Accuracy of automatic image registration software for image guided radiotherapy
Keywords:
Image-guided radiotherapy, Image registration software, MV-EPID, kV-OBI, kV-CBCTAbstract
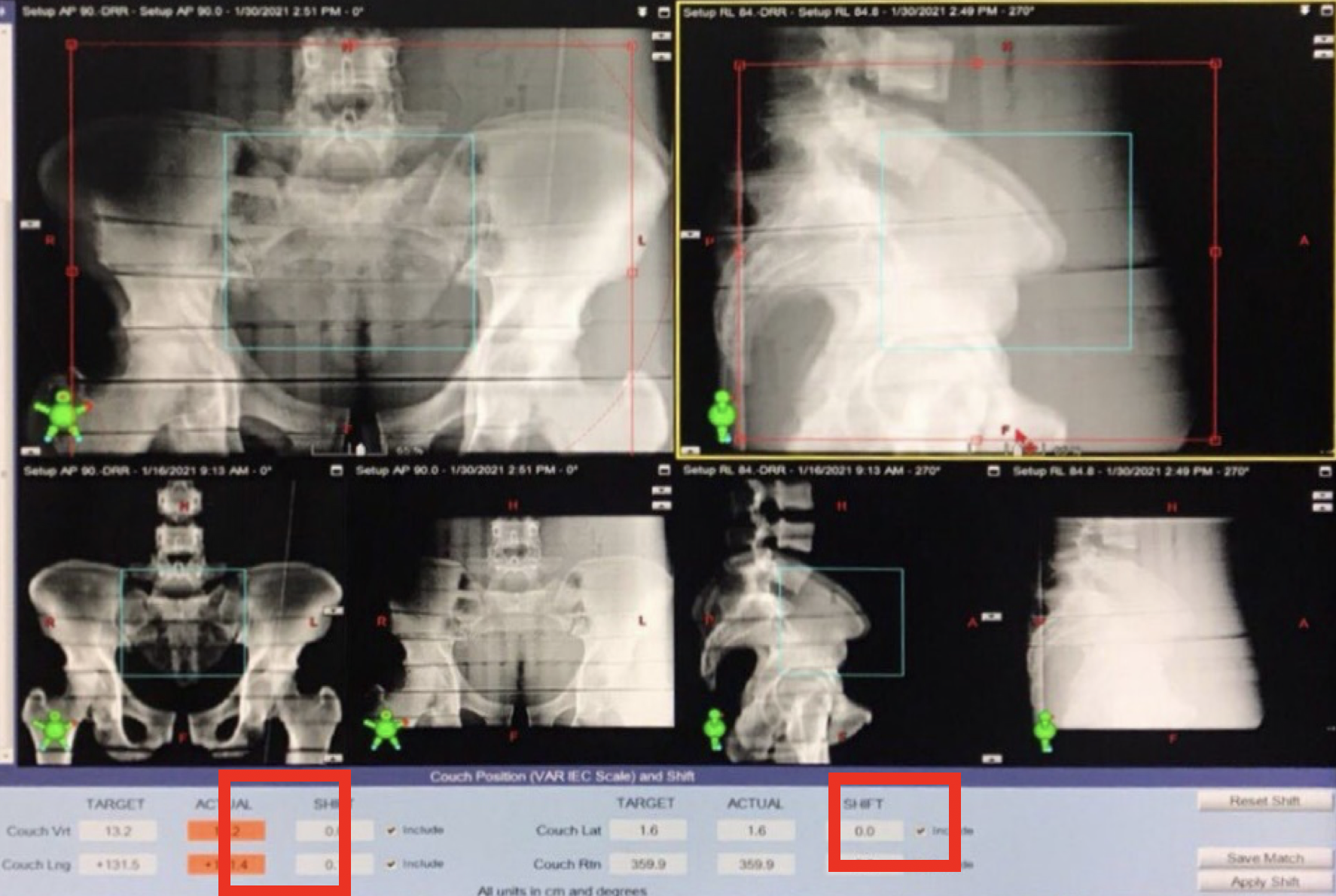
Image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) is a method used the imaging in treatment room to validate patient positioning before treatment. The image registration software is used to find the patient position uncertainties. This research aimed to determine the accuracy of the automatic image registration software of using MV-EPID, kV-OBI, and kV-CBCT to determine the location of patients and cancerous lumps before irradiation. The head, chest, and pelvic regions of anthropomorphic phantom was scanned by CT-simulator. The phantom was set again in treatment room. The treatment couch was moved in vertical, longitudinal, and lateral directions in each axis and all three axes with the known couch shifted of 1, 3, 5, 10 and 20 mm, and then the three IGRT types were performed. The auto shifted software was applied to find the couch shifted. The deviations from auto shifted software and known couch shifted were reported and calculated for mean and SD. The results showed that kV-CBCT data presented the highest accuracy with a mean of shifted error within ±1 mm in all regions and all directions and the overall mean of shifted error values of the head, thorax, and pelvic regions were 0.0±0.8 mm, 0.2±0.6 mm, and 0.1±0.4 mm, respectively. The MV-EPID data presented secondary accuracy with a mean of shifted error of less than ±1.5 mm and the overall mean of error shifted values of the head, thorax, and pelvic regions were -0.1±0.5 mm, -0.3±1.8 mm, and 0.2±0.6 mm, respectively. The kV-OBI presented the least accurate with a mean of shifted error of less than ±2 mm and an overall mean of shifted error values of the head, thorax, and pelvic regions at 0.0±0.9 mm, -0.6±1.6 mm, and -0.9±1.3 mm, respectively. However, the use of MV-EPID and kV-OBI automatic image registration software was incorrected when the large couch shifted was set. Moreover, the automatic registration software was limited in MV-EPID when the large couch shifted was applied.
