Safety and efficacy of the combined use of a facial cleanser and moisturizers containing pseudo-ceramide and a eucalyptus extract for Thai non-oily sensitive skin
Keywords:
lactic acid stinging test, barrier function, ceramide, sensitive skin, ThailandAbstract
Background: In Thailand, many people feel irritation or itching in the sunshine and when they sweat, making them feel that their skin is sensitive.
Objective: To confirm the safety and the efficacy of a combination facial skincare regimen with a weakly acidic well foamed mild facial skin cleanser and moisturizers (lotion and cream) containing pseudo-ceramide and a eucalyptus extract on reducing skin symptoms of Thai non-oily sensitive facial skin.
Methods: We performed a 4-week clinical trial of facial care on 27 Thai females who have sensitive skin with normal or decreased levels of facial sebum. Each subject washed her face with a well foamed cleanser followed by application of an aqueous lotion with a eucalyptus extract and a moisturizing cream containing pseudo-ceramide and a eucalyptus extract twice a day for a total of 4 weeks. Prior to and following the 4 weeks of usage, the skin conditions of each subject were evaluated.
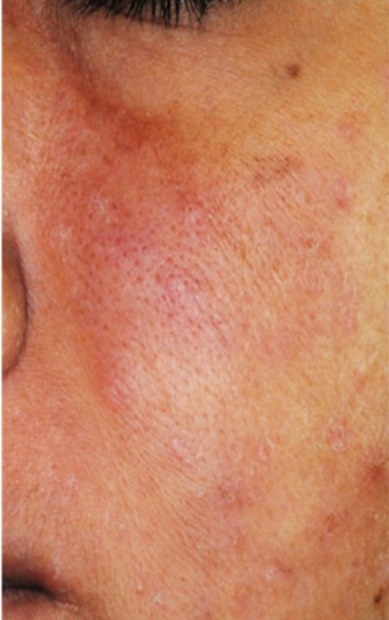
Results: Following 4 weeks of the combination skincare, redness, scaling, and acne were significantly improved. Accompanying those improvements, both skin hydration and cutaneous barrier function improved significantly. A lactic acid sting test indicated a significant decrease in skin sensitivity. No adverse events due to the test samples were observed. The subjects recognized the changes in their skin conditions.
Conclusion: The combination usage of a mild foaming cleanser and an aqueous lotion and moisturizing cream containing pseudo-ceramide and a eucalyptus extract is safe and may be effective for the care of sensitive skin in Thai subjects.
References
Farage MA, Katsarou A, Maibach HI. Sensory, clinical and physiological factors in sensitive skin: a review. Contact Dermatitis 2006; 55: 1-14.
Marriott M, Holmes J, Peters L, Cooper K, Rowson M, Basketter DA. The complex problem of sensitive skin. Contact Dermatitis 2005; 53: 93–99.
Draelos ZD. Sensitive skin: perceptions, evaluation, and treatment. Am J Contact Dermatol 1997; 8: 67-78.
Nojiri H, Ishida K, Yao X, Liu W, Imokawa G. Amelioration of lactic acid sensations in sensitive skin by stimulating the barrier function and improving the ceramide profile. Arch Dermatol Res 2018; 310: 495-504.
Roussaki-Schulze AV, Zafiriou E, Nikoulis D, Klimi E, Rallis E, Zintzaras E. Objective biophysical findings in patients with sensitive skin. Drugs Exp Clin Res 2005; 31: 17-24.
Elias PM, Brown BE. The mammalian cutaneous permeability barrier: defective barrier function is essential fatty acid deficiency correlates with abnormal intercellular lipid deposition. Lab Invest 1978; 39: 574-83.
Imokawa G, Akasaki S, Hattori M, Yoshizuka N. Selective recovery of deranged water-holding properties by stratum corneum lipids J Invest Dermatol 1986; 87: 758-61.
Lampe MA, Burlingame AL, Whitney J, et al. Human stratum corneum lipids: characterization and regional variations. J Lipid Res 1983; 24: 120-30.
Melnik B, Hollmann J, Plewig G. Decreased stratum corneum cerarnides in atopic individuals—a pathobiochemical factor in xerosis? Br J Dermatol 1988; 119: 547-9.
Imokawa G, Abe A, Jin K, Higaki Y, Kawashima M, Hidano A. Decreased level of ceramides in stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis: an etiologic factor in atopic dry skin? J Invest Dermatol 1991; 96: 523-6.
