A Comprehensive Case Series: Outcomes and Insights from the First Three Simultaneous Pancreas Kidney Transplants at Ramathibodi Hospital
Keywords:
Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation, Type 1 diabetes mellitus, End-stage renal disease, Kidney transplantationAbstract
Abstract
Background: Pancreas transplantation, particularly in the context of Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), has emerged as a pivotal therapeutic intervention, substantially ameliorating both the clinical and quality-of-life outcomes for affected individuals. While previous research has underscored its efficacy in enhancing longevity, mitigating cardiovascular risks, and improving overall well-being, its widespread adoption, particularly the simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation (SPK) approach, remains constrained by various factors, notably donor availability and the requisite multidisciplinary care infrastructure.
Methods: This study presents the treatment outcomes of the initial three cases of SPK performed at Ramathibodi Hospital in Thailand. The operative techniques employed adhered to established protocols, including intraoperative porto-enteric drainage for endocrine function and enteric drainage for exocrine function. Noteworthy intraoperative considerations encompassed meticulous vascular reconstruction, heparinization protocols, and vigilant monitoring of hematological parameters to forestall potential complications.
Results: Each case presented unique clinical profiles and postoperative trajectories. Complications, such as postoperative hematoma and declining hematocrit levels, were managed judiciously, with successful resolution and favorable graft outcomes observed during subsequent follow-up periods. Importantly, all patients demonstrated prompt postoperative glycemic control and satisfactory renal function, obviating the need for further dialysis or medical intervention.
Conclusion: SPK emerges as a highly efficacious therapeutic avenue for individuals afflicted with T1DM and ESRD, offering tangible improvements in health outcomes and the prospect of restored quality of life. As evidenced by the outcomes of the initial cases presented herein, SPK holds promise as a viable treatment modality warranting further exploration and dissemination within the clinical landscape.
References
Gross CR, Limwattananon C, Matthees B, et al. Impact of transplantation on quality of life in patients with diabetes and renal dysfunction. Transplantation. 2000;70(12):1736-46. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200012270-00013.
Rajkumar T, Mazid S, Vucak-Dzumhur M, et al. Health-related quality of life following kidney and simultaneous pancreas kidney transplantation. Nephrology (Carlton). 2019;24(9):975-982. doi: 10.1111/nep.13523.
Jiang AT, BHSc, Rowe N, et al. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: The role in the treatment of type 1 diabetes and end-stage renal disease. Can Urol Assoc J. 2014;8(3-4):135-8. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.1597.
Montagud-Marrahi E, Molina-Andújar A, Pané A, et al. Impact of Simultaneous Pancreas-kidney Transplantation on Cardiovascular Risk in Patients With Diabetes. Transplantation. 2022;106(1):158-166. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003710.
Lange UG, Rademacher S, Zirnstein B, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes after simultaneous pancreas kidney transplantation compared to kidney transplantation alone: a propensity score matching analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2021;22(1):347. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02522-8.
Ojo AO, Meier-Kriesche HU, Arndorfer JA, et al. Long-term benefit of kidney-pancreas transplants in type 1 diabetics. Transplant Proc. 2001;33(1-2):1670-2. doi: 10.1016/s0041-1345(00)02635-x.
Kandaswamy R, Stock PG, Miller JM, et al. OPTN/SRTR 2021 Annual Data Report: Pancreas. Am J Transplant. 2023;23(2 Suppl 1):S121-S177. doi: 10.1016/j.ajt.2023.02.005.
Dmitriev IV, Severina AS, Zhuravel NS, et al. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients Following Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation: Time in Range and Glucose Variability. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023;13(9):1606. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13091606.
Douzdjian V, Ferrara D, Silvestri G. Treatment strategies for insulin-dependent diabetics with ESRD: a cost-effectiveness decision analysis model. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998;31(5):794-802. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(98)70048-4.
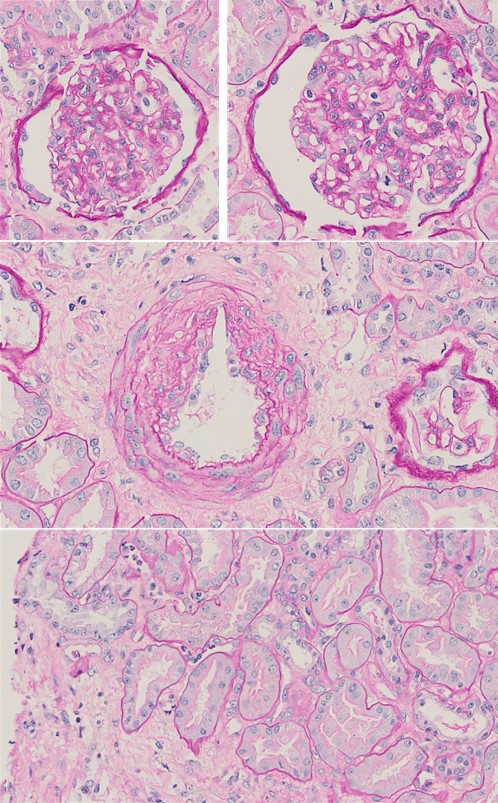
Fioretto P, Steffes MW, Sutherland DE, et al. Reversal of lesions of diabetic nephropathy after pancreas transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(2):69-75. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199807093390202.
Sucher R, Rademacher S, Jahn N, et al. Effects of simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation and kidney transplantation alone on the outcome of peripheral vascular diseases. BMC Nephrol. 2019;20(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1649-7.
Squifflet JP, Gruessner RW, Sutherland DE. The history of pancreas transplantation: past, present and future. Acta Chir Belg. 2008;108(3):367-78. doi: 10.1080/00015458.2008.11680243.
Sharda B, Jay CL, Gurung K, et al. Improved surgical outcomes following simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in the contemporary era. Clin Transplant. 2022;36(11):e14792. doi: 10.1111/ctr.14792.
Manrique A, Jiménez C, López RM, et al. Relaparotomy after pancreas transplantation: causes and outcomes. Transplant Proc. 2009;41(6):2472-4. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.06.165.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Royal College of Surgeons of Thailand

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Articles must be contributed solely to The Thai Journal of Surgery and when published become the property of the Royal College of Surgeons of Thailand. The Royal College of Surgeons of Thailand reserves copyright on all published materials and such materials may not be reproduced in any form without the written permission.


