Effect of substituting crude palm oil with saponified black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens l.) oil on performance and digestive tract characteristics of broiler chickens
Main Article Content
Abstract
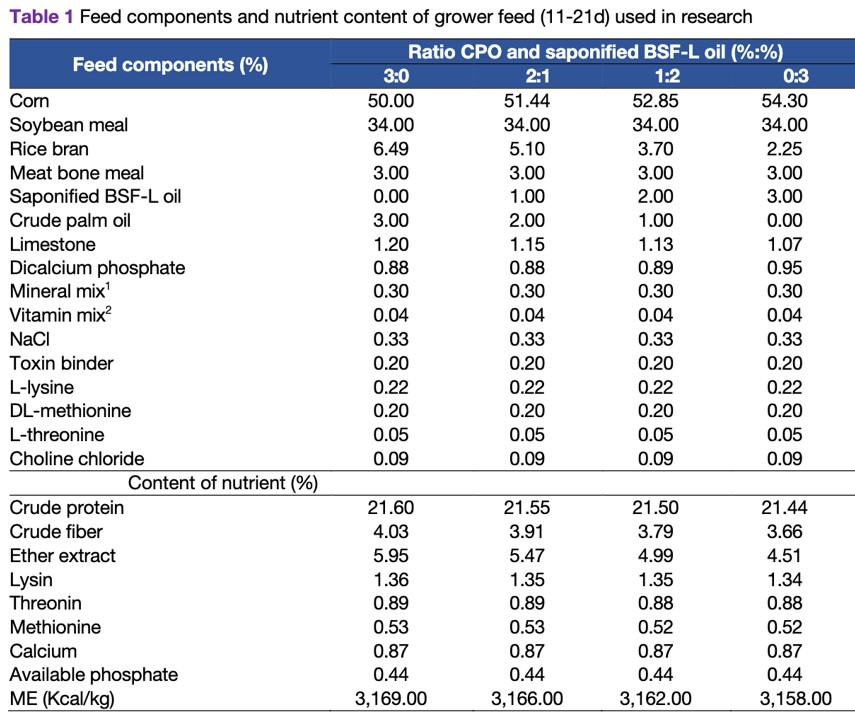
Several studies have shown that black soldier fly larvae (BSF-L) oil is an effective substitute for the use of crude palm oil (CPO) as an energy source in broiler chicken feeds. CPO contains several long-chain fatty acid (LCFA), such as palmitic and oleic acid, while BSF-L oil contains various medium-chain fatty acid (MCFA), namely lauric acid. In addition, lauric acid can function as an antimicrobial and immunomodulator. As an antimicrobial, it can inhibit the activity of enzymes that play a role in energy production and nutrient transport. Lauric acid is also an immunomodulator that preserves the integrity of the intestinal barrier by increasing the permeability of tight junctions. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the effect of substituting CPO with saponified BSF-L oil on broiler chicken performance and digestive tract characteristics. There were 280 male broiler chickens of the New Lohmann Indian River strain (MB 202 Platinum) in the experiment. CPO and saponified BSF-L oil were administered at different ratios, namely 3:0 (0% saponified BSF-L oil in feed), 2:1 (1% saponified BSF-L oil in feed), 1:2 (2% saponified BSF-L oil in feed), and 0:3 (3% saponified BSF-L oil in feed). Each treatment ratio consisted of 7 replications, which were administered to 10 chickens. In this study, the test animals were reared for 35 days, with 3 maintenance phases, including starter, grower, and finisher. The formulated feed was applied in the grower phase, followed by the removal of digestive tract organs to assess various parameters, such as length, weight, and pH of the digesta. The jejunum was also analyzed to obtain the histomorphology of intestinal villi and tight junctions gene expression. The data obtained were analyzed for variance with a one-way pattern and continued with the Duncan Multiple Range Test due to differences. The results showed that the substitution of CPO with saponified BSF-L oil had a significant effect (P<0.05) on feed intake (FI), index performance (IP), duodenal length, ileal pH, and JAM-2 and OCLN gene expression. The treatment also had a significant impact (P<0.01) on body weight (BW), average daily gain (ADG), and ZO-1 gene expression. In addition, the 2:1 treatment could improve the performance of broiler chickens and the ileal digesta's pH value, as well as reduce the length of the duodenum. As the level of saponified BSF-L increased, tight junctions gene expression also increased. However, it did not affect the histomorphology of jejunal villi or the relative weight of the digestive organs
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Publishing an article with open access in Veterinary Integrative Sciences leaves the copyright with the author. The article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC-BY 4.0), which allows users to read, copy, distribute and make derivative works from the material, as long as the author of the original work is cited.
References
Amer, S.A., A-Nasser, A., Al-Khalaifah, H.S., AlSadek, D.M.M., Fattah, D.M.A., Roushdy, E.M., Sherief, W.R.I.A., Farag, M.F.M., Altohamy, D.E., Abdel-Wareth, A.A.A., Metwally, A.E., 2021. Effect of dietary medium-chain α-monoglycerides on the growth performance, intestinal histomorphology, amino acid digestibility, and broiler chickens’ blood biochemical parameters. Animals. 11, 1-14.
