Dietary effects of multi-strain probiotics as an alternative to antibiotics on growth performance, carcass characteristics, blood profiling and meat quality of broilers https://doi.org/10.12982/VIS.2025.059
Main Article Content
Abstract
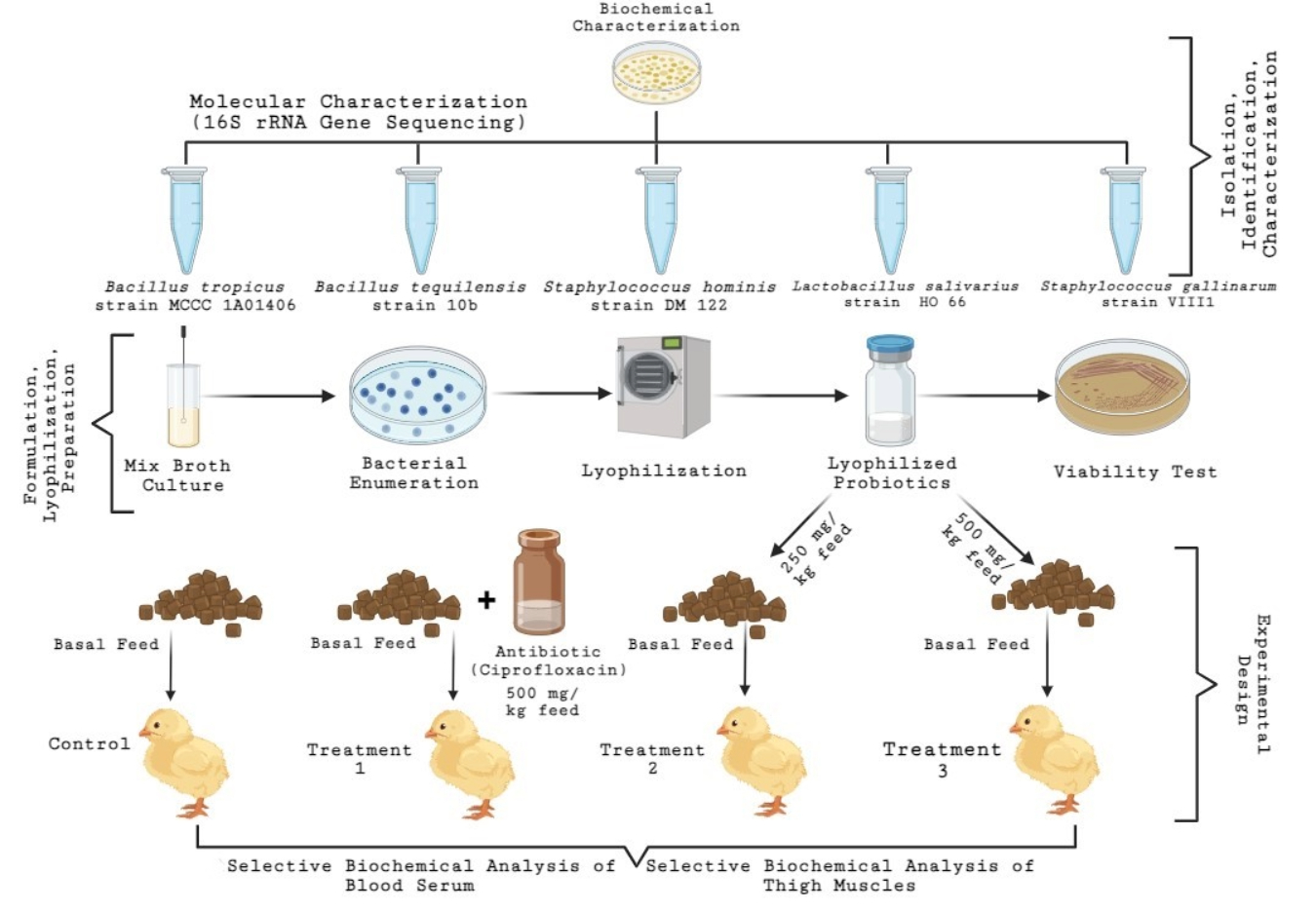
The growing issue of antibiotic resistance, particularly driven by the overuse of antibiotics in poultry farming in developing countries, presents serious public health threats. This situation highlights the urgent need for alternatives that benefit both poultry and human health. Probiotics, as live microorganisms administered in proper amounts, are a promising substitute, enhancing host health without harmful residues. This study evaluated the effects of lyophilized probiotic-based starter feed versus antibiotics on the growth performance, carcass traits, serum metabolites, and meat quality of broiler chicks. As experimental feed additives, ciprofloxacin, often used in the poultry industry of developing nations, and lyophilized multi-strain probiotics (2.8×109 CFU/g) isolated from chicken intestines, included Bacillus tropicus strain MCCC 1A01406, Bacillus tequilensis strain 10b, Staphylococcus gallinarum strain VIII, Lactobacillus salivarius strain HO 66, and Staphylococcus hominis strain DM 122 were utilized. A total of 300 Cobb-500 broiler chicks were divided into four groups, each with three replicates of 25 chicks, in a completely randomized design: (1) control (basal diet), (2) basal diet + 500 mg ciprofloxacin/kg feed (T1), (3) basal diet + 250 mg probiotics/kg feed (T2), and (4) basal diet + 500 mg probiotics/kg feed (T3). Growth performance was measured manually, serum biochemicals via avian diagnostic kits, and meat composition through Kjeldahl (protein) and Soxhlet (lipid) methods. After three weeks, probiotic-fed chicks showed significant increases (P<0.05) in body weight, feed intake, and feed conversion ratio compared to control and antibiotic groups. Serum analysis revealed increased (P<0.05) protein, calcium, and RBC levels and reduced cholesterol and uric acid. Meat from probiotic-fed groups had better (P<0.05) antioxidant properties, higher protein, and fiber, and lower fat, ash, and nitrogen-free extract levels, suggesting probiotics as a sustainable antibiotic alternative for poultry farming and public health improvement.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Publishing an article with open access in Veterinary Integrative Sciences leaves the copyright with the author. The article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC-BY 4.0), which allows users to read, copy, distribute and make derivative works from the material, as long as the author of the original work is cited.
