Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from live shellfish marketed in Korea: antibiotic and heavy metal resistance https://doi.org/10.12982/VIS.2025.072
Main Article Content
Abstract
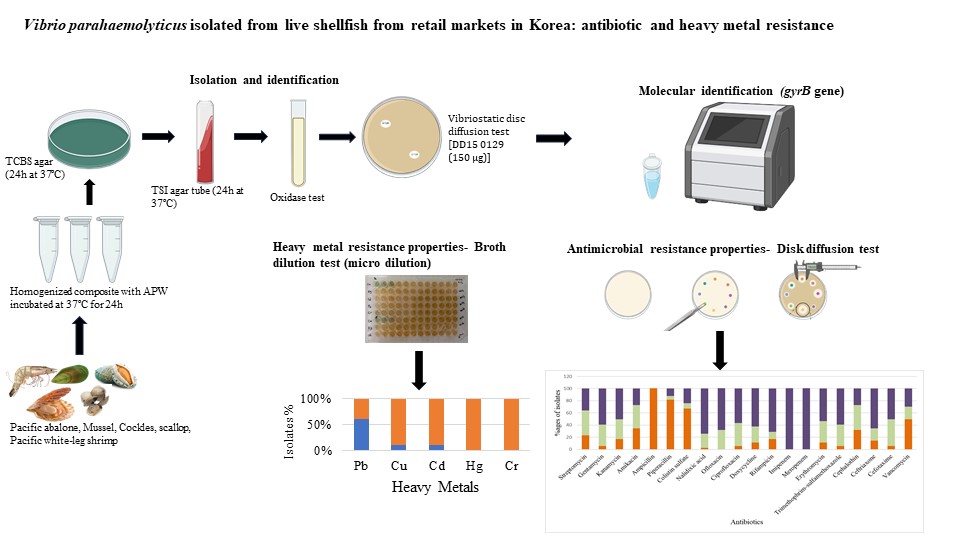
This study examined the antibiotic and heavy metal resistance properties in Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from Korea's five most popular shellfish. Thirty-four V. parahaemolyticus isolates were isolated by conducting biochemical tests and PCR. Isolation frequencies were 4 (cockles), 2 (scallops), 2 (mussels), 1 (Pacific abalone), and 25 (white-leg shrimp). The disc diffusion method was employed to detect antibiotic resistance. All isolates were resistant to ampicillin. Piperacillin, colistin, and vancomycin resistance were detected in 82%, 68%, and 50% of the isolates, respectively. Thirty-two isolates were multidrug resistant [Multiple Antibiotic Resistance (MAR) index ≥0.2]. β-lactam resistant blaSHV gene was the most prevalent gene detected in 68% of the isolates in PCR assays. In addition, blaCTX, aac(6’)-Ib, and blsTEM were detected in 21%, 44%, and 6% of the isolates, respectively. Phenotypic resistance to Pb, Cd, and Cu was detected in 25, 4, and 3 isolates, respectively in broth dilution test. CzcA gene was the prevalent detected in 16 isolates, followed by CopA and merA genes detected in 11 and 7 isolates, respectively. The findings of this study suggest that live shellfish marketed in Korea are a potential source of antibiotic-resistant V. parahaemolyticus.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Publishing an article with open access in Veterinary Integrative Sciences leaves the copyright with the author. The article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC-BY 4.0), which allows users to read, copy, distribute and make derivative works from the material, as long as the author of the original work is cited.
References
Akinbowale, O.L., Peng, H., Barton, M.D., 2007. Diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in bacteria from aquaculture sources in Australia. J. Appl. Microbiol. 103, 2016–2025.
Almansour, A.M., Alhadlaq, M.A., Alzahrani, K.O., Mukhtar, L.E., Alharbi, A.L., Alajel, S.M., 2023. The silent threat: antimicrobial-resistant pathogens in food-producing animals and their impact on public health. Microorganisms. 11, 2127.
Aqib, A.I., Alsayeqh, A.F., 2022. Vancomycin drug resistance, an emerging threat to animal and public health. Front. Vet. Sci. 9, 1010728.
