Systemic review of strongyle infections in horses across Asia: prevalence, diagnosis, and management https://doi.org/10.12982/VIS.2026.028
Main Article Content
Abstract
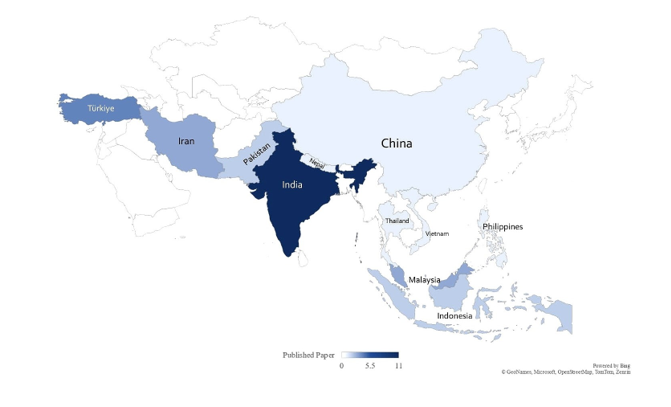
Strongylosis has been one of the most well-known diseases in the equine world. However, there is a lack of substantial knowledge regarding its prevalence in Asia. Hence, this study systematically reviewed data on strongyle species recorded in Asia and the main risk factors, diagnoses, treatment, and control. Four electronic databases were used to search the publications on strongyle species in Asia, and the inclusion and exclusion criteria were established. The chosen publications were accessed to discuss the risk factors, diagnoses, pathogenesis, treatment, and control in Asian countries. A total of 30 articles published between 2000 and 2024 were included. The main strongyle species reported is the large strongyle, with Strongylus edentatus and Strongylus vulgaris being the most prevalent. Small strongyles (cyathostomins) have become remarkably prevalent throughout the year, with Gyalocephalus sp. as the most pervasive. A diverse species prevalence is documented in the western countries with the weather playing an important role. Strongyles were mostly diagnosed by faecal floatation and quantified by the McMaster method, while further diagnosis was done using molecular techniques. Information on the use of anthelmintic drugs is still lacking. Subsequently, a progressive increase in the knowledge of strongyle species over the years in Asia countries has been noted. With the emergence of anthelmintic resistance, more research should be done, focusing on bridging the knowledge gaps to ensure the health of equine species and minimise economic losses associated with strongyle infections.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Publishing an article with open access in Veterinary Integrative Sciences leaves the copyright with the author. The article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC-BY 4.0), which allows users to read, copy, distribute and make derivative works from the material, as long as the author of the original work is cited.
References
Adeppa, J., Ananda, K.J., Krishna murthy, C.M., Satheesha, G.M., 2016. Incidence of gastro-intestinal parasites in horses of Shimoga region, Karnataka state. J. Parasit. Dis. 40, 919–921.
Ai, S., Zhang, Z., Wang, J., Wang, X., Liu, C., Duan, Z., 2023. Prevalence and molecular identification of gastrointestinal nematodes in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. Vet. Med. Sci. 9, 2693–2702.
Alborzi, A., Larki, S., Zeinali, A., 2020. Evaluation of larval culture and conventional PCR methods for the detection of Strongylus vulgaris in equines of Iran. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 44, 814–820.
Ali, S., Yagoob, G., 2015. Survey on fecal gastrointestinal parasitic helminthes in horses of jokey clubs in Ardabil city, Iran. Biol. Forum. Int. J. 7, 106-110.
Amoto, M.G., Leonard, C., Pradera, M., 2002. Prevalence and risk factors associated with equine strongylosis in Baybay City, Leyte, Philippines. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 44, 104-118.
Baran, A.I., Akbari, H., Rafat, S.A., 2019. Coprological prevalence and the intensity of gastrointestinal nematodes infection in working equines, east azerbaijan of Iran. J. Anim. Plant. Sci. 29. 1269-1278.
Bellaw, J.L., Nielsen, M.K., 2020. Meta-analysis of cyathostomin species-specific prevalence and relative abundance in domestic horses from 1975-2020: Emphasis on geographical region and specimen collection method. Parasite. Vectors. 13, 1–15.
Cain, J.L., Slusarewicz, P., Rutledge, M.H., McVey, M.R., Wielgus, K.M., Zynda, H.M., Wehling, L.M., Scare, J.A., Steuer, A.E., Nielsen, M.K., 2020. Diagnostic performance of McMaster, Wisconsin, and automated egg counting techniques for enumeration of equine strongyle eggs in fecal samples. Vet. Parasitol. 284, 109199.