References
Abdel-Hafeez, H.M., Saleh, E.S.E., Tawfeek, S.S., Youssef, I.M.I., Abdel-Daim, A.S.A., 2017. Effects of probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic with and without feed restriction on performance, hematological indices, and carcass characteristics of broiler chickens. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 30(5), 672–682.
Abeer, E.S., Mosaad, S.A., 2015. Effect of dietary probiotic and/or prebiotic supplementation on growth performance, carcass traits and some serum biochemical alterations in broiler chicken. J. Anim. Sci. Adv. 5(11), 1480-1492.
Adil, S., Magray, S.N., 2012. Impact and manipulation of gut microflora in poultry: a review. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 11(6), 873–877.
Fuller, R., 1989. Probiotics in man and animals. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 66, 365–378.
Al-Saad, S., Abbod, M., Abo Yones, A., 2014. Effects of some growth promoters on blood hematology and serum composition of broiler chickens. Int. J. Agric. Res. 9(5), 265–270.
Anjum, M.I., Khan, A.G., Azim, A., Afzal, M., 2005. Effect of dietary supplementation of multi-strain probiotic on broiler growth performance. Pak. Vet. J. 25(1), 25-29.
Argañaraz Martínez, E., Babot, J.D., Lorenzo-Pisarello, M.J., Apella, M.C., Perez Chaia, A., 2016. Feed supplementation with avian Propionibacterium acidipropionici contributes to mucosa development in early stages of rearing broiler chickens. Benef. Microbes. 7(5), 687–698.
Arora, M., Arora, M., Bansal, P., Baldi, A., 2019. Need and recommendations for universal guidelines on regulatory status and quality control/safety of probiotic products. Appl. Clin. Res. Clin. Trials Regul. Aff. 6(3), 231–249.
Ashayerizadeh, A., Dabiri, N., Mirzadeh, K.H., Ghorbani, M.R., 2011. Effect of dietary supplementation of probiotic and prebiotic on growth indices and serum biochemical parameters of broiler chickens. J. Cell Anim. Biol. 5(8), 152–156.
Awad, W.A., Ghareeb, K., Abdel-Raheem, S., Böhm, J., 2009. Effects of dietary inclusion of probiotic and synbiotic on growth performance, organ weights, and intestinal histomorphology of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 88(1), 49–55.
Ayalew, H., Zhang, H., Wang, J., Wu, S., Qiu, K., Qi, G., Tekeste, A., Wassie, T., Chanie, D., 2022. Potential feed additives as antibiotic alternatives in broiler production. Front. Vet. Sci. 9, 916473.