Aviagen, 2018. Indian River Broiler Management Handbook. Available online: https://aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/LIR_Broiler/IR-BroilerHandbook2018 EN.pdf.
Awad, W.A., Hess, C., Hess. M., 2017. Enteric pathogens and their toxin-induced disruption of the intestinal barrier through alteration of tight junctions in chickens. Toxins. 9, 1-22.
Basiron, Y., 2005. Palm oil. In: Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products, 6th edition. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, pp. 333-429.
Chaklader, M.R., 2021. Supplementing insect meal and fish protein hydrolysates in barramundi, lates calcarifer diet improves the inclusion efficiency of poultry by-product meal: a physiological approach (Thesis). School of Molecular and Life Sciences Curtin University Australia.
Coyne, C.B., Ribeiro, C.M., Boucher, R.C., Johnson, L.G., 2003. Acute mechanism of medium chain fatty acid-induced enhancement of airway epithelial permeability. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 305, 440-450.
Coyne, C.B., Kelly, M.M., Boucher, R.C., Johnson, L.G., 2000. Enhanced epithelial gene transfer by modulation of tight junctions with sodium caprate. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 23, 602-609.
Franz, C., Baser, K.H.C., Windisch, W., 2010. Essential oils and aromatic plants in animal feeding –a European perspective. a review. Flavour. Fragr. J. 25, 327-340.
Jackman, J.A., Boyd, R.D., Elrod, C.C., 2020. Medium-chain fatty acids and monoglycerides as feed additives for pig production: towards gut health improvement and feed pathogen mitigation. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 11, 1-15.
Jayanegara, A., Gustanti, R., Ridwan, R., Widyastuti, Y., 2020. Fatty acid profiles of some insect oils and their effects on in vitro bovine rumen fermentation and methanogenesis. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 19, 1311–1318.
Juby, A.G., Cunnane, S.C., Mager, D.R., 2023. Refueling the post COVID-19 brain: potential role of ketogenic medium chain triglyceride supplementation: an hypothesis. Front. Nutr. 10, 1-12.
Kim, S.A., Rhee, M.S., 2016. Microbicidal effects of plain soap vs triclocarban-based antibacterial soap. J. Hosp. Infect. 94, 276–280.
Livak, K.J., Schmittgen, T.D., 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative pcr and the 2−∆∆ct method. Methods. 25, 402-408.
Mjøs, S.A. 2003. Identification of fatty acids in gas chromatography by application of different temperature and pressure programs on a single capillary column. J. Chromatogr. A. 1015, 151–161.
Nastiti, R., 2010. Menjadi Milyarder Budidaya Ayam Broiler. Pustaka Baru Press, Yogyakarta.
Pertiwi, D.D.R., Murwani, R., Yudiarti, T., 2017. Bobot relatif saluran pencernaan ayam broiler yang diberi tambahan air rebusan kunyit dalam air minum. J. Pet. Ind. 19, 60-64.
Proszkowiec-Weglarz, M., Schreier, L.L., Kahl, S., Miska, K.B., Russell, B., Elsasser, T.H., 2020. Effect of delayed feeding post-hatch on expression of tight junction- and gut barrier-related genes in the small intestine of broiler chickens during neonatal development. Poult. Sci. 99, 4714-4729.
Rizal, Y., 2000. Respon ayam broiler terhadap pengganti bungkol kedelai dengan bis dalam ransum. J. Peternakan. dan. Lingkungan. 6, 2.
Shimazaki, T., Tomita, M., Sadahiro, S., Hayashi, M., Awazu, S., 1998. Absorption-enhancing effects of sodium caprate and palmitoyl car-nitine in rat and human colons. Dig. Dis. Sci. 43, 641–645.
Sulastri, E., Mappiratu, Sari, A.K., 2016. Uji aktivitas antibakteri krim asam laurat terhadap Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 Dan Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853. Galenika. J. Pharm. 2, 59-67.
Suzuki, T., 2020. Regulation of the intestinal barrier by nutrients: the role of tight junctions. Anim. Sci. J. 91, 1-12.
Takeuchi, H., Sekine, S., Kojima, K., Aoyama, T., 2008. The application of medium-chain fatty acids: edible oil with a suppressing effect on body fat accumulation. Asia. Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 17, 320-323.
Widodo, T.S., Sulistiyanto, B., Utama, C.S., 2015. Jumlah bakteri asam laktat (BAL) dalam digesta usus halus dan sekum ayam broiler yang diberi pakan ceceran pabrik pakan yang difermentasi. Agripet. 15, 98-103.
Xie, Z., Shen, G., Wang, Y., Wu, C., 2019. Curcumin supplementation regulates lipid metabolism in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 98, 422–429.
Yang, H.S., Wu, F., Long, L.N., Li, T.J., Xiong, X., Liao, P., Liu, H.N., Yin, Y.L., 2016. Effect of yeast products on the intestinal morphology, barrier function, cytokine expression, and antioxidant system of weaned piglets. J. Zhejiang. Univ. Sci. B. 17, 752-762.