Coexistence of juvenile xanthogranuloma and diffuse plane xanthoma in 22-month-old boy could potentially be caused by digenic inheritance of APOB and APOE4 polymorphism
Keywords:
juvenile xanthogranuloma, diffuse plane xanthoma, dyslipidemiaAbstract
SUNANTAWANICH K*, BOONPUEN N*, DENSUPSOONTORN N**, VIPRAKASIT V**, TANTANASRIGUL P*, SUDTIKOONASETH P*, WESSAGOWIT V*. COEXISTENCE OF JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA AND DIFFUSE PLANE XANTHOMA IN 22-MONTH-OLD BOY COULD POTENTIALLY BE CAUSED BY DIGENIC INHERITANCE OF APOB AND APOE4 POLYMORPHISM. THAI J DERMATOL 2020; 36: 25-30.
*INSTITUTE OF DERMATOLOGY, DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL SERVICES, MINISTRY OF PUBLIC HEALTH, BANGKOK, THAILAND.
**DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICSFACULTY OF MEDICINE SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL, BANGKOK, THAILAND.
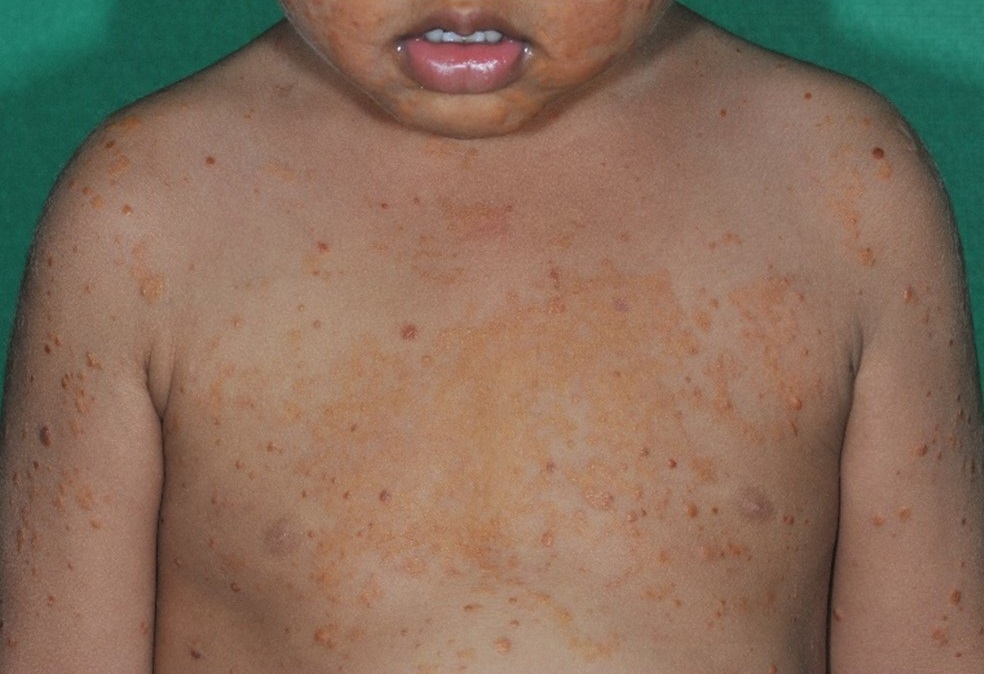
The coexistence of juvenile xanthogranuloma and diffuse plane xanthoma is considered a rare phenomenon. We report a 22-month-old boy with multiple orange-tan papules and yellow plaques on his entire body for 18 months. Two types of histological findings confirmed the diagnosis of juvenile xanthogranuloma and plane xanthoma, respectively. Additionally, the patient’s blood test showed high cholesterol level, which could be associated with familial or secondary dyslipidemia.
References
Pajaziti L, Hapciu SR and Pajaziti A. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Res Notes 2014; 7: 174.
Reserva J, Chamlin SL. An 8-month-old girl with an enlarging lesion on her face. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. Pediatr Ann 2014; 43: e22-24.
Marcoval J, Moreno A, Bordas X, Gallado F, Peyri J. Diffuse plane xanthoma: clinicopathologic study of 8 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol 1998; 39: 439-42.
Le Bidre E, Delage M, Lejars O, Machet MC, Lorette G, Maruani A. Xanthelasma and juvenile xanthogranuloma in a 7-year-old boy. Ann Dermatol Venereol 2009;136:723-6.
Gooding HC, Rodday A, Wong JB, et al. Application of pediatric and adult guidelines for treatment of lipid levels among US adolescents transitioning to young adulthood. JAMA Pediatrics 2015; 169: 569-74.
Hernandez-Martin A, Baselga E, Drolet BA, Estery NB. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. J Am Acad Dermatol 1997; 36: 355-6.
Cypel TK, Zuker RM. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: case report and review of the literature. Can J Plast Surg 2008; 16: 175-7
Dehner LP. Juvenile xanthogranulomas in the first two decades of life: a clinicopathologic study of 174 cases with cutaneous and extracutaneous manifestations. Am J Surg Pathol 2003; 27: 579-93
Freyer DR, Kennedy R, Bostrom BC, Kohut G, Dehner LP. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: forms of systemic disease and their clinical implications. J Pediatr 1996; 129: 227-37.
Fenot M, Stalder JF, Barbarot S. Juvenile xanthogranulomas are highly prevalent but transient in young children with neurofibromatosis type 1. J Am Acad Dermatol 2014; 71: 389-90.
Iyengar V, Golomb CA and Schachner L. Neurilemmomatosis, NF2, and juvenile xanthogranuloma. J Am Acad Dermatol 1998;39:831-4.
Chakraborty R, Hampton OA, Abhyankar H, et al. Activating MAPK1 (ERK2) mutation in an aggressive case of disseminated juvenile xanthogranuloma. Oncotarget 2017;8:46065-70.
Zak A, Zeman M, Slaby A, Vecka M. Xanthomas: clinical and pathophysiological relations. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 2014;158:181-8.
Cambiaghi S, Boneschi V, Maffeis L, Gelmetti C. Diffuse normolipemic plane xanthoma in a child with common variable immunodeficiency. Pediatr Dermatol 2011;28: 65-6.
Hofmann M, Zappel K, Trefzer U, et al. Diffuse normolipemic plane xanthoma in a 9-year-old boy. Pediatr Dermatol 2005;22:127-9.
Densupsoontorn N JP, Ruangratanaamporn O. Early atherosclerosis in children with familial hypercholesterolemia: a 2 cases report. Siriraj Hosp Gaz. 2001:310-6.
Fulton JE Jr. Dermabrasion, chemabrasion, and laserabrasion. Historical perspectives, modern dermabrasion techniques, and future trends. Dermatol Surg 1996; 22: 619-28.
Diamond EL, Durham BH, Haroche J, et al. Diverse and Targetable Kinase Alterations Drive Histiocytic Neoplasms. Cancer Discov 2016; 6:154–65.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใดๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารฯ หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใดๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากบรรณาธิการวารสารโรคผิวหนังก่อนเท่านั้น