Bengtsson, B., Wierup, M., 2006. Antimicrobial resistance in scandinavia after ban of antimicrobial growth promoters. Anim. Biotechnol. 17(2), 147–156.
Broeckx, G., Vandenheuvel, D., Claes, I.J.J., Lebeer, S., Kiekens, F., 2016. Drying techniques of probiotic bacteria as an important step towards the development of novel pharmabiotics. Int. J. Pharm. 505(1), 303–318.
Chawla, S., Katoch, S., Sharma, K.S., Sharma, V.K., 2013. Biological response of broiler supplemented with varying dose of direct fed microbial. Vet. World. 6(8), 521–524.
Cramer, T.A., Kim, H.W., Chao, Y., Wang, W., Cheng, H.W., Kim, Y.H.B., 2018. Effects of probiotic (Bacillus subtilis) supplementation on meat quality characteristics of breast muscle from broilers exposed to chronic heat stress. Poult. Sci. 97(9), 3358–3368.
Dipankar, S., Taslim, H., 2022. Impacts of gut microbiota on human health and diseases. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 21(3), 231–241.
Dousa, B.M., Malik, H.E., Ali, O.H., Elhassan, M., Elamin, K.M., Elagib, H.A., Adam, M.S., 2016. Impact of probiotics and acidifiers on growth performance and blood chemistry of broiler chickens. Int. J. Sci. Res. 5(10), 1670-1674.
El-Baky, A.A.A., 2013. Clinicopathological and immunological effects of multistrain probiotic on broiler chicken vaccinated against avian influenza virus. Glob. Vet. 10(5), 534–541.
FAO, 2023. Food outlook – biannual report on global food markets. Available online: https://doi.org/10.4060/cc3020en.
Fathi, M.M., Ebeid, T.A., Al-Homidan, I., Soliman, N.K., Abou-Emera, O.K., 2017. Influence of probiotic supplementation on immune response in broilers raised under hot climate. Br. Poult. Sci. 58(5), 512–516.
Fujisaka, S., Ussar, S., Clish, C., Devkota, S., Dreyfuss, J.M., Sakaguchi, M., 2016. Antibiotic effects on gut microbiota and metabolism are host dependent. J. Clin. Invest. 126(12), 4430–4443.
Ghasemi, H.A., Shivazad, M., Mirzapour Rezaei, S.S., Karimi Torshizi, M.A., 2016. Effect of synbiotic supplementation and dietary fat sources on broiler performance, serum lipids, muscle fatty acid profile and meat quality. Br. Poult. Sci. 57(1), 71-83.
Hasan, B., Faruque, R., Drobni, M., Waldenström, J., Sadique, A., Ahmed, K.U., Islam, Z., Parvez, M.B., Olsen, B., Alam, M., 2011.
High prevalence of antibiotic resistance in pathogenic escherichia coli from large- and small-scale poultry farms in Bangladesh. Avian. Dis. 55(4), 689-692.
Hossain, M.T., Sardar, D., Afsana, S., Datta, M., Habib, M.A., 2024. Comparative analysis between multi-strain probiotics and antibiotic as starter feed supplement of poultry on growth performance, serum metabolites and meat quality. Vet. Anim. Sci. 24, 100346.
Humam, A.M., Loh, T.C., Foo, H.L., Samsudin, A.A., Mustapha, N.M., Zulkifli, I., Izuddin, W.I., 2019. Effects of feeding different postbiotics produced by Lactobacillus plantarum on growth performance, carcass yield, intestinal morphology, gut microbiota composition, immune status, and growth gene expression in broilers under heat stress. Animals. 9(9), 644.
Huyghebaert, G., Ducatelle, R., Van Immerseel, F., 2011. An update on alternatives to antimicrobial growth promoters for broilers. Vet. J. 187(2), 182–188.
Isolauri, E., Kirjavainen, P.V., Salminen, S., 2002. Probiotics: a role in the treatment of intestinal infection and inflammation? Gut. 50(3), iii54–59.
Kalavathy, R., Abdullah, N., Jalaludin, S., Ho, Y.W., 2003. Effects of Lactobacillus cultures on growth performance, abdominal fat deposition, serum lipids and weight of organs of broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 44(1), 139–144.
Kashmir, A., 2005. Effect of probiotic and growth promoters on chemical composition of broiler carcass. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 7, 1036–1037.
Khan, R.U., Naz, S., 2013. The applications of probiotics in poultry production. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 69(3), 621–632.
