นวัตกรรมซิลิโคนโบลัสราคาถูกในงานทางรังสีรักษา จากเครื่องพิมพ์สามมิติ
คำสำคัญ:
ซิลิโคนโบลัส, การดูดกลืนรังสี, ปริมาณรังสีที่ผิว, เครื่องพิมพ์ 3 มิติบทคัดย่อ
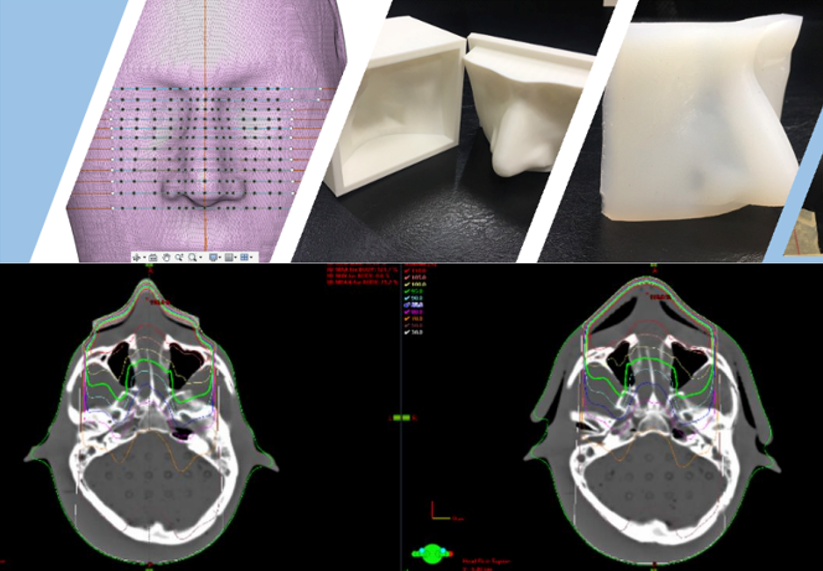
บทนำ: โบลัสเป็นวัสดุสมมูลเนื้อเยื่อถูกนำมาใช้ในงานทางรังสีรักษาเพื่อเพิ่มปริมาณรังสีที่ผิวผู้ป่วยและชดเชยเนื้อเยื่อที่ขาดหายไป โดยโบลัสแบบแผ่นเรียบ (superflab bolus) ในท้องตลาดมีราคาค่อนข้างสูงและไม่สามารถวางแนบชิดผิวผู้ป่วยที่มีความโค้งเว้า การศึกษานี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาคุณสมบัติของยางซิลิโคนที่สร้างขึ้น เพื่อนำมาใช้เป็น bolus ในงานทางรังสีรักษาสำหรับเพิ่มปริมาณรังสีที่ผิวให้ผู้ป่วย วิธีการศึกษา: วิธีการเริ่มจากสร้างซิลิโคนโบลัส (silicone bolus) โดยการผสมสารละลาย RA-00A และ 00B ให้เป็นเนื้อเดียวกัน เทขึ้นรูปขนาด 30x30 ซม2 หนา 1 เซนติเมตร และนำไปศึกษาคุณสมบัติทางกายภาพด้านความหนา ความหนาแน่น ความแข็ง เปรียบเทียบกับโบลัสที่วางขายในท้องตลาดเชิงพาณิชย์ (commercial bolus) จากนั้นนำโบลัสที่ได้ไปสแกนด้วยเครื่องเอกซเรย์คอมพิวเตอร์ หาค่า Hounsfield unit (HU) และวัดการดูดกลืนปริมาณรังสีของ silicone bolus จากเครื่องวางแผนการรักษา Eclipse จากนั้นทำการสร้าง bolus แบบ 3 มิติบริเวณจมูก โดยใช้เครื่องพิมพ์สามมิติ ผลการศึกษา: งานวิจัยนี้พบว่า commercial bolus และ silicone bolus มีความหนา 1.05±0.00 เซนติเมตร และ 1.07±0.01 เซนติเมตร, ความหนาแน่น 1.03 และ 0.99 กรัม/ลูกบาศก์เซนติเมตร, และความแข็งที่ 2.5 HA และ 1.5 HA ตามลำดับ ขณะที่ค่า HU อยู่ที่ -124±63.3 และ -73±42.5 ตามลำดับ โดยที่ความแตกต่างของปริมาณรังสีที่ผิวระหว่าง commercial bolus และ silicone bolus ที่พลังงาน 6 MV, 10 MV, 6 MeV, และ 9 MeV อยู่ที่ 0.4%, 0.9%, 0.7%, และ -0.4% ตามลำดับ โดย silicone bolus สามารถเพิ่มปริมาณรังสีที่ผิว 68.5%, 67.1%, 17.7%, and 7.4% เมื่อเทียบกับปริมาณรังสีที่ผิวเมื่อไม่มีโบลัสจะอยู่ที่ 30,23.1,81.5และ 86.9 ที่พลังงาน 6 MV, 10 MV, 6 MeV, และ 9 MeV ตามลำดับ ซึ่งใกล้เคียงกับผลจาก commercial bolus และพบว่า bolus แบบสามมิติวางได้แนบชิดกับหุ่นจำลองบริเวณที่มีความโค้งเว้าได้เป็นอย่างดี สรุปผลการศึกษา: โดยสรุป silicone bolus เป็นอีกหนึ่งทางเลือกที่นำมาใช้ทดแทน commercial bolus โดยมีคุณสมบัติเทียบเคียงที่ใกล้เคียงกัน แต่มีราคาถูกมากกว่า 20 เท่า และยังสามารถขึ้นรูปเป็นแบบ 3 มิติตามอวัยวะและรอยโรคได้
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Podgorsak EB. Radiation oncology physics: a handbook for teacher and students. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency.
Gunhan B, Kemikler G, Koca A. Determination of surface dose and the effect of bolus to surface dose in electron beams. Med Dos. 2003;28:193-8.
