เทคนิคการให้รังสีที่เหมาะสมสำหรับการถ่ายภาพเอกซเรย์กระดูกสันหลังส่วนเอว: การศึกษาในหุ่นจำลอง
คำสำคัญ:
เทคนิคการให้รังสี, หุ่นจำลองร่างกายมนุษย์, ปริมาณรังสีต่อพื้นที่, ดัชนีชี้วัดปริมาณรังสีบทคัดย่อ
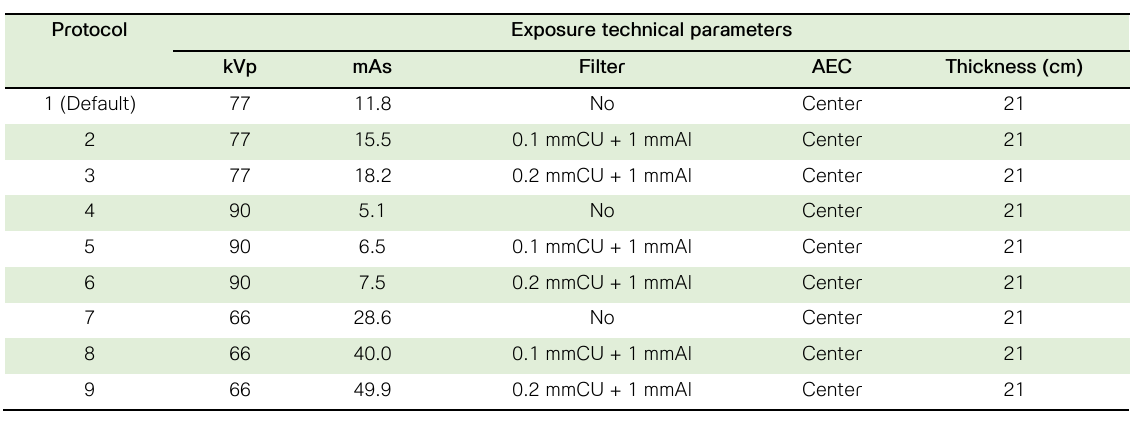
บทนำ: การถ่ายภาพเอกซเรย์กระดูกสันหลังส่วนเอว เป็นหนึ่งในการถ่ายภาพประจำในผู้ป่วย โดยปริมาณรังสีที่ผู้ป่วยได้รับจากการถ่ายภาพมีค่าสูงกว่าการถ่ายภาพเอกซเรย์บริเวณอื่น ดังนั้นการกำหนดเทคนิคในการให้รังสีที่เหมาะสม โดยพิจารณาค่าปริมาณรังสีที่ได้รับร่วมกับคุณภาพของภาพจึงเป็นสิ่งสำคัญ วัตถุประสงค์การศึกษา: เพื่อหาค่าพารามิเตอร์ที่เหมาะสมในการถ่ายภาพเอกซเรย์กระดูกสันหลังส่วนเอว โดยการประเมินปริมาณรังสีและคุณภาพของภาพตามโปรโตคอลประจำและโปรโตคอลปรับค่าใหม่ ณ ฝ่ายรังสีวิทยา โรงพยาบาลจุฬาลงกรณ์ สภากาชาดไทย วิธีการศึกษา: ถ่ายภาพเอกซเรย์กระดูกสันหลังส่วนเอว หุ่นจำลองร่างกายมนุษย์ ยี่ห้อ Kyoto Kagaku รุ่น PBU-60 ด้วยเครื่องเอกซเรย์ทั่วไประบบดิจิทัล ยี่ห้อ Philips รุ่น Digital Diagnost ร่วมกับอุปกรณ์รับภาพแบบดิจิทัลตามโปรโตคอลที่กำหนด ในทิศทางลำรังสีเข้าทางด้านหน้าและทางด้านข้าง บันทึกค่าปริมาณรังสีต่อพื้นที่ ค่าดัชนีชี้วัดปริมาณรังสี ค่าดัชนีชี้วัดความเบี่ยงเบนของปริมาณรังสีที่อุปกรณ์รับภาพได้รับ และประเมินคุณภาพของภาพรังสีโดยนักรังสีเทคนิคที่มีประสบการณ์จำนวน 3 คน ผลการศึกษา: การถ่ายภาพเอกซเรย์กระดูกสันหลังส่วนเอว ในทิศทางลำรังสีเข้าทางด้านหน้าด้วยการกำหนดค่าศักย์ไฟฟ้าที่ 66 กิโลโวลต์พีค และการเพิ่มความหนาแผ่นกรองรังสีที่ 0.2 มิลลิเมตรทองแดง + 1 มิลลิเมตรอลูมิเนียม ร่วมกับการใช้ระบบตัดรังสีอัตโนมัติ ให้ค่าดัชนีชี้วัดความเบี่ยงเบนของปริมาณรังสีที่อุปกรณ์รับภาพได้รับและค่าปริมาณรังสีต่อพื้นที่ที่เหมาะสมโดยมีคะแนนประเมินคุณภาพดีที่สุด ขณะที่ในทิศทางลำรังสีเข้าทางด้านข้างการกำหนดค่าศักย์ไฟฟ้าที่ 90 กิโลโวลต์พีค และการเพิ่มความหนาแผ่นกรองรังสีที่ 0.2 มิลลิเมตรทองแดง + 1 มิลลิเมตรอลูมิเนียม ร่วมกับการใช้ระบบตัดรังสีอัตโนมัติ ให้ค่าดัชนีชี้วัดความเบี่ยงเบนของปริมาณรังสีที่อุปกรณ์รับภาพได้รับ ค่าปริมาณรังสีต่อพื้นที่ และภาพถ่ายรังสีที่มีคุณภาพ สรุปผลการศึกษา: การใช้ระบบตัดรังสีอัตโนมัติ ร่วมกับการเพิ่มความหนาแผ่นกรองรังสีในการถ่ายภาพเอกซเรย์กระดูกสันหลังส่วนเอว ทั้งในทิศทางลำรังสีเข้าทางด้านหน้าและทางด้านข้าง ช่วยลดปริมาณรังสีในการถ่ายภาพ และได้ภาพถ่ายรังสีที่มีคุณภาพเหมาะสม
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Metter FA. Medical effects and risks of exposure to ionizing radiation. J Radiol Prot 2012; 32: N9-N13.