Khaziahmetov, F., Khabirov, A., Avzalov, R., Tsapalova, G., Tagirov, K., Giniyatullin, S., 2018. Effects of Paenibacillus-based probiotic (Bacispecin) on growth performance, gut microflora and hematology indices in goslings. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 13(S8), 6541–6545.
Krysiak, K., Konkol, D., Korczyński, M., 2021. Review overview of the use of probiotics in poultry production. Animals. 11(6), 1620.
Lewis, GF., 2003. Lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 14(1), 103–106.
Li, X., Bi, R., Xiao, K., Roy, A., Zhang, Z., Chen, X., Peng, J., Wang, R., Yang, R., Shen, X., Irwin, D.M., Shen, Y., 2022. Hen raising helps chicks establish gut microbiota in their early life and improve microbiota stability after H9N2 challenge. Microbiome. 10(1), 14.
Li, Y.B., Xu, Q.Q., Yang, C.J., Yang, X., Lv, L., Yin, C.H., Liu, X.L., Yan, H., 2014. Effects of probiotics on the growth performance and intestinal micro flora of broiler chickens. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 27(3 Suppl), 713-717.
López-Bascón-Bascon, M.A., Luque de Castro, M.D., 2019. Soxhlet extraction. Liq. Extr. 327–354.
Mancinelli, A.C., Mattioli, S., Twining, C., Bosco, A.D., Donoghue, A.M., Arsi, K., 2022. Poultry meat and eggs as an alternative source of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids for human nutrition. Nutrients. 14(9), 1969.
Manessis, G., Kalogianni, A.I., Lazou, T., Moschovas, M., Bossis, I., Gelasakis, A.I., 2020. Plant-derived natural antioxidants in meat and meat products. Antioxidants. 9(12), 1–30.
Mansoub, N.H., 2010. Effect of probiotic bacteria utilization on serum cholesterol and triglycrides contents and performance of broiler chickens. Glob. Vet. 5(3), 184–186.
Melillo, A., 2013. Applications of serum protein electrophoresis in exotic pet medicine. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 16(1), 211–225.
Mehr, M.A., Shargh, M.S., Dastar, B., Hassani, S., Akbari, M., 2007. Effect of different levels of protein and protexin on broiler performance. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 6(8), 573-577.
Meunier, M., Guyard-Nicodème, M., Dory, D., Chemaly, M., 2016. Control strategies against Campylobacter at the poultry production level: Biosecurity measures, feed additives and vaccination. J. Appl. Microbiol. 120(5), 1139–1173.
Mir, N.A., Rafiq, A., Kumar, F., Singh, V., Shukla, V., 2017. Determinants of broiler chicken meat quality and factors affecting them: a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 54(10), 2997–3009.
Mishra, P., Thakur, M.S., Khan, A., 2023. Proximate analysis of poultry and fish feed ingredients in Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh states. Pharma. Innov. J. 12(9), 1659–1662.
Mohammadi, H., Saghaian, S., Boccia, F., 2023. Antibiotic-free poultry meat consumption and its determinants. Foods. 12(9), 1776.
Mountzouris, K.C., Tsitrsikos, P., Palamidi, I., Arvaniti, A., Mohnl, M., Schatzmayr, G., 2010. Effects of probiotic inclusion levels in broiler nutrition on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, plasma immunoglobulins, and cecal microflora composition. Poult. Sci. 89(1), 58–67.
Ndukui, J.G., Gikunju, J.K., Aboge, G.O., Mbaria, J.M., 2021. Antimicrobial Use in Commercial Poultry Production Systems in Kiambu County, Kenya: A Cross-Sectional Survey on Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices. Open J. Anim. Sci. 11(4), 658–681.
Olnood, C.G., Beski, S.S.M., Choct, M., Iji, PA., 2015. Novel probiotics: their effects on growth performance, gut development, microbial community and activity of broiler chickens. Anim. Nutr. 1(3), 184–191.
Olubamiwa, O., Otun, A.R., Longe, O.G., 2002. Dietary inclusion rate of cocoa husk for starter cockerels. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 1(5), 133–135.
Omara, II., 2012. Nutritive value of skimmed milk and whey, added as natural probiotics in broiler diets. Egypt. J. Anim. Prod. 49(2), 207–217.
Owusu-Apenten, R., 2002. Kjeldahl method, quantitative amino acid analysis and combustion analysis. Food protein analysis. CRC Press, New York, pp. 218-247.