Wong G, Lam E, Bosnic S, et al. Quantitative effect of bolus on skin dose in postmastectomy radiation therapy. Research. 2020;51:462-9.
Lu Y, Song J, Yao X, An M, Shi Q, Huang X. 3D printing polymer-based bolus used for radiotherapy. Int J Bioprint. 2021;7:27-42.
Gong P, Dai G, Wu X, et al. Application of thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) bolus in postmastectomy radiotherapy. The Breast. 2022;66:317-23.
Chaloeiparb C, Wiriyatharakij T, Apipanyasopon L. Formation and surface dose determination of natural rubber bolus for a 9-MeV therapeutic electron beam. J Th Asso Rad Oncol. 2020;26:R55-67.
Sutanto H, Marhaendrajaya I, Wiratma G, et al. The properties of bolus material using silicone rubber. IOP Conf. Series: Mater Sci Eng. 2019;622:012002.
Butson MJ, Cheung T, Yu P, et al. Effects on skin dose from unwanted air gaps under bolus in photon beam radiotherapy. Radiat Meas. 2000;32:201-4.
Kong M, Holloway L. An investigation of central axis depth dose distribution perturbation due to an air gap between patient and bolus for electron beams. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2007;30:111-9.
Wang KM, Rickards A, Bingham T, Tward JD, Price RG, Technical note: Evaluation of a silicone-based custom bolus for radiation therapy of a superficial pelvic tumor. J Appl Clin Med Phys.2022;23:e13538.
Fujimoto K, Shiinoki T, Yuasa Y, et al. Efficacy of patient‐specific bolus created using three‐dimensional printing technique in photon radiotherapy. Phys Med. 2017;38:1-9.
Zhang C, Lewin W, Cullen A, Thommen D, Hill R. Evaluation of 3D-printed bolus for radiotherapy using megavoltage X-ray beams. Rad Phys Tech. 2023;16:1-8.
Wang X, Wang X, Xiang Z, et al. The clinical application of 3D-printed boluses in superficial tumor radiotherapy. Front Oncol. 2021;11:698773.
Yu S, Ahn SH, Choi SH, Ahn WS, Jung IH. Clinical application of a customized 3D-printed bolus in radiation therapy for distal extremities. Life. 2023;13:362-70.
Biltekin F, Yazici G, Ozyigit G. Characterization of 3D-printed bolus produced at different printing parameters. Med Dos. 2021;46:157-163.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2023 สมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย (The Thai Society of Radiological Technologists)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทยและบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆในสมาคม ฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




