavior, 36(1), 127-137.
Schoenthaler, A., Ogedegbe, G., & Allegrante, J. P. (2009). Self-efficacy mediates the relationship between depressive symptoms and medication adherence among hypertensive African Americans. Health Education & Behavior: The Official Publication of the Society for Public Health Education, 36(1), 127–137. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090198107309459
Shen, Z., Shi, S., Ding, S., & Zhong, Z. (2020). Mediating effect of self-efficacy on the relationship between medication literacy and medication adherence among patients with hypertension. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 11, 569092.
Taufek, N. H. M. (2025). Global initiatives for improving health and medication literacy. In Health literacy in medicines use and pharmacy (pp. 289-305). Massachusetts: Academic press, Elsevier.
The Writing Committee of the Annual Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China. (2022). Interpretation of the annual report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2020. Cardiology Discovery, 2(4), 269-285.
Thuy, L. T., Monkong, S., Pookboonmee, R., Leelacharas, S., & Viwatwongkasem, C. (2020). Factors explaining medication adherence of older adults with hypertension: a cross-sectional study. Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research, 24(3), 306-320.
Turan, G. B., Aksoy, M., & Çiftçi, B. J. J. o. V. N. (2019). Effect of social support on the treatment adherence of hypertension patients. Journal of Vascular Nursing, 37(1), 46-51.
Uchmanowicz, B., Chudiak, A., Uchmanowicz, I., Rosińczuk, J., & Froelicher, E. S. (2018). Factors influencing adherence to treatment in older adults with hypertension. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 13, 2425–2441. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S182881
Wei, J., Mi, Y., Li, Y., Xin, B., & Wang, Y. J. B. P. H. (2021). Factors associated with awareness, treatment and control of hypertension among 3579 hypertensive adults in China: Data from the China Health and Nutrition Survey. BMC Public Health, 21, 1-11.
Wei, J., Mi, Y., Li, Y., Xin, B., & Wang, Y. (2021). Factors associated with awareness, treatment and control of hypertension among 3579 hypertensive adults in China: Data from the China Health and Nutrition Survey. BMC Public Health, 21(1), 423. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-10417-4
Yang, A., Wang, B., Zhu, G., Jiao, Z., Fang, Y., Tang, F., Ma, C., Zhao, Y., Cheng, C., & Zhong, M. (2014). Validation of Chinese version of the Morisky medication adherence scale in patients with epilepsy. Seizure, 23(4), 295–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2014.01.003
Yu, H. M., Wang, L., & Pan, C. Z. (2024). The impact of cognitive behavioural therapy-based psychological intervention on emotional improvement in elderly patients with extensive burns. International Wound Journal, 21(2), e14594. https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.14594
Zhang, N. J., Terry, A., & McHorney, C. A. (2014). Impact of health literacy on medication adherence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 48(6), 741–751. https://doi.org/10.1177/1060028014526562
Zhong, Y., Wang, J., & Nicholas, S. (2020). Social support and depressive symptoms among family caregivers of older people with disabilities in four provinces of urban China: The mediating role of caregiver burden. BMC Geriatrics, 20(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-019-1403-9
Zimet, G. D., Dahlem, N. W., Zimet, S. G., & Farley, G. K. J. J. o. p. a. (1988). The multidimensional scale of perceived social support. Journal of Personality Assessment, 52(1), 30-41.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.




