การเปรียบเทียบภาพเอกซเรย์คอมพิวเตอร์ระหว่างภาพตัดจริง ก่อนฉีดสารทึบรังสีและภาพ Virtual non-contrast ที่สร้างขึ้น ด้วยเครื่อง IQon Spectral CT
คำสำคัญ:
เครื่องเอกซเรย์คอมพิวเตอร์สองค่าพลังงาน, Virtual non-contrast, True non-contrast, เลขซีทีบทคัดย่อ
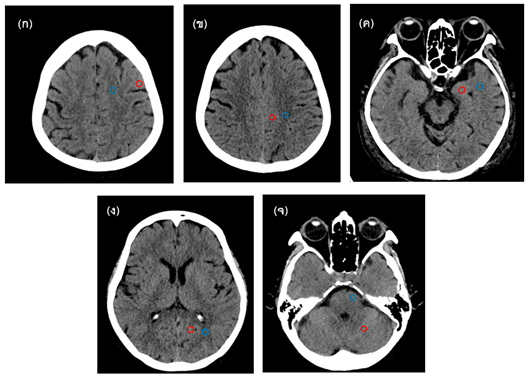
Dual-layer CT เป็นเทคโนโลยีของเครื่อง dual-energy CT ที่ใช้หลักการหัววัดรังสีที่มีสองชั้นในการรับพลังงานเพื่อให้เกิดภาพสองค่าพลังงาน ข้อมูลที่ได้สามารถนำมาสร้างภาพได้หลายชนิด เช่น virtual mono-energetic image, virtual non-contrast image เป็นต้น งานวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาความแตกต่างของค่า CT number ของภาพ CT ที่ตัดจริงก่อนฉีดสารทึบรังสีหรือ True non-contrast (TNC) กับ Virtual non-contrast (VNC) ของสมอง โดยการเก็บข้อมูลย้อนหลังของผู้ป่วยที่มารับการตรวจ CT แบบไม่ฉีดและฉีดสารทึบรังสีด้วยเครื่อง dual-layer IQon Spectral CT ณ ศูนย์รังสีวินิจฉัยก้าวหน้า จำนวน 35 คน ทำการวัด CT number ของ white matter และ gray matter ของเนื้อสมองทั้งซีกซ้ายและขวา จากภาพ TNC และ VNC ณ ตำแหน่ง frontal lobe parietal lobe temporal lobe occipital lobe และ pons (WM) & cerebellum (GM) และทำการเปรียบเทียบทางสถิติด้วย T-test (two-tailed) ผลการทดลองพบว่า อายุเฉลี่ยของผู้ป่วย 65.6±7.8 ปี และมีค่า CTDIvol อยู่ในช่วง 45.5–58.3 มิลลิเกรย์ จากการศึกษาพบว่าค่าเฉลี่ย CT number รวมทุกตำแหน่ง จากภาพ TNC และ VNC มีค่าเท่ากับ 27.1±1.3 และ 27.1±1.80 HU สำหรับ white matter และ 34.0±1.6 และ 28.9±2.6 HU สำหรับ gray matter ตามลำดับ ค่า CT number ของ white matter จากภาพ TNC และ VNC ไม่แตกต่างอย่างมีนัยสำคัญ (P=0.05) ต่างจาก gray matter ที่มีความแตกต่างกันอย่างมีนัยสำคัญ (P<0.05) ดังนั้น VNC ให้ภาพที่มีความแตกต่างของ white matter และ gray matter ที่ด้อยกว่า TNC สรุปได้ว่า การใช้ภาพ VNC แทนภาพ TNC ต้องมีความระมัดระวัง โดยเฉพาะในกรณีที่ต้องการแยกรอยโรค white matter และ gray matter แต่อาจใช้ได้ในกรณีติดตามการรักษารอยโรค เพื่อเป็นการลดปริมาณรังสีผู้ป่วย
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Johnson T. R. C.. Dual-Energy CT: General Principles. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2012;199(5, Suppl):S3–S8.
Mangesius S., et al. Dual-energy computed tomography in acute ischemic stroke: state-of-the-art. Eur. Radiol. 2021; 31:4138–4147.
McCollough CH, Leng S, Yu L, Fletcher JG. Dual-and multi-energy CT: principles, technical approaches, and clinical applications. Radiology 2015;276(3):637-53.
Postma AA, Das M, Stadler AA, Wildberger JE. Dual-energy CT: what the neuroradiologist should know. Curr Radiol Rep 2015;3(5):16.
Naruto N, Itoh T, Noguchi K. Dual energy computed tomography for the head. Jpn J Radiol 2018;36(2):69-80.
Angelo TD., et al. Dual energy computed tomography virtual monoenergetic imaging: technique and clinical applications. Br J Radiol 2019; 92:20180546
Albrecht MH., et al. Review of Clinical Applications for Virtual Monoenergetic Dual-Energy CT. Radiology 2019; 293:260–271.
Weinstein MA, Duchesneau PM, MacIntyre WJ. White and gray matter of the brain differentiated by computed tomography. Radiology 1977;122(3):699-702.
Jiang XY, et al. Evaluation of Virtual Noncontrast images obtained from dual-energy CTA for diagnosing subarachnoid hemorrahge. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol May 2015; 36:855–60.
Niehoff JH., Woeltjen MM., Laukamp KR. And Borggrefe J. Virtual non-contrast versus true non-contrast computed tomography: initial experience with photon counting scanner approved for clinical use. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2377.
Kanal KM, Butler PF, Sengupta D, Bhargavan-Chatfield M, Coombs LP, Morin RL. US diagnostic reference levels and achievable doses for 10 adult CT examinations. Radiology 2017;284(1):120-33.
Dance D, Christofides S, Maidment A, McLean I, Ng K. Diagnostic radiology physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students. IAEA Vienna, 2014: 260.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2022 สมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย (The Thai Society of Radiological Technologists)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทยและบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆในสมาคม ฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




