Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like lupus erythematosus: A case report
Keywords:
Toxic epidermal necrolysis, lupus erythematosus, epidermal necrolysisAbstract
Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like lupus erythematosus, a rare variant of cutaneous lupus erythematosus is characterized by sheet-like desquamation of the skin predominating on photo-distributed area. Clinically, the lesions can present similar to classical toxic epidermal necrolysis. This condition is complicated to be diagnosed due to the rarity of the disease and less information.
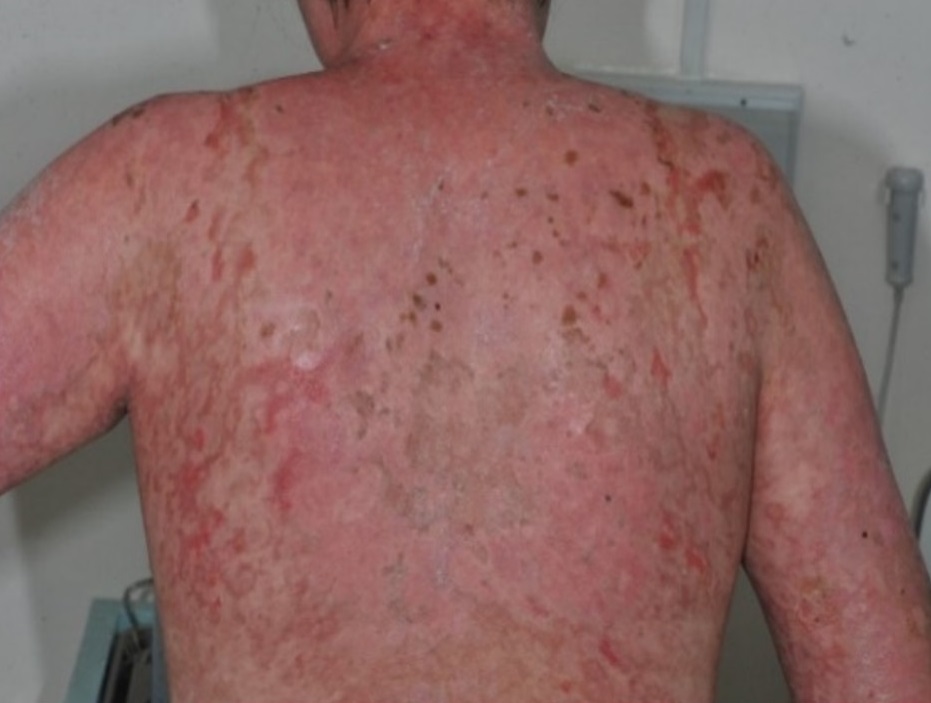
We report a case of 32-year-old Thai woman who has had a long-standing history of systemic lupus erythematosus. The patient presented with a 2-month history of developing widespread, targetoid, red to violaceous photosensitive rash, which then progressed to sheet-like desquamation predominating on sun-exposed area. Histopathology and direct immunofluorescence are compatible with lupus erythematosus. The patient was diagnosed as TEN-like LE. She was prescribed high dosage of intravenous corticosteroid and other immunosuppressive drugs, together with hydroxychloroquine. She responded well to the treatment within a few days.
References
Lissia M, Mulas P, Bulla A, Rubino C. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's disease). Burns 2010; 36: 152-63.
Takeda H, Mitsuhashi Y, Kondo S, Kato Y, Tajima K. Toxic epidermal necrolysis possibly linked to hyperacute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Dermatol 1997; 24: 635-41.
Fournier S, Bastuji-Garin S, Mentec H, Revuz J, Roujeau JC. Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1995; 14: 558-9.
Ball R, Ball LK, Wise RP, Braun MM, Beeler JA, Salive ME. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis after vaccination: reports to the vaccine adverse event reporting system. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2001; 20: 219-23.
Mandelcorn R, Shear NH. Lupus-associated toxic epidermal necrolysis: a novel manifestation of lupus? J Am Acad Dermatol 2003; 48: 525-9.
Boontaveeyuwat E, Silpa-archa N, Kulthanan K. Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (TEN-like ACLE) in SLE patients: a report of two cases. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 2012; 30: 83-7.
Lee HY, Tey HL, Pang SM, Thirumoorthy T. Systemic lupus erythematosus presenting as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a report of three cases. Lupus 2011; 20: 647-52.
Ryan E, Marshman G, Astill D. Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Australas J Dermatol 2012; 53: 303-6.
Sontheimer RD. The lexicon of cutaneous lupus erythematosus--a review and personal perspective on the nomenclature and classification of the cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus. Lupus 1997; 6: 84-95.
Ting W, Stone MS, Racila D, Scofield RH, Sontheimer RD. Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus and the spectrum of the acute syndrome of apoptotic pan-epidermolysis (ASAP): a case report, concept review and proposal for new classification of lupus erythematosus vesiculobullous skin lesions. Lupus 2004; 13: 941-50.
Ziemer M, Kardaun SH, Liss Y, Mockenhaupt M. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in patients with lupus erythematosus: a descriptive study of 17 cases from a national registry and review of the literature. Br J Dermatol 2012; 166: 575-600.
Horne NS, Narayan AR, Young RM, Frieri M. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 2006; 5: 160-4.
Murphy M, Carmichael AJ. Fatal toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with hydroxychloroquine. Clin Exp Dermatol 2001; 26: 457-8.
Primka EJ 3rd, Camisa C. Methotrexate-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient with psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1997; 36: 815-8.
Mori H, Yamanaka K, Kaketa M, et al. Drug eruption caused by azathioprine: value of using the drug-induced lymphocytes stimulation test for diagnosis. J Dermatol 2004; 31: 731-6.
Patel MP, Kute VB, Vanikar AV, Trivedi HL. Cyclophosphamide-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis: vigilance needed. Clin Kidney J 2014; 7: 323-4.
L V-A, Roujeau JC. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine, 8th ed. New York: McGraw Hill; 2012. Chapter 40: Epidermal necrolysis (Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis); p.439-448.
Tankunakorn J, Sawatwarakul S, Vachiramon V, Chanprapaph K. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis-Like Lupus Erythematosus. J Clin Rheumatol. 2018;00: 00-00.
Simsek I, Cinar M, Erdem H, Pay S, Meric C, Dinc A. Efficacy of plasmapheresis in the treatment of refractory toxic epidermal necrolysis-like acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2008; 17: 605-6.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใดๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารฯ หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใดๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากบรรณาธิการวารสารโรคผิวหนังก่อนเท่านั้น