Baker-Austin, C., McArthur, J.V., Tuckfield, R.C., Najarro, M., Lindell, A.H., Gooch, J., Stepanauskas, R., 2008. Antibiotic resistance in the shellfish pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from the coastal water and sediment of Georgia and South Carolina USA. J. Food. Prot. 71, 2552–2558.
Blakely, G.W., 2024. Mechanisms of horizontal gene transfer and DNA recombination. In: Tang, Y.W., Hindiyeh, M.Y., Zhang, J.R. (Eds.), Molecular medical microbiology, (3rd edition). Academic Press, London, pp. 309-324.
Banerjee, S.K., Farber, J.M., 2018. Trend and pattern of antimicrobial resistance in molluscan Vibrio species sourced to Canadian estuaries. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 62, 1–9.
Bouskill, N.J., Barnhart, E.P., Galloway, T.S., Handy, R.D., 2007. Quantification of changing Pseudomonas aeruginosa sodA, htpX and mt gene abundance in response to trace metal toxicity: a potential in situ biomarker of environmental health. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 60, 276–286.
Campbell, V.M., Chouljenko, A. Hall, S.G., 2022. Depuration of live oysters to reduce Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus: a review of ecology and processing parameters. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 21, 3480-3506.
Cantón, R., González-Alba, J.M., Gaán, J.C., 2012. CTX-M enzymes: origin and diffusion. Front. Microbiol. 3, 110.
Cattoir, V., Poirel, L., Rotimi, V., Soussy, C.J., 2007. Multiplex PCR for detection of plasmid mediated quinolone resistance qnr genes in ESBL-producing enterobacterial isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 60, 394–397.
Çardak, M., Toğay, S.Ö. Ay, M., 2023. Genotypic and phenotypic evaluation of heavy metal resistance of enterococcal isolates from seafood products for consumption. Commagene. J. Biol. 7, 58-64.
Chikwendu, C., 2014. Multiple antimicrobial resistance in vibrio spp. isolated from river and aquaculture water sources in Imo State, Nigeria. Br. Microbiol. Res. J. 4, 560–569.
CLSI, 2021. Performance standards for antimicrobial sus-ceptibility testing of bacteria isolated from aquatic animals; second informational supplement. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
Dallenne, C., Da Cost A., Decre D., Favier, C., 2010. Development of a set of multiplex PCR assays for the detection of genes encoding important b-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 65, 490–495.
Santos, M.D.S., Salomon, D., Li, P., Krachler, A.M., Orth, K., 2015. Vibrio parahaemolyticus virulence determinants. In: Alouf, J.E., Popoff, M.R. (Eds.), The comprehensive sourcebook of bacterial protein toxins. Elsevier, Waltham, pp. 230–260.
Diaz, M.A., Cooper, R.K., Cloeckaer, A., Siebeling, R.J., 2006. Plasmid-mediated high-level gentamicin resistance among enteric bacteria isolated from pet turtles in Louisiana. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 306– 312.
Dickinson, A.W., Power, A., Hansen, M.G., Brandt, K.K., Piliposian, G., Appleby, P., O’Neill, P.A., Jones, R.T., Sierocinski, P., Koskella, B., Vos, M., 2019. Heavy metal pollution and co-selection for antibiotic resistance: a microbial palaeontology approach. Environ. Int. 132, 105-117.
Di Pinto, A., Terio, V., Novello, L., Tantillo, G., 2011. Comparison between thiosulphate-citrate-bile salt sucrose (TCBS) agar and CHROMagar Vibrio for isolating Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food. Control. 22, 124-127.
Dutta, D., Kaushik, A., Kumar, D., Bag, S., 2021. Food-borne pathogenic vibrios: antimicrobial resistance. Front. microbiol. 12, 638331.
Džidić, S., Šušković, J., Kos, B., 2008. Antibiotic resistance mechanisms in bacteria: Biochemical and genetic aspects. Food. Technol. Biotech. 46, 11–21.
Fasulkova, R., Stratev, D., 2024. Insights into food-borne Vibrio parahaemolyticus–a review. Food. Res. 8, 190-209.
Farag, M.A., Mansour, S.T., Nouh, R.A., Khattab, A.R., 2023. Crustaceans (shrimp, crab, and lobster): A comprehensive review of their potential health hazards and detection methods to assure their biosafety. J. Food. Saf. 43, e13026.
