Efficacy of tuberculosis screening using the AI chest 4All (DMS–TU) for Thai people innovation at Udonthani Cancer Hospital
Keywords:
Chest X–ray image, Artificial Intelligence, TuberculosisAbstract
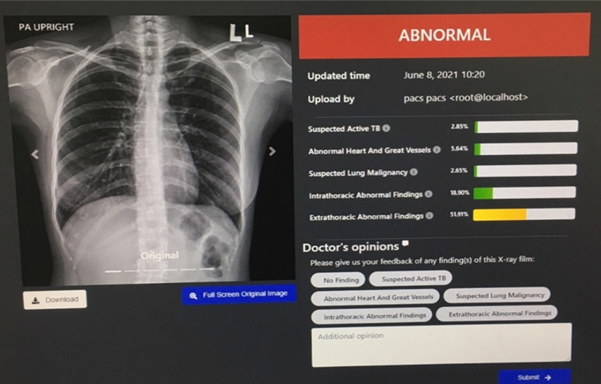
Background: The chest X–ray images could be interpreted utilizing "AI Chest 4All (DMS–TU) For Thai People". This study aimed to evaluate the performance of this artificial intelligence system in tuberculosis screening. Methods: A total of 7,175 chest X–ray images from the check–up group at Udonthani Cancer Hospital were employed as the subjects. Data were collected retrospectively between July 2nd, 2020, and September 30th, 2023. The interpretation results of the AI Chest 4All (DMS–TU) For Thai People were compared with those of the radiologist, focusing on sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy. Results: The findings revealed that the values for sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 87.50, 98.60, and 98.53 respectively. Conclusion: These results demonstrate the potential of AI Chest 4 All (DMS–TU) For Thai People in efficiently screening for tuberculosis, rapidly identifying patients, enabling immediate treatment, achieving more effective tuberculosis control, and reducing the number of tuberculosis cases.
Downloads
References
Kulkarni S, Jha S. Artificial intelligence, radiology, and tuberculosis: a review. Acad Radiol. 2020;27(1):71–5.
Qin ZZ, Ahmed S, Sarker MS, Paul K, Adel ASS, Naheyan T, et al. Tuberculosis detection from chest X-rays for triaging in a high tuberculosis-burden setting: an evaluation of five artificial intelligence algorithms. Lancet Digit Health. 2021;3(9):e543–54.
Cao X, Li Y, Xin H, Zhang H, Pai M, Gao L. Application of artificial intelligence in digital chest radiography reading for pulmonary tuberculosis screening. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2021;7(1):35–40.
Thammarach P, Khaengthanyakan S, Vongsurakrai S, Phienphanich P, Pooprasert P, Yaemsuk A, et al. AI chest 4 all. In: 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC) [Internet]. IEEE; 2020 [cited 2024 Jul 22]. p. 1229–33. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9175862/
Qin ZZ, Sander MS, Rai B, Titahong CN, Sudrungrot S, Laah SN, et al. Using artificial intelligence to read chest radiographs for tuberculosis detection: a multi-site evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of three deep learning systems. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15000.
Geric C, Qin ZZ, Denkinger CM, Kik SV, Marais B, Anjos A, et al. The rise of artificial intelligence reading of chest X-rays for enhanced TB diagnosis and elimination. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2023;27(5):367–72.
Liao Q, Feng H, Li Y, Lai X, Pan J, Zhou F, et al. Evaluation of an artificial intelligence (AI) system to detect tuberculosis on chest X-ray at a pilot active screening project in Guangdong, China in 2019. J X-Ray Sci Technol. 2022;30(2):221–30.
Nijiati M, Ma J, Hu C, Tuersun A, Abulizi A, Kelimu A, et al. Artificial intelligence assisting the early detection of active pulmonary tuberculosis from chest X-rays: a population-based study. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:874475.
พัชริดา มหัสฉริยพงษ์. การประเมินความแม่นยำของเครื่องมืออ่านภาพรังสีทรวงอกอัตโนมัติ ปัญญาประดิษฐ์ (Artificial Intelligence; AI) ในการแปลผลวัณโรคปอดจากภาพรังสีทรวงอกในผู้ป่วยนอกที่มีอาการสงสัยวัณโรคปอด อ.แม่ระมาด จ.ตาก. วารสารระบบบริการปฐมภูมิและเวชศาสตร์ครอบครัว. 2564;4:35–45.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The Thai Society of Radiological Technologists

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย (The Thai Society of Radiological Technologists)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทยและบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆในสมาคม ฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