Carminatti, A., Chitolina, M.B., Ribeiro, A.B., Forest, M., Collet, S.G., Prestes, A.M., Camillo, G., 2023. Occurrence and risk factors associated with gastrointestinal parasitism in horses reared in different systems. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 42, 100890.
Çirak, V.Y., Güleğen, E., Bauer, C., 2004. Benzimidazole resistance in cyathostomin populations on horse farms in western Anatolia, Turkey. Parasitol. Res. 93, 392–395.
Çırak, V.Y., Gülegen, E., Bauer, C., 2005. The prevalence of strongyle infections and persistent efficacy of pyrantel embonate, ivermectin, and moxidectin in Turkish horses. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 29(1), 28.
Corning, S., 2009. Equine cyathostomins: a review of biology, clinical significance and therapy. Parasite. Vectors. 2 (Suppl 2), S1.
Devkota, R.P., Subedi, J.R., Wagley, K., 2021. Prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites in equines of Mustang district, Nepal. Biodiversitas. 22, 3958–3963.
Embang, J.L., 2022. Identification of gastrointestinal nematode species in an equestrian park in Terengganu (Thesis). Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, pp. 32.
Elghryani, N., McOwan, T., Mincher, C., Duggan, V., de Waal, T., 2023. Estimating the prevalence and factors affecting the shedding of helminth eggs in Irish equine populations. Animals. 13(4), 581.
Ghafar, A., Abbas, G., Beasley, A., Bauquier, J., Wilkes, E.J.A., Jacobson, C., McConnell, E., El-Hage, C., Carrigan, P., Cudmore, L., Tennent-Brown, B., Hurley, J., Nielsen, M.K., Gauci, C.G., Beveridge, I., Hughes, K.J., Jabbar, A., 2023. Molecular diagnostics for gastrointestinal helminths in equids: Past, present and future. Vet. Parasitol. 313, 109851.
Girma, S., Tilahun, B., Gurmu, G., Hassennur, I., Fufa, G., Godana, J., Moa, M., Ayalew, S.M., 2017. Prevalence of equine strongyle infection and its associated risk factors in Jimma Town, Southwest Ethiopia. Int. J. Livest. Prod. 8, 187–191.
Gokbulut, C., McKellar, Q.A., 2018. Anthelmintic drugs used in equine species. Vet. Parasitol. 261, 27–52.
Halvarsson, P., Grandi, G., Hägglund, S., Höglund, J., 2024. Gastrointestinal parasite community structure in horses after the introduction of selective anthelmintic treatment strategies. Vet. Parasitol. 326, 11011.
Hamad, M.H., Islam, S.I., Jitsamai, W., Chinkangsadarn, T., Naraporn, D., Ouisuwan, S., Taweethavonsawat, P., 2024. Patterns of equine small strongyle species infection after ivermectin intervention in Thailand: egg reappearance period and nemabiome metabarcoding approach. Animals. 14, 574.
Hodgkinson, J.E., Freeman, K.L., Lichtenfels, J.R., Palfreman, S., Love, S., Matthews, J.B., 2005. Identification of strongyle eggs from anthelmintic-treated horses using a PCR-ELISA based on intergenic DNA sequences. Parasitol. Res. 95, 287–292.
Holland, W.G., Geurden, T., Do, T.T., Dorny, P., Vercruysse, J., 2001. Strongyle infections in horses from North Vietnam. Rev. Elev. Med. Vet. Pays Trop. 54, 29–31.
Kachhawa, J.P., Dedar, R.K., 2017. Epidemiological studies on helminthiasis in horses in Bikaner region of Rajasthan. Indian Vet. J. 92, 100-101.
Kaur, S., Singh, E., Singla, L., 2019. Strongylosis in equine: an overview. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 7(5), 43–46.
Khan, M.A., Roohi, N., Rana, M.A.A., 2015. Strongylosis in equines: a review. J. Anim. Plant. Sci. 25, 1-9.
Khan, M.A., Ruhi, N., Qaiser, H., 2020. Presence of strongyle infection in thoroughbred horses of Punjab Province, Pakistan. Chiang Mai Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 19, 222–234.
Khan, S., Ashfaque, M., Fakhruddin, Tanwar, R.K., 2013. Prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites in horses (EQUUS caballus) in and around Bikaner. Vet. Pract. 14. 294-295.
