Localized Cutaneous Nodular Chromoblastomycosis Caused by Diaporthe phaseolorum; A Case Report and Literature Review
Keywords:
Chromoblastomycosis, phaeohyphomycosis, Diaporthe phaseolorumAbstract
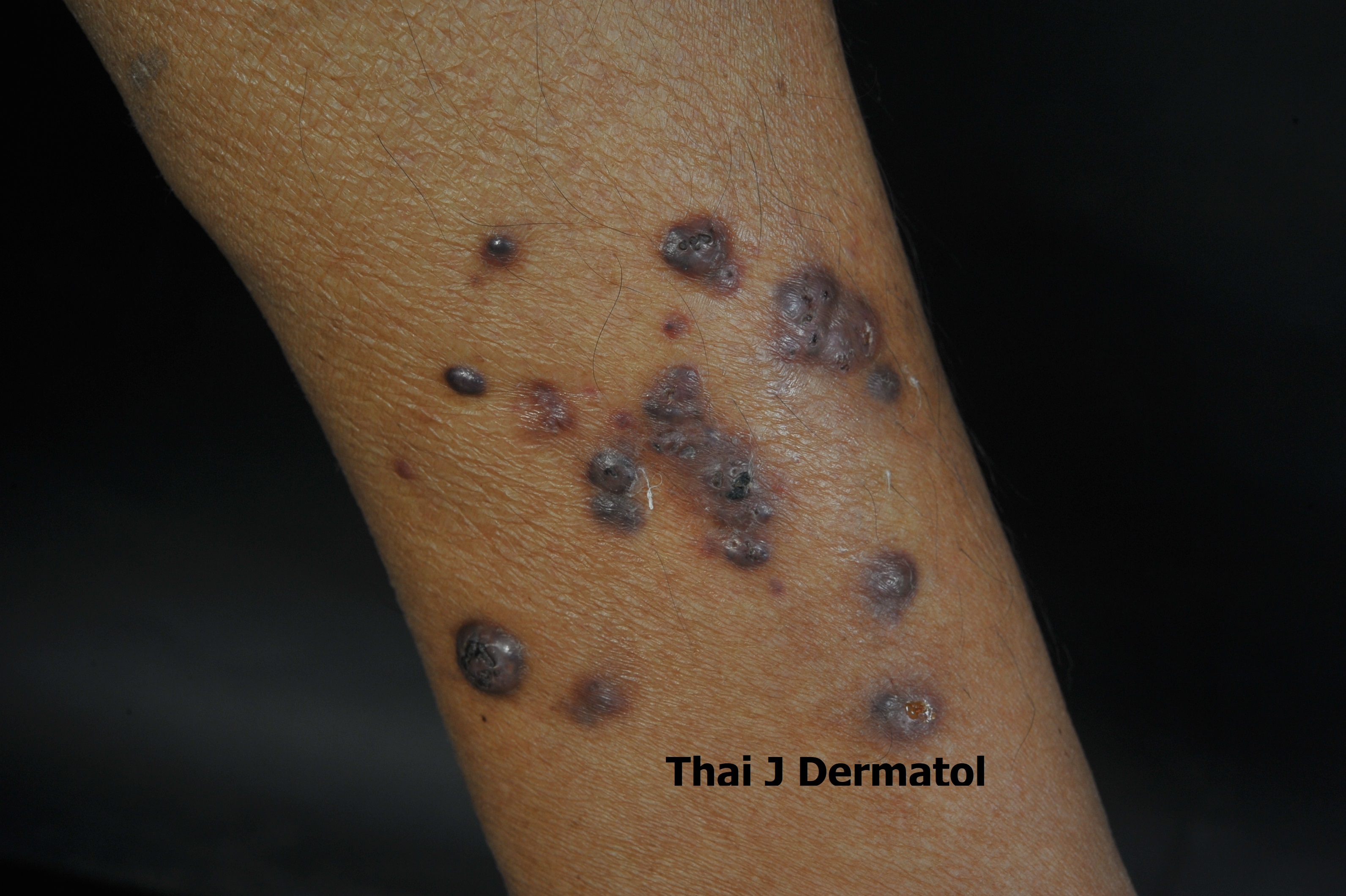
We report an unusual case of localized cutaneous nodular chromoblastomycosis caused by Diaporthe phaseolorum in a diabetic patient with previous kidney transplantation. Clinical presentation showing a group of multiple cutaneous brownish nodules located on unilateral leg was initially suspicious of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis. Diagnosis was confirmed by histological evaluation, mycological culture and molecular identification of causative organism. This was the first case presentation of chromoblastomycosis caused by Diaporthe phaseolorum. We encourage that the combination of clinical suspicion, skin biopsy, tissue culture and molecular diagnosis are important and remain the mainstay for making a diagnosis of the atypical cutaneous fungal infection especially from the uncommon causative fungi.
References
Brandt M, Warnock D. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and therapy of infections caused by dematiaceous fungi. Journal of Chemotherapy 2003;15(sup2):36-47.
Brito ACd, Bittencourt MdJS. Chromoblastomycosis: an etiological, epidemiological, clinical, diagnostic, and treatment update. Anais brasileiros de dermatologia 2018;93:495-506.
Gomes R, Glienke C, Videira SIR, Lombard L, Groenewald J, Crous P. Diaporthe: a genus of endophytic, saprobic and plant pathogenic fungi. Persoonia: Molecular Phylogeny and Evolution of Fungi 2013;31:1.
Mandell KJ, Colby KA. Penetrating keratoplasty for invasive fungal keratitis resulting from a thorn injury involving Phomopsis species. Cornea 2009;28:1167-9.
Sutton DA, Timm WD, Morgan-Jones G, Rinaldi MG. Human phaeohyphomycotic osteomyelitis caused by the coelomycete Phomopsis saccardo 1905: criteria for identification, case history, and therapy. Journal of clinical microbiology 1999;37:807-11.
Iriart X, Binois R, Fior A, Blanchet D, Berry A, Cassaing S, et al. Eumycetoma caused by Diaporthe phaseolorum (Phomopsis phaseoli): a case report and a mini‐review of Diaporthe/Phomopsis spp invasive infections in humans. Clinical microbiology and infection 2011;17:1492-4.
Mattei AS, Severo CB, Guazzelli LS, Oliveira FM, Gené J, Guarro J, et al. Cutaneous infection by Diaporthe phaseolorum in Brazil. Medical mycology case reports 2013;2:85-7.
Rakita RM, O'Brien KD, Bourassa L. Diaporthe soft tissue infection in a heart transplant patient. Transplant Infectious Disease 2017;19:e12680.
Howard JC, Chen K, Werno A, Metcalf S. Soft Tissue Infection with Diaporthe phaseolorum in Heart Transplant Recipient with End-Stage Renal Failure. Emerging infectious diseases 2019;25:1748.
Laosakul K, Youngchim S, Chuamanochan M, Rujiwetpongstorn R, Tovanabutra N, Chiewchanvit S. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Diaporthe phaseolorum in an immunocompetent patient in Thailand: a case report. Access Microbiology 2020:acmi000128.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใดๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารฯ หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใดๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากบรรณาธิการวารสารโรคผิวหนังก่อนเท่านั้น


