Efficacy and patients’ satisfaction of anti-inflammatory ointment in xerotic conditions
Keywords:
xerosis, xerosis cutis, anti-inflammatory ointment, moisturizersAbstract
CHAROENPIPATSIN N, SUKAKUL T, VAROTHAI S, LIMPHOKA P, BOONCHAI W. EFFICACY AND PATIENTS’ SATISFACTION OF ANTI-INFLAMMATORY OINTMENT IN XEROTIC CONDITIONS. THAI J DERMATOL 2020;36:55-66.
DEPARTMENT OF DERMATOLOGY, FACULTY OF MEDICINE SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL, MAHIDOL UNIVERSITY, BANGKOK, THAILAND.
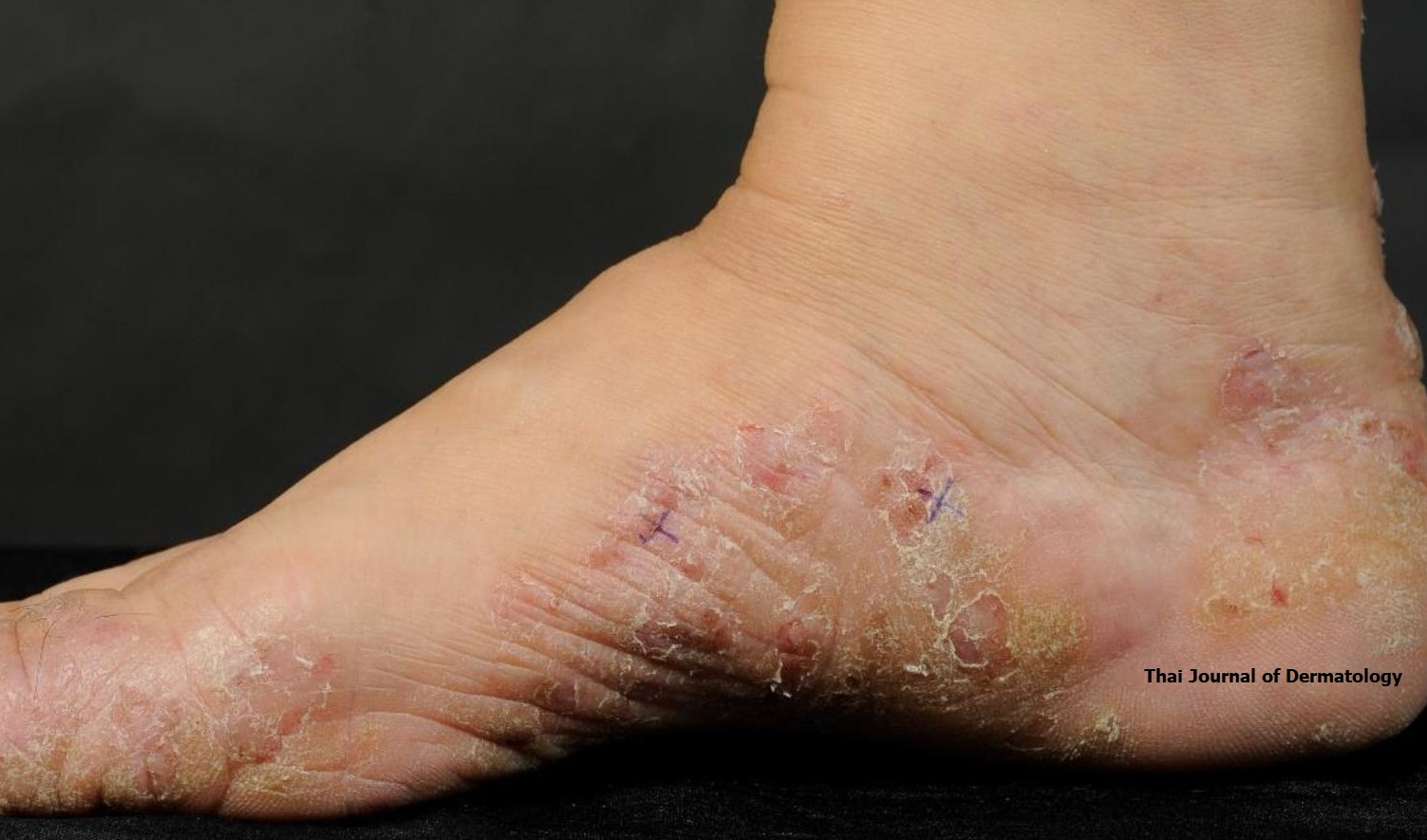
Background: Xerotic conditions are the conditions of severely dry skin which commonly co-manifest in varieties of skin diseases such as eczema or ichthyosis. The mainstay of treatment for patients with xerosis was to well moisturize the skin. Moisturizer with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties may provide treatment benefit in patients with xerosis.
