A comparison of efficiency between 18F-FDG PET neuroimaging analysis software in Alzheimer’s disease patients
Keywords:
Alzheimer’s Disease, brain analysis software, MIM software, the Syngo viaAbstract
Introduction: Alzheimer’s disease is a common type of dementia that affects thinking, memory, and social abilities resulting from nerve cells being damaged or lost. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) brain imaging is most wildly used to detect these conditions and there is various software for analysis.
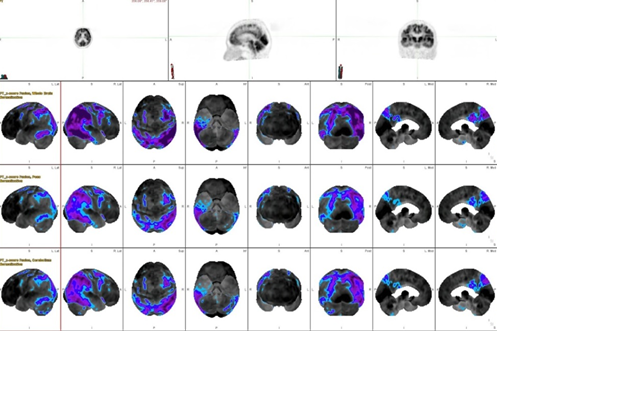
Therefore, the use of appropriate software can support radiologist for improving the efficiency of diagnosis and treatment outcomes for Alzheimer’s disease. Purpose: This study aimed to compare the accuracy and effectiveness of the automated quantitative software of Syngo via and MIM software, and also guided the use of an appropriate analysis software. Methods: A total of 40 patients, aged 56-77 years, consisted of 20 normal patients and 20 diseased patients that were collected and analyzed by the Syngo via and the MIM software. The data analysis for PET subjects were compared with the calculated data and the visual analysis from physicians, respectively. Results: In normal patients, the MIM software show the result of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were 75.68, 66.67, 96.55 and 18.18, while the Syngo via show the result were 91.89, 0.00, 91.89 and 0.00, respectively. For the Alzheimer’s disease patients, the MIM software show the result of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value are 94.74, 47.62, 62.07 and 90.91, while the Syngo via are 100.00, 14.29, 51.53 and 100.00, respectively. Conclusion: This study indicates that the Syngo via software is higher sensitivity than the MIM software. However, the MIM software is more accurate and suitable than the Syngo via software for diagnosis due to there are high specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value.
Downloads
References
วีรศักดิ์ เมืองไพศาล, ภาวะสมองเสื่อม, คลินิกผู้สูงอายุ ภาควิชาเวชศาสตร์ป้องกันและสังคม คณะแพทยศาสตร์ศิริราชพยาบาล
สถาบันประสาทวิทยา กรมการแพทย์, แนวทางเวชปฏิบัติภาวะสมองเสื่อม Clinical Practice Guidelines : Demetia. 2557
Miller CA. Nursing for wellness in older adults. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2021 Nov 24.
ลัดดา เหมาะสุวรรณ และคณะ. การสำรวจสุขภาพประชาชนไทยโดยการตรวจร่างกาย ครั้งที่ 4 พ.ศ. 2551-2: สุขภาพเด็ก. สำนักงานสำรวจสุขภาพประชาชน ไทย; 2552
สมศักด์ ชุณหรัศมิ์. สถานการณ์ผู้สูงอายุไทย พ.ศ.2552. กรุงเทพฯ: มูลนิธิสถาบันวิจัยและพัฒนาผู้สูงอายุไทย.2553
ชนิสา โชติพานิช. PET imaging in dementia การตรวจเพทในภาวะสมองเสื่อม. กรุงเทพฯ: เท็กซ์ แอนด์ เจอร์นัล พับลิเคชั่น; 2561
Buratachwatanasiri W, Chantadisai M, Onwanna J, Chongpison Y, Rakvongthai Y, Khamwan K. Pharmacokinetic Modeling of 18F-FDOPA PET in the Human Brain for Early Parkinson's Disease. Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther. 2021 Jun 3;30(2):69-78.
Piper J. Quantitative comparison of spatial normalization algorithms for 3D PET brain scans. J Nucl Med. 2007;48 Suppl 2:S403
Arain Z, Lodge M, Wahl R. A comparison of SUV parameters across four commercial software platforms. Soc Nuclear Med; 2015.
Knesaurek K, Warnock G, Kostakoglu L, Burger C. Comparison of Standardized Uptake Value Ratio Calculations in Amyloid Positron Emission Tomography Brain Imaging. World J Nucl Med. 2018;17(1):21-6.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 The Thai Society of Radiological Technologists

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย (The Thai Society of Radiological Technologists)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทยและบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆในสมาคม ฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




