Effects of earthworm hydrolysate on health status, laying performance, egg quality, and economic benefit of Cherry Valley laying ducks at the late phase of reproduction https://doi.org/10.12982/VIS.2025.043
Main Article Content
Abstract
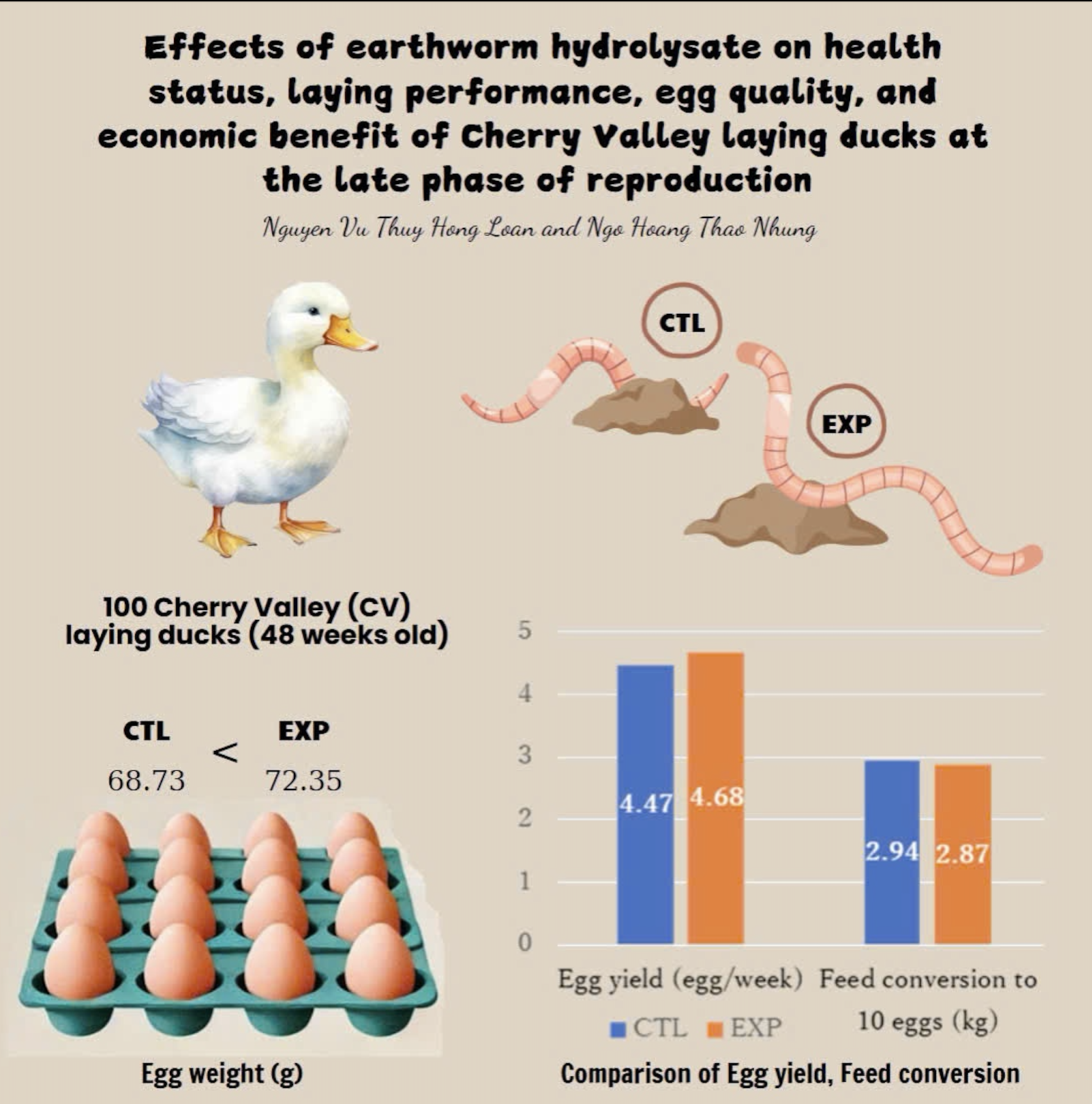
The study aimed to evaluate the effect of the earthworm hydrolysate, including in a complete feed-based diet on laying performance, quality of commercial eggs, and economic return of Cherry Valley (CV) laying ducks at the late phase of reproduction. A total of 100 laying ducks at 48 weeks of age were randomly allocated to 2 dietary treatments, namely CTL (control, in which animals were fed a complete feed and EXP (experiment, in which ducks were fed complete feed and 100 mL of the earworm hydrolysate) and 5 replicates. Animals were kept in the net cage with an earth floor and 10 animals/cage. The results showed that laying rate, number of eggs per week, and egg weight were higher in the EXP than in the CTL, and lower feed consumed per 10 eggs in the EXP than in the CTL (P≤0.05); egg shape index, york percentage, Haugh unit, and shell thickness were higher in the EXP than in the CTL (P≤0.05). On the other hand, the profit was higher in EXP than in CTL. In conclusion, the inclusion of earthworm hydrolysate in a complete feed-based diet improved laying performance, egg quality, and economic return of CV laying ducks at the late phase of reproduction. The ducks fed earthworm hydrolysate diet had higher 4.7% laying rate, higher 6.1% selected egg rate for hatchery and 17% more profit than those fed control diet.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Publishing an article with open access in Veterinary Integrative Sciences leaves the copyright with the author. The article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC-BY 4.0), which allows users to read, copy, distribute and make derivative works from the material, as long as the author of the original work is cited.
References
Akazawa, S.I., Tokuyama, H., Sato, S., Watanabe, T., Shida, Y., Ogasawara, W., 2018. High-pressure tolerance of earthworm fibrinolytic and digestive enzymes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 125(2), 155–159.
