Effect of dietary zinc supplementation on production performance, milk auality, immunity, and blood plasma of dairy cows: A meta-analysis https://doi.org/10.12982/VIS.2025.044
Main Article Content
Abstract
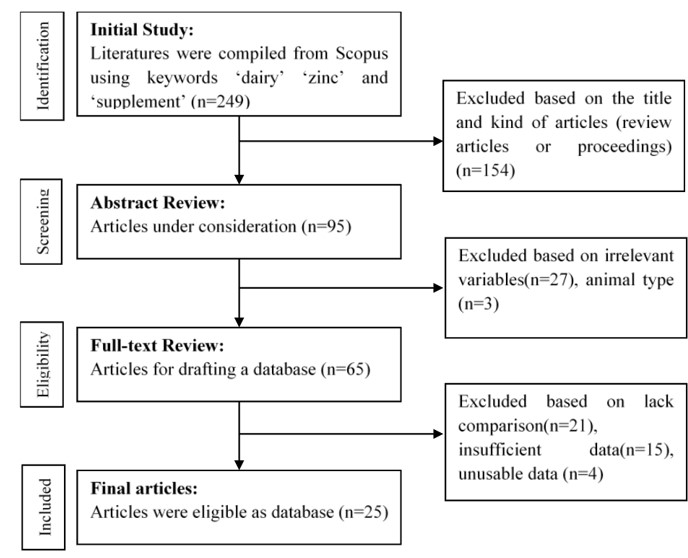
A meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the effects of Zinc supplementation on production performance, milk quality, immunity, and blood plasma of dairy cows. This study analyzed 25 related articles with 117 data points using a mixed model method with SAS web. The results showed that Zinc supplementation level increased (P<0.05) milk yield and decreased somatic cell count (SCC). Zinc supplementation level also linearly increased (P<0.05) IgM, IgG, and blood zinc. However, it does not have any effect on milk quality and blood biochemistry. In comparison to the control, both organic and inorganic Zinc sources increased (P<0.05) IgG, blood zinc, and decreased (P<0.05) SCC respectively. There was an interaction (P<0.05) observed between Zinc level and source on IgM and blood Zinc concentrations. Organic Zinc produced a higher effect (P<0.05) in increasing IgM and blood Zinc concentration than the inorganic source. It can be concluded that the provision of levels and sources of organic Zinc has a more favorable effect on dairy cows than inorganic Zinc.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Publishing an article with open access in Veterinary Integrative Sciences leaves the copyright with the author. The article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC-BY 4.0), which allows users to read, copy, distribute and make derivative works from the material, as long as the author of the original work is cited.
References
Aggarwal, A., Chandra, G., 2018. The effect of additional supplementation of vitamin E and zinc on endocrine and metabolic changes in dairy cows during the peripartal period. Vet. Arhiv. 88, 733-748.
Alhussein, M.N., Tiwari, S., Panda, B.S.K., Pandey, Y., Lathwal, S.S., Dan, A.K., 2021. Supplementation of antioxidant micronutrients reduces stress and improves immune function/response in periparturient dairy cows and their calves. J. TRace. Elem. Med. Biol. 65,1-10.
Azzizzadeh, M., Mohri, M., Seifi, H.A., 2005. Effect of oral zinc supplementation on hematology, serum biochemistry, performance, and health in neonatal dairy calves. Comp. Clin. Path. 14, 67-71.
Bais, B., Singh, J., 2018. Studies on nutritional management of transition cows. Int. J. Curr. Sci. Res. Rev. 1, 26-29
Bakhshizadeh, S., Aghjehgheshlagh, F.M., Taghizadeh, A., Seifdavati, J., Navidshad, B., 2019. Effect of zinc sources on milk yield, milk composition and plasma concentration of metabolites in dairy cows. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 49, 883-889.
Bordignon, R., Volpato, A., Glombowsky, P., Souca, C.F., Baldissera, M.D., Secco, R., Pereira, E.A.B., Leal, M.L.R., Vedovatto, M., Da Silva, A.S., 2019. Nutraceutical effect of vitamins and minerals on performance and immune and antioxidant systems in dairy calves during the nutritional transition period in summer. J. Therm. Biol. 84, 451-459.
Cai, J., Miao, C., Chen, Y., Xie, Y., Liu, J., Wang, D., 2021. Nano-sized zinc addition enhanced mammary zinc translocation without altering health status of dairy cows. Anim. Nutr. 7, 1024-1030.
Chandra, G., Aggarwal, A., Kumar, M., Singh, A.K., Sharma, V.K., Upadhyay, R.C., 2014. Effect of additional vitamin E and zinc supplementation on immunological changes inperipartum Sahiwal cows. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 98, 1166-1175.
