ปัจจัยทำนายพฤติกรรมของมารดาในการส่งเสริมทักษะการคิดเชิงบริหาร เด็กวัยก่อนเรียน
คำสำคัญ:
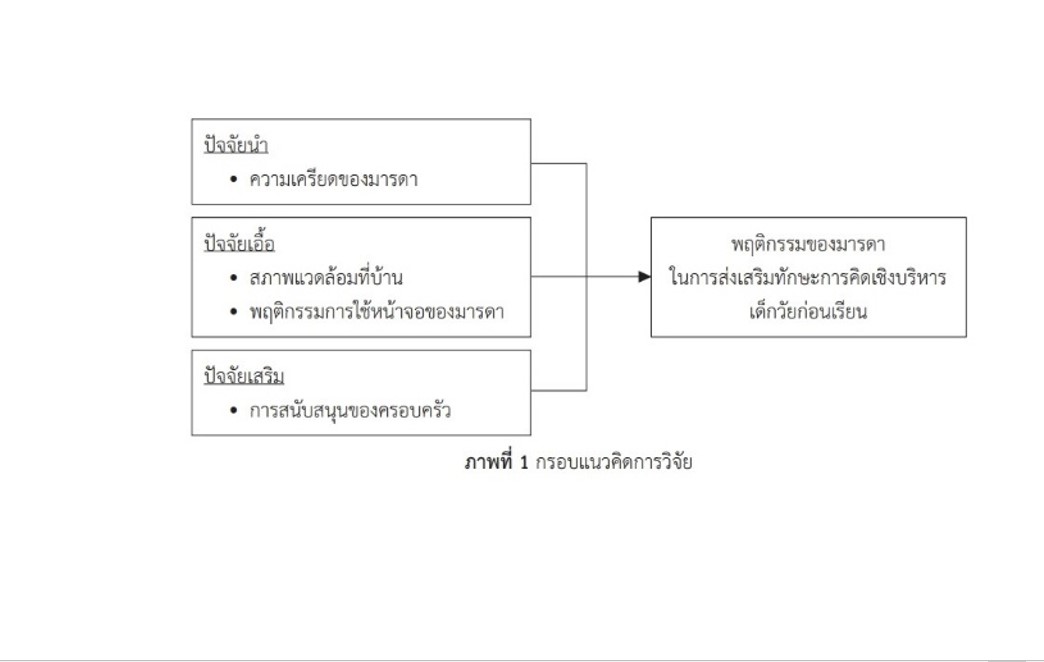
ปัจจัยทำนาย, พฤติกรรมมารดา, สภาพแวดล้อมที่บ้าน, การสนับสนุนของครอบครัว, ทักษะการคิดเชิงบริหาร, เด็กวัยก่อนเรียนบทคัดย่อ
งานวิจัยความสัมพันธ์เชิงทำนายนี้ มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาปัจจัยทำนายพฤติกรรมของมารดาในการส่งเสริมทักษะการคิดเชิงบริหารเด็กวัยก่อนเรียน กลุ่มตัวอย่าง คือ มารดาเด็กวัยก่อนเรียนที่เข้ารับบริการในศูนย์พัฒนาเด็กเล็ก เขตเทศบาลเมือง จังหวัดชลบุรี จำนวน 101 คน คัดเลือกด้วยวิธีการสุ่มอย่างง่าย เก็บข้อมูลเดือนสิงหาคม ถึง กันยายน พ.ศ. 2566 โดยใช้แบบสอบถามจำนวน 6 ชุด ประกอบด้วยแบบสอบถามข้อมูลทั่วไป แบบสอบถามความเครียดของมารดา แบบสอบถามสภาพแวดล้อมที่บ้าน แบบสอบถามพฤติกรรมการใช้หน้าจอของมารดา แบบสอบถามการสนับสนุนของครอบครัว และแบบสอบถามพฤติกรรมของมารดาในการส่งเสริมทักษะการคิดเชิงบริหารเด็กวัยก่อนเรียน มีค่าความเชื่อมั่นของเครื่องมือ เท่ากับ .81, .81, .83, .91, และ .95 ตามลำดับ วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยใช้สถิติพรรณนาและสถิติถดถอยพหุคูณ
ผลการศึกษาพบว่า ปัจจัยที่ร่วมกันทำนายพฤติกรรมของมารดาในการส่งเสริมทักษะการคิดเชิงบริหารเด็กวัยก่อนเรียน ร้อยละ 40.7 ได้แก่ สภาพแวดล้อมที่บ้าน (β = 0.776, p < .05) และการสนับสนุนของครอบครัว (β = 0.503, p < .001) ผลการวิจัยนี้สามารถนำไปใช้เป็นข้อมูลพื้นฐานสำหรับพยาบาล บุคลากรทางสุขภาพ และผู้ดูแลเด็กในการส่งเสริมสิ่งแวดล้อมที่บ้าน และการสนับสนุนของครอบครัวเพื่อให้มารดามีพฤติกรรมในการส่งเสริมทักษะการคิดเชิงบริหารของเด็กวัยก่อนเรียนอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Altun, D. (2022). Family ecology as a context for children’s executive function development: The home literacy environment, play, and screen time. Child Indicators Research, 15(4), 1465-1488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12187-022-09920-w
Chutabhakdikul, N., Thanasetkorn, P., & Lertawasdatrakul, O. (2017). Tool development and evaluation criteria for assessment of executive function in early childhood. Nakon Pathom: Mahidol University. [In Thai]
Cruz-Alaniz, Y., Bonillo, A., & Ballabriga, M. C. (2018). Parents’ executive functions, parenting styles,and oppositional defiant disorder symptoms: A relational model. Universitas Psychologica, 17, 39-48. https://doi.org/10.11144/javeriana.upsy.17-2.pefp
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 155-159. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.112.1.155
De Cock, E. S. A., Henrichs, J., Klimstra, T. A., Janneke, B. M. M. A., Vreeswijk, C., Meeus, W. H. J., & van Bakel, H. J. A. (2017). Longitudinal associations between parental bonding, parenting stress, and executive functioning in toddlerhood. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 26(6), 1723-1733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-017-0679-7
Green, L. W., Gielen, A. C., Ottoson, J. M., Peterson, D. V., & Kreuter, M. W. (2022). Health program planning, implementation, and evaluation: Creating behavioral, environmental and policy change. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Harymatee, S., Pitaksinsuk, T., & Aramlit, P. (2018). Handbook for developing executive functions in the brain for early childhood teachers. Matichon. [In Thai]
Kerdmuang S., & Suwancharoen S. (2022). Health determinants of screening-viewing behaviors among preschool children aged 2-5 years in Suphanburi province. Nursing Journal of The Ministry of Public Health, 32(2), 36-51. [In Thai]