Bahadori, Z., Esmaielzadeh, L., Karimi-Torshizi, M.A., Seidavi, A., Olivares, J., Rojas, S., Salem, A.Z.M., Khusro, A., López, S., 2017. The effect of earthworm (Eisenia foetida) meal with vermi-humus on growth performance, hematology, immunity, intestinal microbiota, carcass characteristics, and meat quality of broiler chickens. Livest. Sci. 202, 74–81.
Cao, Y., Xun, M., Ren, S., Wang, J., 2022. Effects of dietary organic acids and probiotics on laying performance, egg quality, serum antioxidants and expressions of reproductive genes of laying ducks in the late phase of production. Poult. Sci. 101(12), 102189.
Tedesco, D.E.A., Castrica, M., Tava, A., Panseri, S., Balzaretti, C.M., 2020. From a food safety prospective: the role of earthworms as food and feed in assuring food security and in valuing food waste. Insects. 11(5), 293.
Dorigam, J.C.P., Sakomura, N.K., de Lima, M.B., Sarcinelli, M.F., Suzuki, R.M., 2016. Establishing an essential amino acid profile for maintenance in poultry using deletion method. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 100(5), 884–892.
Galić, A., Filipović, D., Pliestić, S., Janječić, Z., Bedeković, D., Kovačev, I., Čopec, K., Koronc, Z., 2019. The comparison of quality characteristics of Pekin duck and Cherry Valley duck eggs from free-range raising system. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 20(4), 1099–1110.
Hesami, Y., Esmaielzadeh, L., Karimi‐Torshizi, M.A., Seidavi, A., Vlčková, R., 2021. Effect of diets containing earthworm powder and vermihumus on egg production, hatchability, blood parameters and immunity of Japanese breeder quails. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 105(2), 316–325.
Ipek, A.Y.D.I.N., Sozcu, A.R.D.A., 2017. Comparison of hatching egg characteristics, embryo development, yolk absorption, hatch window, and hatchability of Pekin duck eggs of different weights. Poult. Sci. 96(10), 3593–3599.
Kim, S.G., Koo, H.Y., Kim, J.E., Kang, S.J., Sun, S.S., 2014. Effect of yellow mealworms (Tenebrio molitor L.) Feed supplementation on egg productivity and quality in broiler. Trends Agric. Life. Sci. 49, 1–7.