Chandra, G., Aggarwal, A., Kumar, M., Singh, A.K., 2019. Effect of zinc and vitamin E supplementation on hormones and blood biochemicals in peri-partum Sahiwal cows. J. TRace. Elem. Med. Biol. 50, 489-497.
Chang, M.N., Wei, J.Y., Hao, L.Y., Ma, F.T., Li, H.Y., Zhao, S.G., Sun, P., 2020. Effects of different types of zinc supplement on the growth, incidence of diarrhea, immune function, and rectal microbiota of newborn dairy calves. J. Dairy. Sci. 103, 6100-6113.
Chen, F., Li, Y., Shen, Y., Guo, Y., Zhao, X., Li, Q., Cao, Y., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Wang, Z., Gao, Y., Li, J.. 2020. Effects of prepartum zinc-methionine supplementation on feed digestibility, rumen fermentation patterns, immunity status, and passive transfer of immunity in dairy cows. J. Dairy. Sci. 103, 8976-8985.
Chen, Y., Chen, Y., Tu, P., Lee, K., Chen, K., Hsu, J., 2023. Effect of supplementing vitamin E, selenium, copper, zinc, and manganese during the transition period on dairy cow reproductive performance and immune function. Vet. Sci. 10, 225.
Costa, M.I., Sarmento-Ribeiro, A.B., Goncalves, A.C., 2023. Zinc: from biological functions to therapeutic potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 4822.
De, L., Pal, S., Prasad, S., Dan, A.K., 2014. Effect of micronutrient supplementation on the immune function of crossbred dairy cows under semi-arid tropical environment. Trop. Anim. Health. Pro. 46, 203-211.
Jackson, K.A., Valentine, R.A., Coneyworth, L.J., Mathers, J.C., Ford, D., 2018. Mechanisms of mammalian zinc-regulated gene expression. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36, 1262.
Kambe, T., Tsuji, T., Hashimoto, A., Itsumura, N., 2015. The physiological, biochemical, and molecular roles of the zinc transporters in zinc homeostasis and metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 95, 749-784.
Kinal, S., Twardon, J., Bednarski, M., Pres, J., Bodarski, R., Slupczynska, M., Ochota, M., Dejneka, G.J., 2011. The influence of administration of biotin and zinc chelate (Zn-methionine) to cows in the first and second trimester of lactation on their health and productivity. Po. J. Nat. Sci. 14, 103-110.
Kumar S., Kumar, V., Kumar, M., Vaswani, S., Kushwaha, R., Kumar, A.. Prakash, A., 2021. Comparing efficiency of nano zinc on performance, nutrient utilization, immune, and antioxidant status in Hariyana cattle. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 91, 707-713.
Lanni, A., Iannaccone, M., Matino, C., Innosa, D., Grotta, L., Bennato, F., Martino, G., 2019. Zinc supplementation of dairy cows: Effects on chemical composition, nutritional quality and volatile profile of Giuncata cheese. Int. Dairy. J. 94, 65-71.
Lanni, A., Martino, C., Innosa, D., Bennato, F., Grotta, L., Martino, G., 2020. Zinc supplementation of lactating dairy cows: effects on chemical nutritional quality and volatile profile of Caciovallo cheese. Asian-autralas. J. Anim. Sci. 33, 825-835.
Liu, J., Ma, F., Degen, A., Sun, P., 2023. The effect of zinc supplementation on growth, diarrhea, antioxidant capacity, and immune function in Holstein Dairy Calves. Animals. 13, 1-10.
Liu, J., Yu, X., Ma, F., Jin, Y., Hashem, N.M., Sun, P., 2023. Early supplementation with zinc proteinate does not change rectal microbiota but increases growth performance by improving antioxidant capacity and plasma zinc concentration in pre-weaned dairy calves. Front. Vet. Sci. 10, 1-10.
Ma, F., Wo, Y., Li, H., Chang, M., Wei, J., Zhao, S., Sun, P., 2020. Effect of the source of zinc on the tissue accumulation of zinc and jejunal mucosal zinc transporter expression in Holstein dairy calves. Animals. 10, 1246.
Nagalakshmi, D., Sridhar, K., Satyanarayana, M., Parashuramulu, S., Narwade, V.S., Vikra, L., 2018. Effect of replacing inorganic zinc with a lower level of organic zinc (zinc propionate) on performance, biochemical constituents, antioxidant, immune and mineral status in buffalo calves. Indian. J. Anim. Res. 52, 1292–1297.