Imokawa G, Akasaki S, Kawamata A, Yano S, Takaishi N. Water retaining function in the stratum corneum and its recovery properties by synthetic pseudoceramides. J Soc Cosmet Chem 1989; 40: 273-285.
Hata M, Tokura Y, Takigawa M, Tamura Y, Imokawa G. Efficacy of using pseudoceramide-containing cream for the treatment of atopic dry skin in comparison with urea cream. Nishi Nihon Hifuka 2002; 64: 606-1.
Matsuki H, Kiyokane K, Matsuki T, Sato S, Imokawa G. Reevaluation of the importance of barrier dysfunction in the nonlesional dry skin of atopic dermatitis patients through the use of two barrier creams. Exog Dermatol 2004; 3: 293–302.
Ishikawa J, Shimotoyodome Y, Chen S, et al. Eucalyptus increases ceramide levels in keratinocytes and improves stratum corneum function. Int J Cosmet Sci 2012; 34: 17-22.
Prottey C, Ferguson T. Factors which determine the skin irritation potential of soaps and detergents. J Soc Cosmet Chem 1975; 26: 29–46.
Takagi Y, Nakagawa H, Higuchi K, Imokawa G. Characterization of surfactant-induced skin damage through barrier recovery induced by pseudoacylceramides. Dermatology 2005; 211: 128–34.
Isoda K, Seki T, Inoue Y, et al. Efficacy of the combined use of a facial cleanser and moisturizers for the care of mild acne patients with sensitive skin. J Dermatol 2015; 42:181-8.
Oh M, Lee J, Kim S, et al. Regional and seasonal differences in skin irritation and neurosensitivity in Chinese and South Korean women. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2015; 29: 115-9.
Kikuchi K, Tagami H; Japanese Cosmetic Scientist Task Force for Skin Care of Atopic Dermatitis. Noninvasive biophysical assessments of the efficacy of a moisturizing cosmetic cream base for patients with atopic dermatitis during different seasons. Br J Dermatol 2008; 158: 969-78.
Rubel D, Thirumoorthy T, Soebaryo RW, Weng SC, Gabriel TM, Villafuerte LL, Chu CY, Dhar S, Parikh D, Wong LC, Lo KK. Asia-Pacific Consensus Group for Atopic Dermatitis. Consensus guidelines for the management of atopic dermatitis: an Asia-Pacific perspective. J Dermatol 2013; 40: 160-171.
Kligman AM, Miller DL, McGinley KJ. Sebutape: A device for visualizing and measuring human sebaceous secretion. J Soc Cosmet Chem 1986; 37: 369-74.
Imokawa G, Tsutsumi H, Kurosaki T. Surface activity and cutaneous effects of monoalkyl phosphate surfactants. J Am Oil Chem Soc 1978; 55: 839-44.
Hayashi N, Akamatsu H, Kawashima M. Establishment of grading criteria for acne severity. J Dermatol 2008; 35: 255-260.
Grafter R, Hackl P, Braun F. Effects of soap and detergents on skin surface pH, stratum corneum hydration and fat content in infants. Dermatology 1997; 195: 258-62.
Sonoda J, Sakai T, Inomata Y. Liquid oil that flows in spaces of aqueous foam without deforming. J Phys Chem B 2014; 118: 9438-44.
Ekanayake Mudiyanselage S, Hamburger M, Elsner P, Thiele JJ. Ultraviolet a induces generation of squalene monohydroperoxide isomers in human sebum and skin surface lipids in vitro and in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 2003; 120: 915-22.
Smith KR, Thiboutot DM. Thematic review series: skin lipids. Sebaceous gland lipids: friend or foe? J Lipid Res 2008; 49: 271-81.
Jananya S, Praewpatoo B, Takagi Y, et al. An Alkyl Ether Carboxylate and Alkyl Carboxylate Formulated Cleanser Decreases Facial Sebum and Inflammatory Acne Without Inducing Dry Xerotic Skin in Thai Females. Int J Clin Dermatol Res 2015; 3: 60-64.
Simion FA, Abrutyn ES, Draelos ZD. Ability of moisturizers to reduce dry skin and irritation and to prevent their return. J Cosmet Sci 2005; 56: 427-44.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใดๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารฯ หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใดๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากบรรณาธิการวารสารโรคผิวหนังก่อนเท่านั้น


