Rituximab-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease in Pemphigus Patients: Two Case Reports and Review of the Literature
Keywords:
Rituximab, Drug-induced interstitial lung disease, PemphigusAbstract
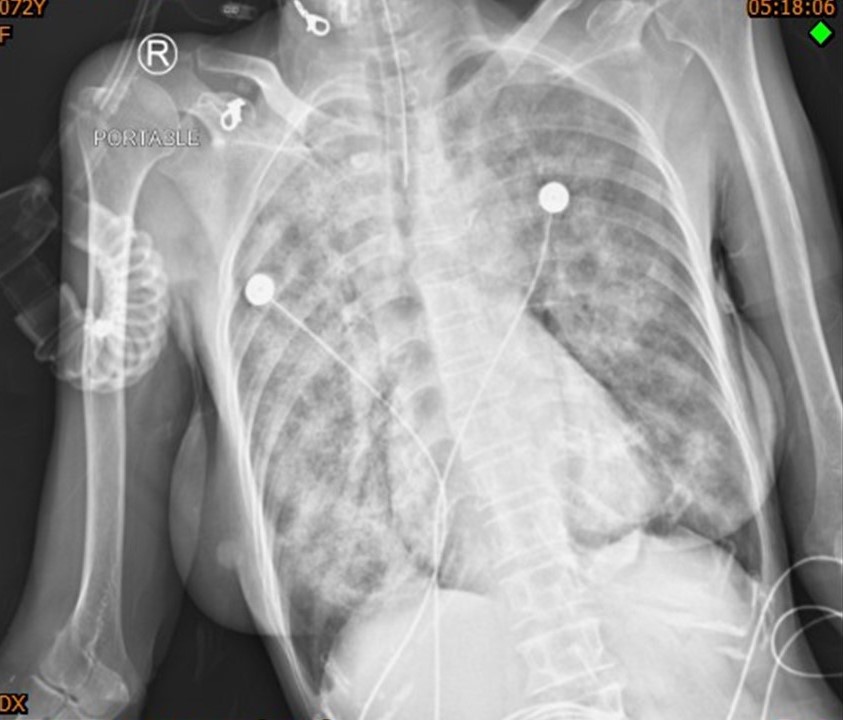
Rituximab is a CD20-directed cytolytic antibody approved as a novel effective first-line treatment for severe pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Rituximab is generally safe, but uncommon fatal adverse events such as drug-induced interstitial lung disease have been reported. We reported two patients who developed rituximab-induced interstitial lung disease despite receiving the recommended standard dosages and review of the literature.
References
Kasperkiewicz M, Ellebrecht CT, Takahashi H, et al. Pemphigus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2017 11;3:17026.
Joly P, Horvath B, Patsatsi A, et al. Updated S2K guidelines on the management of pemphigus vulgaris and foliaceus initiated by the european academy of dermatology and venereology (EADV). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2020;34:1900-13.
Eming R, Nagel A, Wolff-Franke S, et al. Rituximab exerts a dual effect in pemphigus vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol 2008;128:2850-8.
Borradori L, Lombardi T, Samson J, Girardet C, Saurat JH, Hügli A. Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab) for refractory erosive stomatitis secondary to CD20(+) follicular lymphoma-associated paraneoplastic pemphigus. Arch Dermatol 2001;137:269-72.
Research C for DE and. Rituximab (marketed as Rituxan) Information. FDA [Internet]. 2022 Feb 24 [cited 2023 Sep 3]; Available from: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/rituximab-marketed-rituxan-information
Theerasuk K, Yingluk W, Teeraya P, et al. Clinical and radiological correlation of pulmonary complications in CHOP versus rituximab-CHOP regimen treated non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Thailand 2017.
Emery P, Fleischmann R, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, et al. The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: results of a phase IIB randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:1390-400.
Douze M, Sabina V, Adrien J, et al. Rituximab Induced Interstitial Lung Disease Diagnosis, Treatment Outcome, and Risk’s Factor, a Place for Transbronchial Pulmonary Cryobiopsy. Case Reports in Clinical Medicine 2021;10:284-94.
Lioté H, Lioté F, Séroussi B, Mayaud C, Cadranel J. Rituximab-induced lung disease: A systematic literature review. Eur Respir J 2010;35:681-7.
Bitzan M, Anselmo M, Carpineta L. Rituximab (B-cell depleting antibody) associated lung injury (RALI): a pediatric case and systematic review of the literature. Pediatr Pulmonol 2009;44:922-34.
Hadjinicolaou AV, Nisar MK, Parfrey H, Chilvers ER, Ostör AJ. Non-infectious pulmonary toxicity of rituximab: a systematic review. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012;51:653-62.
MASTER AM, LASSER RP, BECKMAN G. Tables of average weight and height of Americans aged 65 to 94 years: relationship of weight and height to survival. J Am Med Assoc 1960;172:658-62.
Wang HH, Liu CW, Li YC, Huang YC. Efficacy of rituximab for pemphigus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of different regimens. Acta Derm Venereol 2015;95:928-32.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Thai Journal of Dermatology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใดๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารฯ หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใดๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากบรรณาธิการวารสารโรคผิวหนังก่อนเท่านั้น