Frana, T.S., Carlson, S.A., Griffith, R.W., 2001. Relative distribution and conservation of genes encoding aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium phage type DT104. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 445–448.
Han, F., Walker, R.D., Janes, M.E., Prinyawiwatkul, W., Ge, B., 2007. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus isolates from Louisiana Gulf and retail raw oysters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 7096–7098.
He, Y., Jin, L., Sun, F., Hu, Q., Chen, L., 2016. Antibiotic and heavy-metal resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from fresh shrimps in Shanghai fish markets, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23, 15033–15040.
Hernández-Montes, G., Argüello, J.M., Valderrama, B., 2012. Evolution and diversity of periplasmic proteins involved in copper homeostasis in gamma proteobacteria. BMC Microbiol. 12, 249.
Hu, Q., Chen, L., 2016. Virulence and antibiotic and heavy metal resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from crustaceans and shellfish in Shanghai, China. J. Food. Prot. 79, 1371–1377.
Jacoby, G.A., Munoz-price, L.S., 2005. The new β-Lactamases. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 380–391.
Jo, S., Shin, C., Shin, Y., Kim, P.H., il Park, J., Kim, M., Park, B., So, J.S., 2020. Heavy metal and antibiotic co-resistance in Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from shellfish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 156, 111246.
Jung, S.W., 2018. A food-borne outbreak of gastroenteritis caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus associated with cross-contamination from squid in Korea. Epidemiol. health. 40, e2018056.
Kavya, I.K., Kochhar, N., Ghosh, A., Shrivastava, S., Rawat, V.S., Ghorai, S.M., Sodhi, K.K., James, A., Kumar, M., 2023. Perspectives on systematic generation of antibiotic resistance with special emphasis on modern antibiotics. Total. Environ. Res. Themes. 8, 100068.
Kim, J., Lim, Y.M., 2005. Prevalence of derepressed AmpC mutants and extended-spectrum β-lactamase producers among clinical isolates of Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter spp., and Serratia marcescens in Korea: Dissemination of CTX-M-3, TEM-52, and SHV-12. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43, 2452–2455.
Kim, T.O., Eum, I.S., Jo, S.M., Kim, H.D., Park, K.S., 2014. Antimicrobial-resistance Profiles and Virulence Genes of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Isolated from Seawater in the Wando Area. Kor. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 47, 220–226.
Krumperman, P.H., 1983. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 46, 165–170.
Lee, L.H., Mutalib, N.S.A., Law, J.W.F., Wong, S.H., Letchumanan, V., 2018. Discovery on antibiotic resistance patterns of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Selangor reveals carbapenemase producing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in marine and freshwater fish. Front. Microbiol. 9, 2513.
Lee, M.F., Peng, C.H., Lin, Y.H., Lin, S.R., 2008. Molecular diversity of class 1 integrons in human isolates of Aeromonas spp. from southern Taiwan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 61, 343–349.
Lee, S.H., Myung, G.E., Choi, E.J., Kim, I.A., Jeong, Y., 2019. Distribution of pathogenic Vibrio species in the coastal seawater of South Korea (2017-2018). Osong. Public. Health. Res. Perspect. 10, 337–342.
Lee, Y., Choi, Y., Lee, S., Lee, H., Kim, S., Ha, J., Lee, J., Oh, H., Kim, Y., Yoon, Y., 2019. Occurrence of pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood distribution channels and their antibiotic resistance profiles in S. Korea. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 68, 128–133.
Lei, T., Zhang, J., Jiang, F., He, M., Zeng, H., Chen, M., Wu, S., Wang, J., Ding, Y., Wu, Q., 2019. First detection of the plasmid-mediated colistin resistance gene mcr-1 in virulent Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 308, 108290.
Letchumanan, V., Yin, W.F., Lee, L.H., Chan, K.G., 2015. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from retail shrimps in Malaysia. Front. microbiol. 6, 1–11.
Li, L., Wang, Q., Zhang, H., Yang, M., Khan, M.I., Zhou, X., 2016. Sensor histidine kinase is a β-lactam receptor and induces resistance to β-lactam antibiotics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 113, 1648–1653.