Kitchenham, B., Charters, S., 2007. Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering, technical report EBSE. J. Softw. Eng. Appl. 001
Kuzmina, T.A., Dzeverin, I., Kharchenko, V.A., 2016. Strongylids in domestic horses: Influence of horse age, breed and deworming programs on the strongyle parasite community. Vet. Parasitol. 227, 56–63.
Laroche, N., Grimm, P., Julliand, S., Sorci, G., 2024. Diet modulates strongyle infection and microbiota in the large intestine of horses. PLoS ONE. 19(4), e0301920.
Lightbody, K.L., Austin, A., Lambert, P.A., von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G., Jürgenschellert, L., Krücken, J., Nielsen, M.K., Sallé, G., Reigner, F., Donnelly, C.G., Finno, C.J., Walshe, N., Mulcahy, G., Housby-Skeggs, N., Grice, S., Geyer, K.K., Austin, C.J., Matthews, J.B., 2024. Validation of a serum ELISA test for cyathostomin infection in equines. Int. J. Parasitol. 54, 23–32.
Lockwood, C., Munn, Z., Porritt, K., 2015. Qualitative research synthesis: Methodological guidance for systematic reviewers utilizing meta-aggregation. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 13, 179–187.
Lyons, E.T., Bolin, D.C., Bryant, U.K., Cassone, L.M., Jackson, C.B., Janes, J.G., Kennedy, L.A., Loynachan, A.T., Boll, K.R., Burkhardt, A.S., Langlois, E.L., Minnis, S.M., Welsh, S.C., Scare, J.A., 2018. Postmortem examination (2016–2017) of weanling and older horses for the presence of select species of endoparasites: Gasterophilus spp., Anoplocephala spp., and Strongylus spp. in specific anatomical sites. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 13, 98–104
Macdonald, S.L., Abbas, G., Ghafar, A., Gauci, C.G., Bauquier, J., El-Hage, C., Tennent-Brown, B., Wilkes, E.J.A., Beasley, A., Jacobson, C., Cudmore, L., Carrigan, P., Hurley, J., Beveridge, I., Hughes, K.J., Nielsen, M.K., Jabbar, A., 2023. Egg reappearance periods of anthelmintics against equine cyathostomins: The state of play revisited. Int. J. Parasitol. 21, 28–39.
MacMillan, F., McBride, K.A., George, E.S., Steiner, G.Z., 2019. Conducting a systematic review: a practical guide. In: Liamputtong, P. (Ed.), Handbook of research methods in health social sciences. Springer, Singapore, pp. 805–826.
Maria, A., Shahardar, R.A., Bushra, M., 2012. Prevalence of gastrointestinal helminth parasites of equines in central zone of Kashmir Valley. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 82, 1276–1280.
Martins, A.V., Coelho, A.L., Corrêa, L.L., Ribeiro, M.S., Lobão, L.F., Palmer, J.P.S., Moura, L.C., Molento, M.B., Barbosa, A.D.S., 2023. First microscopic and molecular parasitological survey of strongylus vulgaris in brazilian ponies. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 32(3), e006323.
Matto, T.N., Bharkad, G.P., Bhat, S.A., 2015. Prevalence of gastrointestinal helminth parasites of equids from organized farms of Mumbai and Pune. J. Parasitol. Dis. 39, 179–185.
Merlin, A., Ravinet, N., Briot, L., Chauvin, A., Hébert, L., Valle-Casuso, J.C., Delerue, M., 2024. Prevalence and seasonal dynamics of gastrointestinal parasites in equids in France during two years. Prevent. Vet. Med. 223, 106100
Nagar, S.R., Khatoon, S., Alam, H.M., Purohit, K., Kumar, J., Dixit, A.K., 2022. Epidemiological studies on gastrointestinal helminths of horses of Udaipur Rajasthan. J. Pharma Innov. J. 11, 82-86.
Negash, W., Wossene, E., Dubie, T., 2021. Prevalence of strongyle infection and associated risk factors in horses and donkeys in and around Mekelle City, Northern Part of Ethiopia. Vet. Med. Int. 2021, 1–7
Nielsen, M.K., Kaplan, R.M., Thamsborg, S.M., Monrad, J., Olsen, S.N., 2007. Climatic influences on development and survival of free-living stages of equine strongyles: Implications for worm control strategies and managing anthelmintic resistance. Vet. J. 174(1), 23–32.
