Using diagnostic molecular technique for Mycobacterium marinum cutaneous infection: A case report
Keywords:
Non-tuberculous mycobacterium, Mycobacterium marinum, 16s rRNA sequencingAbstract
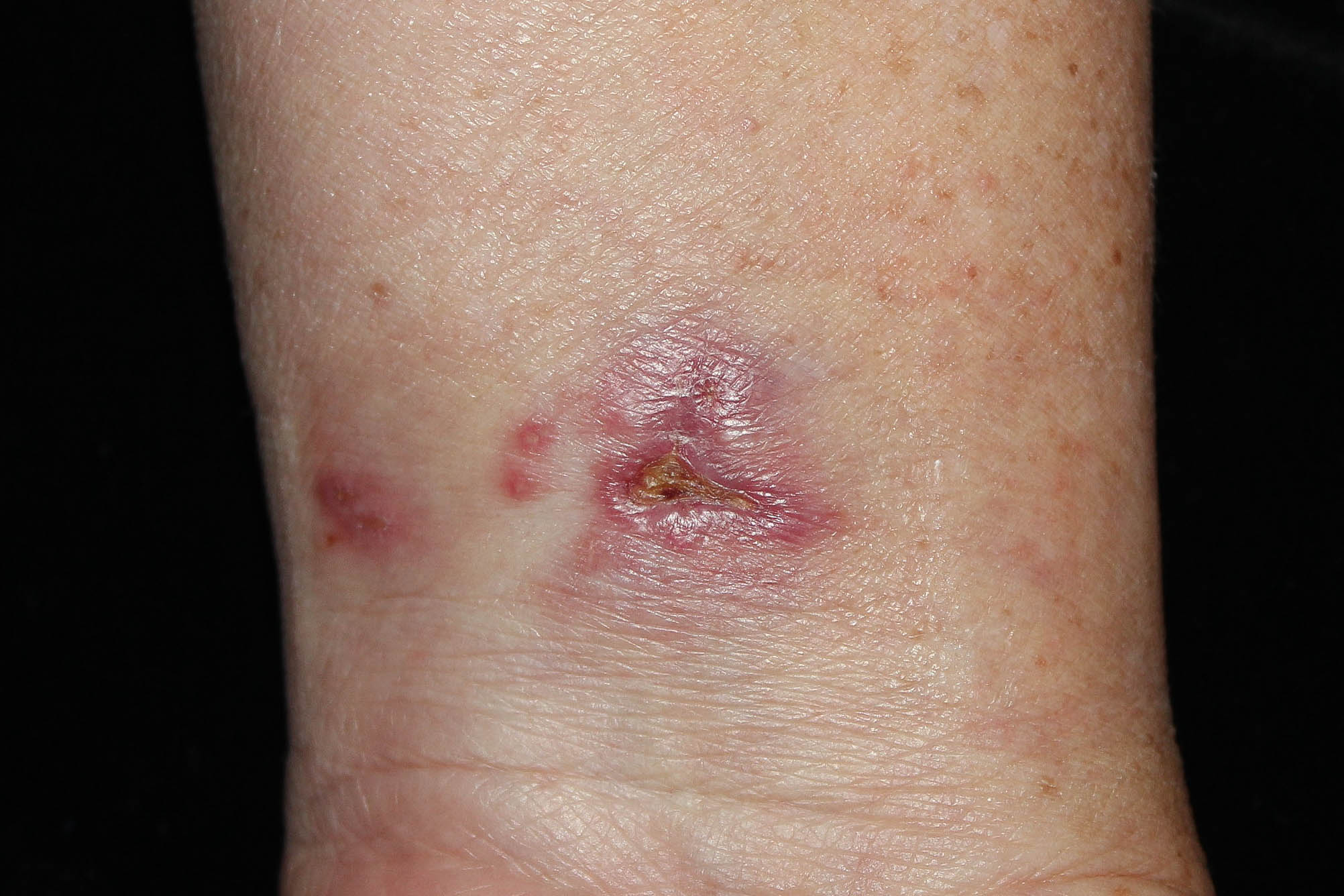
Mycobacterium marinum is the most common slow grower non-tuberculous mycobacteria causing skin infection. The characteristic finding includes subcutaneous nodule which can progress into a sporotrichoid pattern. We report a 66-year-old Thai male who presented with erythematous nodule at left wrist for 3 months. The patient had been treated with topical antibiotic and oral ciprofloxacin without improvement. Skin biopsy showed epitheloid granulomatous formation with positive AFB and fite’s acid fast stain. However, culture for mycobacteria yielded negative result. Subsequent16s rRNA sequencing, a molecular technique using for bacterial identification, detected an organism with 99% compatible with M. marinum. Clarithromycin, ethambutol and doxycycline were started and the patient has significant improvement.
References
2. Johnson MG, Stout JE. Twenty-eight cases of Mycobacterium marinum infection: retrospective case series and literature review. Infection 2015; 43: 655-62.
3. Petrini B. Mycobacterium marinum: ubiquitous agent of waterborne granulomatous skin infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2006; 25: 609-13.
4. Sia TY, Taimur S, Blau DM, et al. Clinical and Pathological Evaluation of Mycobacterium marinum Group Skin Infections Associated With Fish Markets in New York City. Clin Infect Dis 2016; 62: 590-5.
5. El Amin NM, Hanson HS, Pettersson B, Petrini B, Von Stedingk LV. Identification of non-tuberculous mycobacteria: 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis vs. conventional methods. Scand J Infect Dis 2000; 32: 47-50.
6. Travis WD, Travis LB, Roberts GD, Su DW, Weiland LW. The histopathologic spectrum in Myco-bacterium marinum infection. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1985; 109: 1109-13.
7. Nakanaga K, Hoshino Y, Yotsu RR, Makino M, Ishii N. Laboratory procedures for the detection and identification of cutaneous non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections. J Dermatol 2013; 40: 151-9.
8. Chemlal K, Portaels F. Molecular diagnosis of nontuberculous mycobacteria. Curr Opin Infect
Dis 2003; 16: 77-83.
9. Clarridge JE, 3rd. Impact of 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis for identification of bacteria on clinical microbiology and infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004; 17: 840-62, table of contents.
10. Simmon KE, Kommedal Ø, Saebo Ø, Karlsen B, Petti CA. Simultaneous sequence analysis of the 16S rRNA and rpoB genes by use of RipSeq software to identify Mycobacterium species. J Clin Microbiol 2010; 48: 3231-5.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใดๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารฯ หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใดๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากบรรณาธิการวารสารโรคผิวหนังก่อนเท่านั้น