Objective: To examine the efficacy and patients’ satisfactory of anti-inflammatory ointment (Ezerra ointment®) in xerotic conditions.
Materials and methods: We performed a 5-week open-labelled prospective study on 25 patients with xerotic conditions. Patients applied the product for a 4-week period and then discontinue during the
last week. The two selected areas were assessed by a same physician at weeks 0, 2, 4 and 5 using symptoms severity assessment, physician global assessment, and bioengineering assessments consisting of Corneometer® to assess skin hydration and Tewameter® to assess transepidermal water loss. Patients assessed severity of their symptoms at week 0, 4, and 5. Product satisfaction was assessed at week 4.
Results: All patients completed the study. Dryness, scale, and overall assessment assessed by physician and dryness assessed by patients decreased significantly during the application of the ointment and maintained even one week after stopping the treament. Both physician and patient global assessments significantly improved. The skin hydration evaluated by Corneometer® significantly increased during the application of the ointment but at one week after the skin hydration decreased significantly from during the usage.
Conclusion: This anti-inflammatory ointment help to improve symptoms, increase skin hydration and reduce signs of skin inflammation in patients with xerotic conditions.
References
Augustin M, Kirsten N, Korber A, et al. Prevalence, predictors and comorbidity of dry skin in the general population. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2019;33:147-50.
Parker J, Scharfbillig R, Jones S. Moisturisers for the treatment of foot xerosis: a systematic review. J Foot Ankle Res 2017;10:9.
Hon KL, Tsang YC, Pong NH, et al. Patient acceptability, efficacy, and skin biophysiology of a cream and cleanser containing lipid complex with shea butter extract versus a ceramide product for eczema. Hong Kong Med J 2015;21:417-25.
Akarsu S, Ozbagcivan O, Ilknur T, Semiz F, Inci BB, Fetil E. Xerosis cutis and associated co-factors in women with prurigo nodularis. An Bras Dermatol 2018;93:671-9.
Draelos ZD, Raymond I. The efficacy of a ceramide-based Cream in mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 2018;11:30-2.
Del Rosso JQ. Moisturizers: function, formulation and clinical applications. In: Draelos Z DJ, Alam M, editor. Cosmeceuticals. 2nd ed. China: Saunders Elsevier 2009:p.97–102.
Chularojanamontri L, Tuchinda P, Kulthanan K, Pongparit K. Moisturizers for Acne: what are their constituents? J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 2014;7:36-44.
Jirabundansuk P, Ophaswongse S, Udompataikul M. Comparative trial of moisturizer containing spent grain wax, Butyrospermum parkii extract, Argania spinosa kernel oil vs. 1% hydrocortisone cream in the treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis. J Med Assoc Thai 2014;97:820-6.
Lin TK, Zhong L, Santiago JL. Anti-Inflammatory and skin barrier repair effects of topical application of some plant oils. Int J Mol Sci 2017;19.
Kang BC, Kim YE, Kim YJ, Chang MJ, Choi HD, Li K, et al. Optimizing EEMCO guidance for the assessment of dry skin (xerosis) for pharmacies. Skin Res Technol 2014;20:87-91.
Pereira MP, Stander S. Assessment of severity and burden of pruritus. Allergol Int 2017;66:3-7.
Oishi N, Iwata H, Kobayashi N, Fujimoto K, Yamaura K. A survey on awareness of the "finger-tip unit" and medication guidance for the use of topical steroids among community pharmacists. Drug Discov Ther 2019;13:128-32.
Diluvio L, Dattola A, Cannizzaro MV, Franceschini C, Bianchi L. Clinical and confocal evaluation of avenanthramides-based daily cleansing and emollient cream in pediatric population affected by atopic dermatitis and xerosis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol 2019;154:32-6.
Eberlein B, Eicke C, Reinhardt HW, Ring J. Adjuvant treatment of atopic eczema: assessment of an emollient containing N-palmitoylethanolamine (ATOPA study). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2008;22:73-82.
Hengge UR, Ruzicka T, Schwartz RA, Cork MJ. Adverse effects of topical glucocorticosteroids. J Am Acad Dermatol 2006;54:1-15;quiz6-8.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใดๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารฯ หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใดๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากบรรณาธิการวารสารโรคผิวหนังก่อนเท่านั้น