Linh, T.T.T., Anh, T.H., Phuong, N.T.N., 2017. The application of biological foliar fertilizer extracted from earthworm (Perionyx excavatus) in safe vegetable farming in urban households. J. Sci. 14(3), 188–199. (in Vietnamese)
Liu, Z., Chen, Q., Zhong, Y., Wu, Y., Li, J., Kong, Z., Zhang, Q., Lei, X., 2023. Effects of earthworm hydrolysate in production performance, serum biochemical parameters, antioxidant capacity and intestinal function of Muscovy ducks. Poult. Sci. 102(3), 102409.
Nazeri, R., Esmaielzadeh, L., Karimi-Torshizi, M.A., Seidavi, A., Zangeronimo, M.G., 2021. Use of earthworm meal with vermi-humus in diet for laying quail. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 56, e02453.
Nguyen, V.M., Duong, N.L., Du, N.T., Nguyen, V.B., 2010. Effects of supplementation of earthworm in diets on growth performance and dissease registant in Tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). In Proc on Aquatic Biotechnology, Ho Chi Minh, 2 December 2010.
Parolini, M., Ganzaroli, A., Bacenetti, J., 2020. Earthworm as an alternative protein source in poultry and fish farming: current applications and future perspectives. Sci. Total. Environ. 734, 139460.
Prayogi, H.S., 2011. The effect of earthworm meal supplementation in the diet on quail’s growth performance in attempt to replace the usage of fish meal. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 10(10), 804–806.
Rezaeipour, V., Nejad, O.A., Miri, H.Y., 2014. Growth performance, blood metabolites and jejunum morphology of broiler chickens fed diets containing earthworm (Eisenia foeitida) meal as a source of protein. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biomed. Res. 2(8), 2483–2494.
Rodrigues, M., Carlesso, W.M., Kuhn, D., Altmayer, T., Martini, M.C., Tamiosso, C.D., Mallmann, C.A., De Souza, C.F.V., Ethur, E.M., Hoehne, L., 2017. Enzymatic hydrolysis of the Eisenia andrei earthworm: characterization and evaluation of its properties. Biocatal. Biotransform. 35(2), 110–119.
Taye, S., Tesfaye, E., Edea, C., Alewi, M., 2024. Effect of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) supplementation on production performance of layer chickens. Int. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 8(1), 8–13.
Sun, F.S., Yu, G.H., Ning, J.Y., Zhu, X.D., Goodman, B.A., Wu, J., 2020. Biological removal of cadmium from biogas residues during vermicomposting and the effect of earthworm hydrolysates on Trichoderma guizhouense sporulation. Bioresour. Technol. 312, 123635.
Ton, V.D., Hanh, H.Q., Linh, N.D., Duy, N.V., 2009. Use of redworms (Perionyx excavatus) to manage agricultural wastes and supply valuable feed for poultry. Livest. Res. Rural. Dev. 21, 192.
Vemedim, 2020. Earthworm hydrolysates for poultry. Available online: https://vemedim. com/vi/1/chuyen-nganh-chan-nuoi-gia-suc-gia-cam/products/313/dich-trun-que-gsgc.
Xiang, C., Zhang, P., Pan, G., Qiu, D., Chu, Q., 2006. Changes in diversity, protein content, and amino acid composition of earthworms from a paddy soil under different long-term fertilizations in the Tai Lake Region, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 26(6), 1667–1673.
Yen, N.H.L., Trung, N.B., 2014. Experiment using Promin in Macrobrachium rosenbergii larva rearing. Can. Tho. J. Sci. Fishery, 108–113. (in Vietnamese)
Weymouth, A., 2022. An Introduction to some popular duck breeds in the UK. Available online: https://www.flytesofancy.co.uk/blogs/information-centre/deciding-on-your-ducks#:~:text=Cherry%20Valley%20ducks%20are%20a,commercial%20name%20for%20this%20duck.