Panda, A.K., Rao, S.V.R., Raju, M.V.L.N., Sharma, S.R., 2006. Dietary supplementation of lactobacillus sporogenes on performance and serum biochemico - lipid profile of broiler chickens. J. Poult. Sci. 43(3), 235–240.
Patterson, J.A., Burkholder, K.M., 2003. Application of prebiotics and probiotics in poultry production. Poult. Sci. 82(4), 627–631.
Peng, X.P., Nie, C., Guan, W.Y., Qiao, L.D., Lu, L., Cao, S.J., 2019. Regulation of probiotics on metabolism of dietary protein in intestine. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 21(8), 766–771.
Pirgozliev, V., Bravo, D., Rose, S.P., 2014. Rearing conditions influence nutrient availability of plant extracts supplemented diets when fed to broiler chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr (Berl). 98(4), 667–671.
Popova, T., 2017. Effect of probiotics in poultry for improving meat quality. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 14, 72–77.
Rahman, M., Mustari, A., Salauddin, M., Rahman, M., 2014. Effects of probiotics and enzymes on growth performance and haematobiochemical parameters in broilers. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 11(1), 111–118.
Reddy, D.M., Reddy, G.V.B., Mandal, PK., 2018. Application of natural antioxidants in meat and meat products-a review. Food Nutr. J. 7(3), 1-12.
Rehman, A., Arif, M., Sajjad, N., Al-Ghadi, M.Q., Alagawany, M., Abd El-Hack, M.E., 2020. Dietary effect of probiotics and prebiotics on broiler performance, carcass, and immunity. Poult. Sci. 99(12), 6946–6953.
Rezende, M.S., Mundim, A.V., Fonseca, B.B., Miranda, R.L., Oliveira, W., Lellis, C.G., 2017. Profile of serum metabolites and proteins of broiler breeders in rearing age. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 19(4), 583–586.
Sánchez, B., Delgado, S., Blanco-Míguez, A., Lourenço, A., Gueimonde, M., Margolles, A., 2017. Probiotics, gut microbiota, and their influence on host health and disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 61(1), 1600240.
Schwarzer, M., Strigini, M., Leulier, F., 2018. Gut microbiota and host juvenile growth. calcif. Tissue Int. 102(4), 387–405.
Shabani, R., Nosrati, M., Javandel, F., Gothbi, A.A., Kioumarsi, H., 2012. The effect of probiotics on growth performance of broilers. Ann. Biol. Res. 3(12), 5450-5452.
Shim, Y.H., Ingale, S.L., Kim, J.S., Kim, K.H., Seo, D.K., Lee, S.C., 2012. A multi-microbe probiotic formulation processed at low and high drying temperatures: effects on growth performance, nutrient retention and caecal microbiology of broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 53(4), 482–490.
Skrypnik, K., Suliburska, J., 2018. Association between the gut microbiota and mineral metabolism. J. Sci. Food Agric. 98(7), 2449–2460.
Suryadi, U., Nugraheni, Y.R., Prasetyo, A.F., Awaludin, A., 2019. Evaluation of effects of a novel probiotic feed supplement on the quality of broiler meat. Vet. World. 12(11), 1775.
Tasmim, S.T., Hasan, M.M., Talukder, S., Mandal, A.K., Parvin, M.S., Ali, M.Y., Ehsan, M.A., Islam, M.T., 2023. Sociodemographic determinants of use and misuse of antibiotics in commercial poultry farms in Bangladesh. Int. J. Infect. Dis. Reg. 7, 146-158.
Tsai, T.C., Ockerman, H.W., 1981. Water binding measurement of meat. J. Food Sci. 46(3), 697-701.
Vuong, C.N., Chou, W.K., Hargis, B.M., Berghman, L.R., Bielke, L.R., 2016. Role of probiotics on immune function and their relationship to antibiotic growth promoters in poultry, a brief review. Int. J. Probiotics Prebiotics. 11(1), 1–6.
Wang, J., Ji, H., 2018. Influence of probiotics on dietary protein digestion and utilization in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 20(2), 125–131.
Xing, R., Yang, H., Wang, X., Yu, H., Liu, S., Li, P., 2020. Effects of calcium source and calcium level on growth performance, immune organ indexes, serum components, intestinal microbiota, and intestinal morphology of broiler chickens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 29(1), 106–120.
Yazhini, P., Visha, P., Selvaraj, P., Vasanthakumar, P., Chandran, V., 2018. Dietary encapsulated probiotic effect on broiler serum biochemical parameters. Vet. World. 11(9), 1344–1348.