Ministry of Public Health. (2022, 20 December). Indicator 002.2: Percentage of early childhood children developing appropriately for their age. Retrieved from http://healthkpi.moph.go.th/kpi2/kpi/index/?id=1851&kpi_year=2565 [In Thai]
Nontapan, P. (2019). Factors related to behaviors promoting preschooler development among child care providers, Songkhla province. Journal of Prachomklao College og Nursing, Phetchaburi Province, 1(3), 10-24. [In Thai]
Palitponganpim, P. (2022). How to raise a child to EF. Bangkok: Amarin Printing. [In Thai]
Pornsawat, D. (2015). Husband support, family support and some personal factors influencing the role of adolescent mother. Master’s thesis, Department of Nursing, Burapha University. [In Thai]
Sangsai, N., Chaimongkon, N., & Phaktoop, M. (2011). Predictors of adaptive behavior of preschoolers receiving service in child daycare center. The Journal of Faculty of Nursing Burapha University, 19(2), 97-109. [In Thai]
Sonsee, S., Pongjaturawit, Y., & Chaimongkol, N. (2017). Factors associated with maternal behavior in promoting play for their preschool children. Journal of Phrapokklao Nursing College, 28(1), 90-99. [In Thai]
Thanasetkorn, P. (2018). Cognitive brain development in early childhood. In Harymatee, S., Pitaksinsok, T., & Aramlit, P. (Eds.), Executive Functions Brain Development Manual for Early Childhood Teachers. Bangkok: Matichon. [In Thai]
Thisara, P., Ponmark, J., Seekhao, P., & Sinlapawitthayathon, B. (2017). Predictive factors of parental behaviors on promoting early childhood development in Phayao province. Journal of Nursing and Health Care, 35(2), 169-176. [In Thai]
Thohinung, U., Boonyapuk, P., & Kodyee, S. (2022). Predictive factors of parental behaviors on promote development of executive functions (EF) skills among early childhood in Chaing Rai province. Journal of The Royal Thai Army Nurses, 23(1), 344-352. [In Thai]
Valcan, D. S., Davis, H. L., Pino-Pasternak, D., & Malpique, A. A. (2020). Executive functioning as a predictor of children’s mathematics, reading and writing. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 70, 101196. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2020.101196
Vanden Abeele, M. M. P., Abels, M., & Hendrickson, A. T. (2020). Are parents less responsive to young children when they are on their phones? A systematic naturalistic observation study. Cyberpsychology Behavior and Social Networking, 23(6), 363-370. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2019.0472
Vissers, C., Koolen, S., Hermans, D., Scheper, A., & Knoors, H. (2015). Executive functioning in preschoolers with specific language impairment. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1574. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01574
Wongpakaran, N., & Wongpakaran, T. (2010). The Thai version of the PSS-10: An investigation of its psychometric properties. BioPsychoSocial Medicine, 4(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1751-0759-4-6
Zvara, B. J., Keim, S. A., Boone, K. M., & Anderson, S. E. (2019). Associations between parenting behavior and executive function among preschool-aged children born very preterm. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 48, 317-324.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.