Lopatek, M., Wieczorek, K., Osek, J., 2015. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from raw shellfish in Poland. J. Food Prot. 78, 1029–1033.
Luo, P., Hu, C., 2008. Vibrio alginolyticus gyrB sequence analysis and gyrB-targeted PCR identification in environmental isolates. Dis. Aquat. Org. 82, 209-216.
Munita, J.M., Arias, C.A., 2016. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 22, 481-511.
Mondal, A.H., Khare, K., Saxena, P., Debnath, P., Mukhopadhyay, K., Yadav, D., 2024. A review on colistin resistance: an antibiotic of last resort. Microorganisms. 12, 772.
Mok, J.S., Cho, S.R., Park, Y.J., Jo, M.R., Ha, K.S., Kim, P.H., Kim, M.J., 2021. Distribution and antimicrobial resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from fish and shrimp aquaculture farms along the Korean coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 171, 112785.
Oh, E.G., Son, K.T., Yu, H., Lee, T.S., Lee, H.J., Shin, S., Kwon, J.Y., Park, K., Kim, J., 2011. Antimicrobial resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus strains isolated from farmed fish in Korea from 2005 through 2007. J. Food. Prot. 74, 380–386.
Ottaviani, D., Bacchiocchi, I., Masini, L., Leoni, F., Carraturo, A., Giammarioli, M., Sbaraglia, G., 2001. Antimicrobial susceptibility of potentially pathogenic halophilic vibrios isolated from seafood. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 18, 135–140.
Park, C.H., Robicsek, A., Jacoby, G.A., Sahm, D., 2006. Prevalence in the United States of aac(6’)-Ib-cr encoding a ciprofloxacin-modifying enzyme. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 50, 3953–3955.
Park, K., Mok, J.S., Kwon, J.Y., Ryu, A.R., Kim, S.H., Lee, H.J., 2018. Food-borne outbreaks, distributions, virulence, and antibiotic resistance profiles of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Korea from 2003 to 2016: a review. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 21, 1-10.
Pepi, M., Focardi, S., 2021. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquaculture and climate change: a challenge for health in the Mediterranean area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 18, 5723.
Rahman, A., Olsson, B., Jass, J., Nawani, N., 2007. Genome sequencing revealed chromium and other heavy metal resistance genes in E. cloacae B2-Dha. J. microbiol. Biochem. technol. 9, 191–199.
Samadi, N., Pakzad, I., Monadi, S.A., Hosainzadegan, H., 2015. Study of aminoglycoside resistance genes in Enterococcus and Salmonella strains isolated from Ilam and Milad hospitals, Iran. Jundishapur. J. Microbiol. 8, e18102.
Sunde, M., Norstrom, M., 2005. The genetic background for streptomycin resistance in Escherichia coli influences the distribution of MICs. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 56, 87–90.
Su, Y.C., Liu, C., 2007. Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a concern of seafood safety. Food Microbiol. 24, 549–558.
Tan, C.W., Rukayadi, Y., Hasan, H., Thung, T.Y., Lee, E., Rollon, W.D., Hara, H., Kayali, A.Y., Nishibuchi, M., Radu, S., 2020. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance patterns of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from different types of seafood in Selangor, Malaysia. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 27, 1602–1608.
Wang, Q., Wei, S., Silva, A.F., Madsen, J.S., 2023a. Cooperative antibiotic resistance facilitates horizontal gene transfer. ISME J. 17, 846-854.
Wang, W., Weng, Y., Luo, T., Wang, Q., Yang, G., Jin, Y., 2023b. Antimicrobial and the resistances in the environment: ecological and health risks, influencing factors, and mitigation strategies. Toxics. 11(2), 185.
Xie, T., Yu, Q., Tang, X., Zhao, J., He, X., 2020. Prevalence, antibiotic susceptibility and characterization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates in China. FEMS. Microbiol. Letters. 367, 136.
Yang, Y., Xie, J., Li, H., Tan, S., Chen, Y., Yu, H., 2017. Prevalence, antibiotic susceptibility and diversity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates in seafood from South China. Front. Microbiol. 8, 2566.