ปัจจัยที่มีอิทธิพลต่อพฤติกรรมการรับประทานอาหารของผู้เป็นเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2
คำสำคัญ:
พฤติกรรมการรับประทานอาหาร, ผู้เป็นเบาหวานชนิดที่2, ความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ, ความทุกข์ยากจากการเจ็บป่วยด้วยโรคเบาหวานบทคัดย่อ
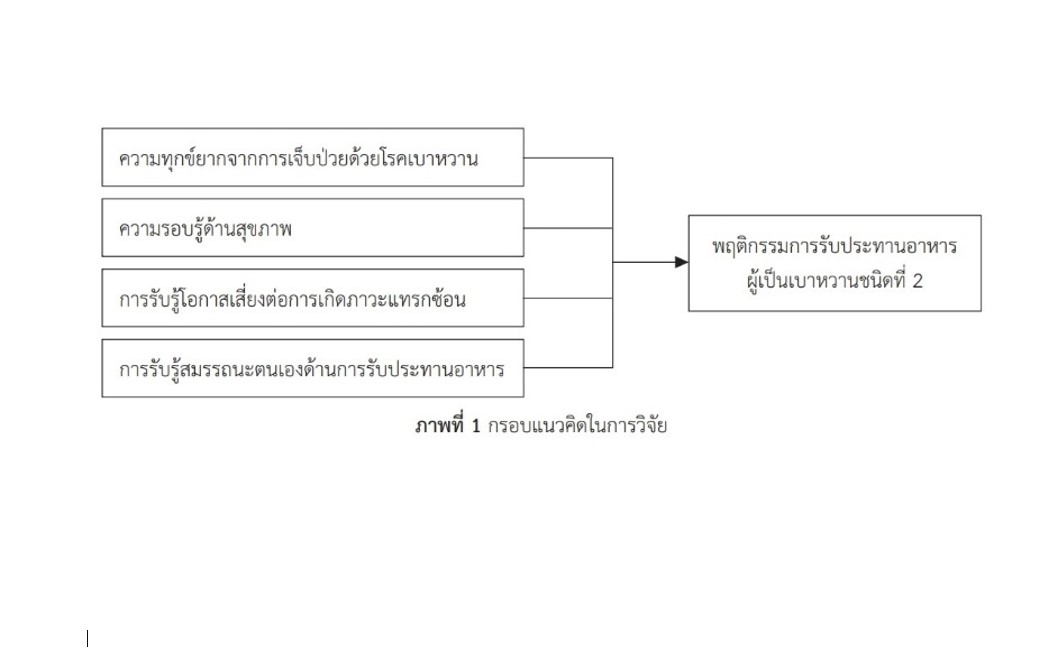
การวิจัยครั้งนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาพฤติกรรมการรับประทานอาหารของผู้เป็นเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 และปัจจัยที่มีอิทธิพลต่อพฤติกรรมการรับประทานอาหารของผู้เป็นเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 กลุ่มตัวอย่างเป็นผู้เป็นเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่เข้ารับการรักษาที่คลินิกโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้อรัง โรงพยาบาลด่านขุนทด จังหวัดนครราชสีมา ช่วงระหว่างเดือนพฤศจิกายนถึงเดือนธันวาคม พ.ศ.2564 สุ่มตัวอย่างตามแบบสะดวก จำนวน 108 ราย เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการวิจัยประกอบด้วย แบบสอบถามข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลและบันทึกประวัติสุขภาพ แบบสอบถามความทุกข์ยากจากการเจ็บป่วยด้วยโรคเบาหวาน แบบสอบถามความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ แบบสอบถามการรับรู้สมรรถนะตนเองด้านการรับประทานอาหาร แบบสอบถามการรับรู้โอกาสเสี่ยงต่อการเกิดภาวะแทรกซ้อน และแบบสอบถามการจัดการตนเองด้านพฤติกรรมการรับประทานอาหาร วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยสถิติพรรณาและสถิติถดถอยพหุคูณแบบเลือกเข้า
ผลการศึกษาพบว่า พฤติกรรมการรับประทานอาหารของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง ( M =12.08, S.D.=2.83) โดยปัจจัยความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ และสามารถทำนายพฤติกรรมการรับประทานอาหารของผู้เป็นเบาหวานได้ร้อยละ9.2 (R2 adjust =.902 ) (β = 114, p <.05 )
ผลการวิจัยเสนอแนะว่า ควรมีการส่งเสริมความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพในผู้เป็นเบาหวานทุกรายเพื่อให้สามารถปฏิบัติพฤติกรรมการรับประทานอาหารได้อย่างเหมาะสม
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Ellis, P. D. (2010).The essential guide to effect size: Statistical power, meta analysis and the interpretation of research result.New York : Cambridge University press
Health Education Division. (2018). Health literacy and Health behavior. Retrieved from http://164.115.27.97/digital/items/show/9588.
International Diabetes Federation. (2019). IDF Diabetes Atlas. Retrieved from https://www.diabetesatlas.org
Intharabut, M., & Muktabhant, B. (2005). The perception and practices of type2 diabetic patient in the control of their dietary intake. Srinagarind Medical Journal, 22(3), 283-290.
Khonghom, C. (2014). Factors influencing self behavior of diabetes mellitus patients at the Klongluang hospital Pathumthani province. EAU Heritage Journal Science and Technology, 8(2), 248-258.
Moeini ,B, Maghsodi,S , Kangavari, M, Afshari, M., &Tagh, J. (2016). Factor associated with health literacy and self care behaviors among Iranian diabetes pateirnt: A crossectional study. Journal of Communication in Healthcare, 9(4), 279-287
Pasar, S, Aghamohammadi, M, & Abazari, M. (2019). Diabetes distress and its clinical determinants in patients with type II diabetes. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 13(2), 1275-1279.
Phermsin, S. (2011). The effect of application by health belief model and social support to control blood sugar among diabetes mellitus type 2 patients, Ubolratana hospital, Ubolratana district, Khon Kaen province. Master’s thesis, Nursing, Graduate study, Khon Kaen University.
Quek, J., Tan, G., Lim, K., Yap, C. K., Wong, M., & Soon, J. (2019). Diabetes distress and self-management in primary care in Singapore: Explorations through illness perception. International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health, 6(2), 473-479.
Sanmuanngka, O., Muktabhant, B., & Srila, S. (2017). Self care behavior relating to nutrition among type 2 diabetic patients living in a village of Chiangyuen district, Mahasarakam province. Journal of Health Science, 26(2), 227-236.
Thanakwang, K, Thinganjana, W., & Konggumnerd ,R. (2015). Depression among older adults in Thailand. Retrieved from http://164.115.27.97/digital/items/show/9588.
Yangdon, K , Masingboon, K., & Samartkit, N. (2020). Factors influencing diabetes self management among Bhutanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The Journal of Faculty of Nursing Burapha University, 28(4), 75-86.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.




