Nagashima-Type Palmoplantar Keratosis with Uncommon Homozygous Frameshift Mutations in SERPINB7
Keywords:
Nagashima type, palmoplantar keratosis, SERPINB7, autosomal recessiveAbstract
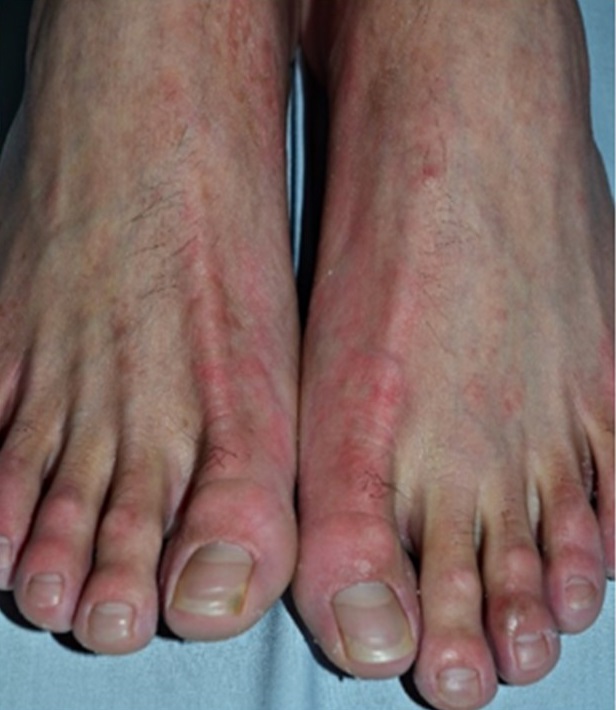
Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis (NPPK, MIM6155998) is a non-epidermolytic, non-progressive, non-syndromic (isolated), diffuse palmoplantar keratosis inherited by autosomal recessive pattern. It is characterized by diffuse, erythematous palmoplantar hyperkeratosis that extends to the dorsal surfaces of hands, feet, inner wrists, ankles, and Achilles tendon area. Loss-of-function mutations in SERPINB7 have been identified as a cause of NPPK. Here, we report a Chinese male with NPPK, confirmed as having one basepair duplication at nucleotide 522 (c.522dupT), likely homozygous variant, which created a shift in the reading frame and expected to result in a prematurely truncated protein (p.Val175Cysfs*46) in SERPINB7. We review the genomic structure of SERPINB7 and all probable mutations.
References
Kubo A. Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis: a common Asian type caused by SERPINB7 protease inhibitor deficiency. J Invest Dermatol 2014;134:2076-9.
Kubo A, Shiohama A, Sasaki T, et al. Mutations in SERPINB7, encoding a member of the serine protease inhibitor superfamily, cause Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis. Am J Hum Genet 2013;93:945–56.
Hida T, Okura M, Kamiya T, Yamashita T. Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis caused by compound heterozygous mutations in SERPINB7. Eur J Dermatol 2015;25:202-3.
Yin J, Xu G, Wang H, et al. New and recurrent SERPINB7 mutations in seven Chinese patients with Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis. J Invest Dermatol 2014;134:2269–72.
Zhang J, Zhang G, Ni C, et al. Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis in a Chinese Han population. Mol Med Rep 2016;14:4049–54.
On HR, Lee SE, Nomura T, et al. Identification of SERPINB7 mutations in Korean patients with Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis. J Dermatol 2017;44:840–1.
Hua S, Miao X, Mao W, Hua L, Chen J, Li B. A novel frameshift SERPINB7 mutation in a Chinese case with Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis: case report and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol 2018;43:953–5.
Ohguchi Y, Nomura T, Suzuki S, et al. Gentamicin-Induced Readthrough and Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay of SERPINB7 Nonsense Mutant Transcripts. J Invest Dermatol 2018;138:836–43.
Songsantiphap C, Suwanwatana J, Ittiwut C, Asawanonda P, Rerknimitr P, Shotelersuk V. Nagashima-Type Palmoplantar Keratosis with Compound Heterozygous Mutations in SERPINB7. Case Rep Dermatol 2020;12:241-8.
Shotelersuk V, Wichadakul D, Ngamphiw C, et al. The Thai reference exome (T-REx) variant database. Clin Genet 2021;100:703-12.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Thai Journal of Dermatology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใดๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารฯ หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใดๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากบรรณาธิการวารสารโรคผิวหนังก่อนเท่านั้น