Nayeri, A., Upah, N.C., Sucu, E., Sanz-fernandez, M.V., Defrain, J.M., Gorden, P.J., Baumgard, L.H., 2014. Effect of zinc amino acid complex-to-zinc sulfate ration on performance of Holstein cows. J. Dairy. Sci. 97, 1-13.
Neto, M.A.T., Dadalt, J.C., Se, M.L.P., 2020. Dietary combination of chelated zinc and threonine and effect on egg production, egg quality, and nutrient balance of Brown laying hens from 20 to 49 weeks of age. Anim. Feed. Sci. Tech. 267, 1-15.
Pandey, P., Kumar, M., Kumar, V., Kushwaha, R., Vaswani, S., Kumar, A., Singh, Y., Shukla, P.K., 2022. The dietary supplementation of copper and zinc nanoparticles improves health condition of young dairy calves by reducing the incidence of diarrhea and boosting immune function and antioxidant activity. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 201, 3791-3803.
Sauvant, D., Schmidely, P., Daudin, J.J., St-Piere, N.R., 2008. Meta-analysis of experimental at in animal nutrition. Anim. Conserv. 2, 1203-1214.
Schwarz, D., Santschi, D.E., Durocher, J., Lefebvre, D.M., 2020. Evaluation of new differential somatic cell count parameter as a rapid and inexpensive supplementary tool for udder health management through regular milk recording. Prev. Vet. Med. 18, 1-12.
Singh, A., Randhawa, S.S., Singh, R.S., 2019. The effect of biotin and zinc supplementation on dairy cows hoof health and milk quality. Vet. Arhiv. 89, 799-820.
Singh, H.P., Jain, R.K., Tiwari, D., Mehta, M.K., Mudgal, V., 2020. Strategic supplementation of antioxidant micronutrients in peri-parturient Murrah Buffaloes helps augment the udder health and milk production. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 199, 2182-2190.
Sobhanirad, S., Carlson, D., Kashani, R.B., 2010. Effect of zinc methionine or zinc sulfate supplementation on milk production and composition of milk in lactating dairy cows. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 136, 48-54.
Sobhanirad, S., Naserian, A.A., 2012. Effects of high dietary zinc concentration and zinc sources on hematology and biochemistry of blood serum in Holstein dairy cows. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 177, 242-246.
Sundrum, A., 2015. Metabolic disorders in the transition period indicate that the dairy cows’ ability to adapt is overstressed. Animals. 5(4), 978-1020.
Tufarelli, V., Puvaca, N., Glamocic, D., Pugliese, G., Colonna, M.A., 2024. The most important metabolic diseases in dairy cattle during the transition period. Animals. 14, 1-18.
Vanegas, J.A., Reynolds, J., Atwill, E.R., 2007. Effect of an injectable trace mineral supplement on first-service conception rate of dairy cows. J. Dairy. Sci. 87, 3665-3671.
Wang, C., Xu, Y.Z., Han, L., Liu, Q., Guo, G., Huo, W.J., Xhang, J., Chen, L., Zhang, Y. L., Pei, C.X., Zhang, S.L., 2021. Effect of zinc sulfate and coated zinc sulfate on lactation performance, nutrient digestion, and rumen fermentation in Holstein dairy cows. Livest. Sci. 251, 1-8.
Wang, R.L., Liang, J.G., Lu, L., Zhang, L.Y., Li, S.F., Luo, X.G., 2013. Effect of zinc source on performance, zinc status, immune response, and rumen fermentation of lactating cows. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 152, 16-24.
Wiking, L., Larsen, T., Sehested, J., 2008. Transfer of dietary zinc and fat to milk evaluation of milk fat quality, milk fat precursors, and mastitis indicators. ADSA. 91, 1544-1551.
Wo, Y., Jin, Y., Gao, D., Ma, F., Ma, C., Liu, Z., Chu, K., Sun, P., 2022. Supplementation with zinc proteinate increases the growth performance by reducing the incidence of diarrhea and improving the immune function of dairy calves during the first month of life. Front. Vet. Sci. 9, 1-9.
Zhang L., Guo, Q., Duan, Y., Lin, X., Ini, H., Zhou, C., Li, F., 2022. Comparison of the effects of inorganic or amino acid-chelated zinc on mouse myoblast growth in vitro and growth performance and carcass traits in growing-finishing pigs. Front. Nutr. 9, 1-14.
Yusuf, S., Senarto, Y., Juffrie, M., Lestariana, W., 2019. The effect of zinc supplementation on pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1 AND IL-6) in mice with Escherichia coli LPS-induced diarrhea. Iran. J. Microbiol. 11, 412-418.