อิทธิพลของพฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองและความมั่นใจในการดูแลตนเอง ต่อการควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ในโรงพยาบาลทุติยภูมิ จังหวัดนครศรีธรรมราช
คำสำคัญ:
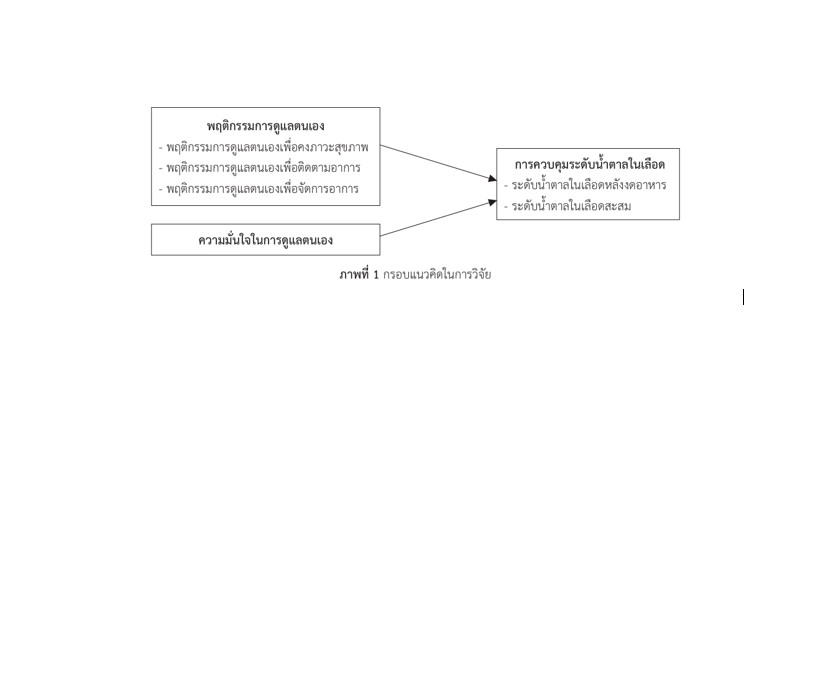
พฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเอง , ความมั่นใจในการดูแลตนเอง, การควบคุมระดับน้ำตาล, ผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2บทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยแบบหาความสัมพันธ์เชิงทำนายนี้ มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาอิทธิพลของพฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองและความมั่นใจในการดูแลตนเองต่อการควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 กลุ่มตัวอย่างเป็นผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่เข้ารับการรักษาที่แผนกผู้ป่วยนอก โรงพยาบาลทุติยภูมิ จังหวัดนครศรีธรรมราช จำนวน 155 คน ซึ่งได้มาด้วยการสุ่มอย่างง่าย เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการเก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล ประกอบด้วย แบบประเมินพฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองของผู้ป่วยเรื้อรัง และแบบประเมินความมั่นใจในการดูแลตนเอง มีค่าสัมประสิทธิ์แอลฟ่าครอนบาค เท่ากับ 0.71 และ 0.93 ตามลำดับ เก็บi;[I;,ข้อมูลระหว่างเดือนมิถุนายน ถึงกรกฎาคม พ.ศ. 2567 วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยใช้สถิติพรรณนาและสถิติการวิเคราะห์สมการถดถอยพหุคูณแบบมาตรฐาน
ผลการวิจัยพบว่า ปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดหลังงดอาหารและระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดสะสมอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (p < .01) ได้แก่ พฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองเพื่อคงภาวะสุขภาพ (r = -.390, r = -.380 ตามลำดับ) พฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองเพื่อติดตามอาการ (r = -.414, r = -.399 ตามลำดับ) พฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองเพื่อจัดการอาการ (r = -.286, r = -.369 ตามลำดับ) และความมั่นใจในการดูแลตนเอง (r = -.329, r = -.360 ตามลำดับ) นอกจากนี้พบว่า พฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองเพื่อคงภาวะสุขภาพ (β = -.247) พฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองเพื่อติดตามอาการ (β = -.207) และความมั่นใจในการดูแลตนเอง (β = -.201) สามารถร่วมกันทำนายระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดหลังงดอาหารได้อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติร้อยละ 23.1 (Adjusted R2 = .231, p < .001) ในขณะที่พฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองเพื่อติดตามอาการ (β = -.198) และความมั่นใจในการดูแลตนเอง (β = -2.419) สามรถร่วมกันทำนายระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดสะสมของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานได้อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติร้อยละ 24.9 (Adjusted R2 = .249, p < .001)
ผลการวิจัยสามารถนำไปพัฒนาโปรแกรมการส่งเสริมพฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเอง โดยเน้นพฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองเพื่อคงภาวะสุขภาพ การติดตามอาการ และการจัดการอาการ รวมทั้งเสริมสร้างความมั่นใจในการดูแลตนเอง เพื่อควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ให้ดียิ่งขึ้น
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Almutairi, N., Hosseinzadeh, H., & Gopaldasani, V. (2020). The effectiveness of patient activation intervention on type 2 diabetes mellitus glycemic control and self-management behaviors: A systematic review of RCTs. Primary Care Diabetes, 14(1), 12-20.
