A progressive erythematous plaque on the central face and nose after mesotherapy, an uncommon presentation of Mycobacterium marinum infection
Keywords:
Mycobacterium marinum infection, Cosmetic procedures, Facial infectionAbstract
CHUMSAENGSRI C, BOONPUEN N. A PROGRESSIVE ERYTHEMATOUS PLAQUE ON THE CENTRAL FACE AND NOSE AFTER MESOTHERAPY, AN UNCOMMON PRESENTATION OF MYCOBACTERIUM MARINUM INFECTION. THAI J DERMATOL 2020; 36: 31-37.
INSTITUTE OF DERMATOLOGY, DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL SERVICES, MINISTRY OF PUBLIC HEALTH, BANGKOK, THAILAND.
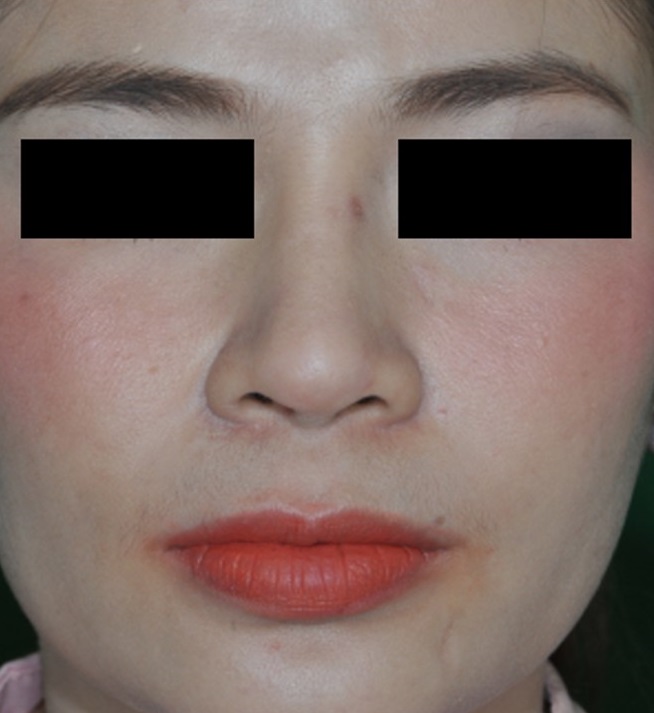
Mycobacterium marinum is a slowly growing photochromogenic nontuberculous mycobacterium and its ability to cause localized skin and soft tissue infections in individuals with exposure to contaminated freshwater or salt water. So far, only small amount cases of M. marinum infection on the face have been reported worldwide and all cases have been linked to aquatic exposure. No previous documented history of cosmetic procedures related to M. marinum facial infection. We reported a case 32-year-old Thai female who presented with atypical infected site of multiple erythematous indurated plaques on predominately central face from M. marinum infection suspected from mesotherapy. Diagnosis was made by using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique from skin biopsy. She was treated with clarithromycin plus ciprofloxacin for 2 months then switched to azithromycin plus ethambutol for 7 months due to pregnancy. After total 9-month therapeutic treatment, the lesions healed gradually without scar.
References
Franco-Paredes C, Marcos LA, Henao-Martínez AF, et al. Cutaneous Mycobacterial Infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 2018; 32: 1-25.
Aubry A, Mougari F, Reibel F, Cambau E. Mycobacterium marinum. Microbiol Spectr 2017; 5: 17-38.
Guglielmetti L, Mougari F, Lopes A, Raskine L, Cambau E. Human infections due to nontuberculous mycobacteria: the infectious diseases and clinical microbiology specialists' point of view. Future Microbiol 2015; 10: 1467-83.
Jabbour SF, Malek AE, Kechichian EG, Tomb RR, Nasr MW. Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections After Cosmetic Procedures: A Systematic Review and Management Algorithm. Dermatol Surg 2019; 3: 1-10.
Hypolite T, Grant-Kels JM, Chirch LM. Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections:a potential complication of cosmetic procedures. Int J Womens Dermatol 2015; 1: 51-4.
Ko DY, Song KH. Mycobacterium marinum occuring on the face. J Dermatol 2013; 40:773-4.
Oh HW, Youn SH, Kim MS, et al. Mycobacterium marinum Infection on the Face Diagnosed by Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification and Direct Sequencing. Ann Dermatol 2015; 27: 639-41.
Feng H, Su Y, Fu S, et al. Image Gallery: Fish tank granuloma on the face with sporotrichoid cervicofacial lymphadenitis and abscesses due to Mycobacterium marinum infection. Br J Dermatol 2019; 180: e180.
Gang Sun, Chao Chen, Jing Li, et al. Discriminatory potential of a novel set of Variable Number of Tandem Repeats for genotyping Mycobacterium marinum. Vet Microbiol 2011; 152: 200-4.
Ramos-e-Silva M, Ribeiro Castro MC. Mycobacterial infections: non-tuberculous mycobacterioses. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2018: 1309-16.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใดๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารฯ หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใดๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากบรรณาธิการวารสารโรคผิวหนังก่อนเท่านั้น


