ประสิทธิภาพการคัดกรองวัณโรคของนวัตกรรม “AI Chest 4AII (DMS-TU) For Thai People” ที่โรงพยาบาลมะเร็งอุดรธานี
คำสำคัญ:
ภาพถ่ายรังสีทรวงอก, ปัญญาประดิษฐ์, วัณโรคปอดบทคัดย่อ
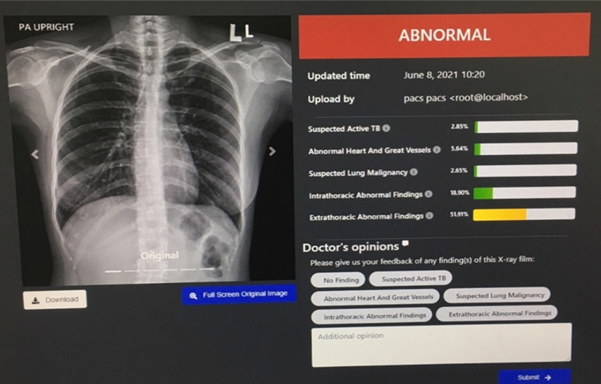
บทนำ: “AI Chest 4All (DMS–TU) For Thai People” มีความสามารถในการแปลผลภาพถ่ายรังสีทรวงอก การศึกษานี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อทดสอบประสิทธิภาพการคัดกรองวัณโรคของปัญญาประดิษฐ์ดังกล่าว วิธีการศึกษา: กลุ่มตัวอย่างในการศึกษาเป็นภาพถ่ายรังสีทรวงอกของกลุ่มผู้รับบริการตรวจสุขภาพในโรงพยาบาลมะเร็งอุดรธานี จำนวนทั้งหมด 7,175 ภาพ เก็บข้อมูลย้อนหลังตั้งแต่วันที่ 2 กรกฎาคม 2563 ถึงวันที่ 30 กันยายน 2566 บันทึกข้อมูลการแปลผลภาพถ่ายรังสีทรวงอกของนวัตกรรม AI Chest 4All (DMS–TU) For Thai People เปรียบเทียบกับการแปลผลของรังสีแพทย์ ด้วยค่าความไว (Sensitivity), ค่าความจำเพาะ (Specificity) และค่าความแม่นยำ (Accuracy) ผลการศึกษา: พบว่า ค่าความไว, ความจำเพาะ และความแม่นยำ เท่ากับร้อยละ 87.50, 98.60 และ 98.53 ตามลำดับ สรุปผลการศึกษา: แสดงให้เห็นถึงศักยภาพของ AI Chest 4 All (DMS–TU) For Thai People ในการคัดกรองวัณโรคได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ ช่วยค้นหาผู้ป่วยได้รวดเร็ว ทำให้ผู้ป่วยเข้าสู่การรักษาได้ทันที ช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพในการควบคุมการแพร่กระจายของวัณโรค และลดจำนวนผู้ป่วยวัณโรคลง
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Kulkarni S, Jha S. Artificial intelligence, radiology, and tuberculosis: a review. Acad Radiol. 2020;27(1):71–5.
Qin ZZ, Ahmed S, Sarker MS, Paul K, Adel ASS, Naheyan T, et al. Tuberculosis detection from chest X-rays for triaging in a high tuberculosis-burden setting: an evaluation of five artificial intelligence algorithms. Lancet Digit Health. 2021;3(9):e543–54.
Cao X, Li Y, Xin H, Zhang H, Pai M, Gao L. Application of artificial intelligence in digital chest radiography reading for pulmonary tuberculosis screening. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2021;7(1):35–40.
Thammarach P, Khaengthanyakan S, Vongsurakrai S, Phienphanich P, Pooprasert P, Yaemsuk A, et al. AI chest 4 all. In: 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC) [Internet]. IEEE; 2020 [cited 2024 Jul 22]. p. 1229–33. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9175862/
Qin ZZ, Sander MS, Rai B, Titahong CN, Sudrungrot S, Laah SN, et al. Using artificial intelligence to read chest radiographs for tuberculosis detection: a multi-site evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of three deep learning systems. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15000.
Geric C, Qin ZZ, Denkinger CM, Kik SV, Marais B, Anjos A, et al. The rise of artificial intelligence reading of chest X-rays for enhanced TB diagnosis and elimination. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2023;27(5):367–72.
Liao Q, Feng H, Li Y, Lai X, Pan J, Zhou F, et al. Evaluation of an artificial intelligence (AI) system to detect tuberculosis on chest X-ray at a pilot active screening project in Guangdong, China in 2019. J X-Ray Sci Technol. 2022;30(2):221–30.
Nijiati M, Ma J, Hu C, Tuersun A, Abulizi A, Kelimu A, et al. Artificial intelligence assisting the early detection of active pulmonary tuberculosis from chest X-rays: a population-based study. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:874475.
พัชริดา มหัสฉริยพงษ์. การประเมินความแม่นยำของเครื่องมืออ่านภาพรังสีทรวงอกอัตโนมัติ ปัญญาประดิษฐ์ (Artificial Intelligence; AI) ในการแปลผลวัณโรคปอดจากภาพรังสีทรวงอกในผู้ป่วยนอกที่มีอาการสงสัยวัณโรคปอด อ.แม่ระมาด จ.ตาก. วารสารระบบบริการปฐมภูมิและเวชศาสตร์ครอบครัว. 2564;4:35–45.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2025 สมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย (The Thai Society of Radiological Technologists)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทยและบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆในสมาคม ฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