Downloads
References
Jason C. Ye, M. M. (2015). Daily patient setup error in prostate image guided radiation therapy with fiducial-based kilovoltage onboard imaging and conebeam computed tomography. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 5(5), 665–672.
Britton KR, T. Y. (2005). Evaluation of Inter- and Intrafraction organ motion during Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) for localized prostate cancer measured by a newly developed on-board image-guided system. Radiat Med, 23(1), 14-24.
กมลรัตน์ เสืองามเอี่ยม, ศิวลี สุริยาปี, ทวีป แสงแห่งธรรม. (2560). การกำหนดค่าความคลาดเคลื่อนของตำแหน่งการฉายรังสีในผู้ป่วยมะเร็งต่อมลูกหมากที่รักษาด้วยเทคนิคการปรับความเข้มของลำรังสี (VMAT) โดยใช้เครื่องถ่ายภาพเอกซเรย์คอมพิวเตอร์แบบโคน. มะเร็งวิวัฒน์ วารสารสมาคมรังสีรักษาและมะเร็งวิทยาแห่งประเทศไทย, 23(1), 27-37.
Bentel GC, M. L. (1997). Impact of cradle immobilization on setup reproducibility during. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 38(3), 527-531.
Balter JM, C. G. (1993). Online repositioning during treatment of the prostate: A study of potential limits and gains. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 27(1), 137-143.
ยคชา ตินทุกานนท์, สุธี เดซะวงศ์สุวรรณ, วนีรนุช ทวีบุญ. (2561). การศึกษาเปรียบเทียบความคลาดเคลื่อนของตำแหน่ง isocenter ระหว่างแนวเหนือและใต้ต่อ nipple สำหรับการฉายรังสีมะเร็งบริเวณทรวงอกและช่องท้องโดยการใช้ภาพ KV Orthogonal หรือ Cone-beam computedtomography (CBCT) ของโรงพยาบาลศิริราช. มะเร็งวิวัฒน์ วารสารสมาคมรังสีรักษาและมะเร็งวิทยาแห่งประเทศไทย, 24(1), 25-34.
Nithya Kanakavelu, E. J. (2016). Accuracy in automatic image registration between MV cone beam computed tomography and planning kV computed tomography in image guided radiotherapy. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 21(5), 487–494.
Shamurailatpam Dayananda Sharma, P. D. (2012). Evaluation of automated image registration algorithm for image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT). Australas Phys Eng Sci Med, 35(3), 311-319.
Thai Society of Radiological Technologists (TSRT). (2021). Preliminary Survey for IGRT Reference Guide. กรุงเทพ: Thai Society of Radiological Technologists.
Eric E. Klein, J. H.-F. (2009). Task Group 142 report: Quality assurance of medical accelerators. Med Phys, 36(9), 4197-4212.
Cheng Chen, C. W. (2020). A new registration algorithm of electronic portal imaging devices images based on the automatic detection of bone edges during radiotherapy. Scientific Reports, 10(10253), 1-9.
Chen C, Wu C, Zhong Y, Xie C, Zhou Y, Liu H, et al. A new registration algorithm of electronic portal imaging devices images based on the automatic detection of bone edges during radiotherapy. Scientific Reports 2020;10(1)10253
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย (The Thai Society of Radiological Technologists)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทยและบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆในสมาคม ฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