Al-Qerem, W., Jarab, A. S., Badinjki, M., Hammad, A., Ling, J., & Alasmari, F. (2022). Factors associated with glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 26(7), 2415-2421.
Alor, S. K., Kretchy, I. M. A., Glozah, F. N., & Adongo, P. B. (2023). Factors associated with glycaemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Ho, Ghana: A cross-sectional study. Metabolism Open, 20, 100265.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: W.H. Freeman.
Bin Rakhis, S. A., AlDuwayhis, N. M., Aleid, N., AlBarrak, A. N., & Aloraini, A. A. (2022). Glycemic control for type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A systematic review. Cureus, 14(6), e26180.
Bunsuk, C., Suwanno, J., Klinjun, N., Kumanjan, W., Srisomthrong, K., Phonphet, C., & Thiamwong, L. (2023). Cross-cultural adaptation and psychometric evaluation of the Thai version of self-care of chronic illness inventory version 4.c. International Journal of Nursing Sciences, 10(3), 332-344.
Caruso, R., Rebora, P., Dellafiore, F., Fabrizi, D., Riegel, B., Ausili, D., & Di Mauro, S. (2019). Clinical and socio-demographic determinants of inadequate self-care in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus: the leading role of self-care confidence. Acta Diabetologica, 56(2), 151-161.
Çetinkaya, A., Bayar Üniversitesi Sağlık Yüksekokulu, C., Bölümü, H., Eşlik, M., & Hemşirelik Dergisi, K. (2019). Self-efficacy perceptions in coping of the patients’ post-coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Turkish Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing, 10(22), 41-49.
Chindankutty, N. V., & Devineni, D. (2023). Self-efficacy and adherence to self-care among patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Journal of Population & Social Studies, 31.
Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health. (2022). Diabetes reports. Retrieved from https://datariskcom-ddc.moph.go.th/download
Diabetes Association of Thailand, Endocrine Society of Thailand, & National Health Security Office. (2023). Clinical practice guideline for diabetes 2023. Bangkok: Srimuang Printing.
Dinavari, M. F., Sanaie, S., Rasouli, K., Faramarzi, E., & Molani-Gol, R. (2023). Glycemic control and associated factors among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A cross-sectional study of Azar cohort population. BMC Endocrine Disorders, 23(1), 273.
Houle, J., Lauzier-Jobin, F., Beaulieu, M. D., Meunier, S., Coulombe, S., Côté, J., Lespérance, F., Chiasson, J. L., Bherer, L., & Lambert, J. (2016). Socioeconomic status and glycemic control in adult patients with type 2 diabetes: A mediation analysis. BMJ open diabetes research & care, 4(1), e000184.
Joeliantina, A. Norontoko, D.A., Wuryaningsih, S.H. & Padoli. (2023). Self-confidence and foot self-care behavior in patients with diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study. Advances in Health Sciences Research 72, 23-31.
Nakhon Si Thammarat Provincial Public Health Office. (2023). Diabetes report. Retrieved from https://nakhonsihealth.moph.go.th/new/?page_id=528
Pachariyanon, W., Kessomboon, P., Suwanmola, L., Chongwarin, S., & Puhern, N. (2018). Factors associated with poor control of diabetes mellitus. Mahasarakham Hospital Journal, 15(1), 118-127.
Phajan, T., Suwannaphant, K., Anarat, B., & Thalakorn, N. (2022). Factors associated with glycemic control among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Thabo, Nong Khai, Thailand. Regional Health Promotion Center 9 Journal, 16(1), 285-298.
Phonphet, C., Suwanno, J., Bunsuk, C., Kumanjan, W., & Thiamwong, L. (2024). Psychometric testing of the cross-culturally adapted Thai version of the self-care self-efficacy scale version 3.0 in individuals with chronic illnesses. International Journal of Nursing Sciences, 11(4), 473-484.
Phuwilert, P., Khiewkhern, S., Phajan, T., Wongprachum, K., Wibuloutai, J., Srichomphoo, C., & Tudpor, K.(2024). Factors affecting glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes in Kalasin province, Thailand: An analytical cross-sectional study. Healthcare, 12(19), 1916.
Riegel, B., De Maria, M., Barbaranelli, C., Luciani, M., Ausili, D., Dickson, V. V., & Vellone, E. (2024). Measuring self-care: A Description of the Family of disease-specific and generic instruments based on the theory of self-care of chronic illness. The Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing. https://doi.org/10.1097/JCN.0000000000001146
Riegel, B., Jaarsma, T., & Strömberg, A. (2012). A middle-range theory of self-care of chronic illness. Advances in Nursing Science, 35(3), 194-204.
Riegel, B., Jaarsma, T., Lee, C. S., & Strömberg, A. (2019). Integrating symptoms into the middle-range theory of self-care of chronic illness. Advances in Nursing Science, 42(3), 206-215.
Ruan, Y., Yan, Q., Hua, X., Ji, Y., Yang, Q., Di, Y., & Shi, R. (2016). Epidemiology of diabetes in adults aged 35 and older from Shanghai, China. BioMed Research International, 2016, Article 7858015.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.