Wambani JS, Onditi EG, Korir GK, Korir JK. Patient doses in general radiography examinations. The South African Radiographer. 2015; 53(1): 22-26.
Minaei ES, Firouzi F, Khosravi HR. Patient doses in radiographic examinations in Western and Eastern Azerbyjaan provinces of Iran. Journal of Paramedical Sciences. 2014; 5(3): 77-81.
Akpochafor MO, Omajola AD, Soyebi KO, Adeneye SO, Aweda AM, Ajayi BH. Assessment of peak kilovoltage accuracy in ten selected X-ray centers in Lagos metropolis, south-western Nigeria. A quality control test to determine energy output accuracy of an ex-ray generator. J Health Res Rev. 2016; 3(2): 60-65.
Moore CS, Wood TJ, Beavis AW, Saunderson JR. Correlation of the clinical and physical image quality in chest radiography for average adults with a computer radiography imaging systems. British Journal of Radiology. 2013; 86: 2-12.
Gyan E, Inkoom S, Amoako G. Optimal exposure factors for lumbar spine AP in computed radiography examinations. Int J Rad Res. 2021; 19(2): 421-427.
England A, Evans P, Harding L, Taylor EM, Charnock P, Williams G. Increasing source-to-image detector distance to reduce radiation dose from digital radiography pelvic examination. Rad Sciences. 2015; 86(3): 246-256.
Lai ZH, dos Reis CS, Su Z. Effective dose and image optimization of lateral lumbar spine radiography: a phantom study. Eur Radiol Exp. 2020; 4(13): DOI: 10.1186/s41747-019-0132-3.
Kyoto Kagaku, Available from: https://www/kyotokagaku.com/en/products_data/ph-2b/
European commission. European guidelines on quality criteria for diagnostic radiographic images. Luxembourg, EUR 16260 EN. 1996.
Chan TPC, Fung KKL. Dose optimization in lumbar spine radiographic examination by air gap method at CR and DR systems: A phantom study. Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences. 2015; 46(1): 65-77.
Seeram E, Davidson R, Bushong S, Swan H. Optimizing the exposure indicator as a dose management strategy in computed radiography. Radiologic Technology. 2016; 87(4): 380-391.
Wang J, Shepard SJ, Flynn M, et al. An exposure indicator for digital radiography: AAPM Task Group 116 (Executive summary). Med Phys. 2009; 36(7): 2898-2914.
Dave JK, Jones AK, Fisher R, et al. Current state of practice regarding digital radiography exposure indicators and deviation indices: Report of AAPM imaging physics committee Task Group 232. Med Phys. 2018; 45(11): e1146-e1180.
Ries C, Goncalves J, Klompmaker C, Barbara AR, Bloor C, Hegarty R, et al. Image quality and dose analysis for a PA chest X-ray: comparison between AEC mode acquisition and manual mode using the 10 kVp rule. Radiography. 2014; 20: 339-345.
Chusin T, Kaewlek T. An exposure indicator in digital radiography systems. Thai J Rad Tech 2018; 43(1): 21-28.
Tsai HY, Yang CH, Huang KM, et al. Analyses of patient dose and image quality for chest digital radiography. Radiat Meas. 2010; 45: 722-725.
Bak KA, Pasieka E, Jankowska D, Ustymonicz A. Analysis of the dose area product variable in radiography of the lumbar-sacral spine using a water phantom. Eur J Med Tech. 2017; 2(15): 1-8.
Ofori EK, Ofori-Manteaw BB, Gawugah JNK, Nathan JA. Relationship between patient anatomical thickness and radiographic exposure factors for selected radiologic examinations. Journal of Health, Medical and Nursing. 2016; 23: 150-162.
Suwan-o-pas S, Suwanpradit P, Arjhansiri K, Khamwan K. Optimization of radiation dose and image quality in abdominal radiography using digital mobile x-ray system. Thai J Rad Tech 2018; 43(1): 13-20.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 สมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทย (The Thai Society of Radiological Technologists)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมรังสีเทคนิคแห่งประเทศไทยและบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆในสมาคม ฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