Nielsen, M.K., Branan, M.A., Wiedenheft, A.M., Digianantonio, R., Scare, J.A., Bellaw, J.L., Garber, L.P., Kopral, C.A., Phillippi-Taylor, A.M., Traub-Dargatz, J.L., 2018. Risk factors associated with strongylid egg count prevalence and abundance in the United States equine population. Vet. Parasitol. 257, 58–68
Nu’man, N.N.S., 2024. Detection of strongyles in horses in Klang Valley and Selangor (Thesis). Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universiti Putra Malaysia.
Okoli, C., 2015. A Guide to conducting a standalone systematic literature review. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 37, 43.
Page, M.J., McKenzie, J.E., Bossuyt, P.M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T.C., Mulrow, C.D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J.M., Akl, E.A., Brennan, S.E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J.M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M.M., Li, T., Loder, E.W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., McGuinness, L.A., Stewart, L.A., Thomas, J., Tricco, A.C., Welch, V.A., Whiting, P., Moher, D., 2021. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372, n71.
Periyasamy, U.D., 2017. Prevalence of gastrointestinal nematodes among horses from various establishments (Thesis). Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universiti Putra Malaysia.
Phetkarl, T., Fungwithaya, P., Lewchalermvong, K., Sontigun, N., 2024. Prevalence of gastrointestinal and blood parasites in horses of Nakhon Si Thammarat province, Thailand. Vet. World. 17(11), 2460–2468.
Pihl, T.H., Nielsen, M.K., Olsen, S.N., Leifsson, P.S., Jacobsen, S., 2017. Nonstrangulating intestinal infarctions associated with Strongylus vulgaris: clinical presentation and treatment outcomes of 30 horses (2008-2016). Equine Vet. J. 50(4), 474–480.
Relf, V.E., Morgan, E.R., Hodgkinson, J.E., Matthews, J.B., 2013. Helminth egg excretion with regard to age, gender and management practices on UK Thoroughbred studs. Parasitology. 140(5), 641–652.
Saeed, K., Qadir, Z., Ashraf, K., Ahmad, N., 2010. Role of intrinsic and extrinsic epidemiological factors on strongylosis in horses. J. Anim. Plant. Sci. 20, 277–280.
Salem, S.E., Abd El-Ghany, A.M., Hamad, M.H., Abdelaal, A.M., Elsheikh, H.A., Hamid, A.A., Saud, M.A., Daniels, S.P., Ras, R., 2021. Prevalence of gastrointestinal nematodes, parasite control practices and anthelmintic resistance patterns in a working horse population in egypt. Equine. Vet. J. 53(2), 339-348.
Scala, A., Tamponi, C., Sanna, G., Predieri, G., Dessì, G., Sedda, G., Buono, F., Cappai, M.G., Veneziano, V., Varcasia, A., 2020. Gastrointestinal strongyles egg excretion in relation to age, gender, and management of horses in Italy. Animals. 10(12), 2283.
Sengupta, P.P., 2003. Prevalence of gastro-intestinal helminths in equines in some hilly pockets of western Himalayas. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 73 (4), 394-396.
Shaffril, H.A.M., Samah, A.A., Samsuddin, S.F., 2021. Guidelines for developing a systematic literature review for studies related to climate change adaptation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 22265–22277.
Sharma, S., Shukla, P.C., Dixit, P., Dixit, A.K., 2011. Prevalence of gastrointestinal helminths in horses in Malwa Region of Madhya Pradesh. Vet. Pract. 12(1), 68-69.
Sinaga, L., Tanjung, M., 2022. Manifestation of endoparasitic helminths in Sumba Horse (Equus caballus) in Citra Pesona Ladangku Animal Park. OP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1115, 110048.
Singh, G., Angad, G., Soodan, J.S., 2012. Epidemiological studies on gastrointestinal helminths in horses and mules. Vet. Pract. 13 (1). 24-27.
Singh, G., Singh, N.K., Singh, H., Rath, S.S., 2016. Assessment of risk factors associated with prevalence of strongyle infection in equines from Central Plain Zone, Punjab. J. Parasit. Dis. 40, 1381–1385.
Stancampiano, L., Usai, F., Marigo, A., Rinnovati, R., 2017. Are small strongyles (Cyathostominae) involved in horse colic occurrence? Vet. Parasitol. 247, 33–36.
Stoughton, W.B., Begin, S., Outman, S., Stryhn, H., Yu, J., Conboy, G., Nielsen, M.K., 2023. Occurrence and control of equine strongyle nematode infections in Prince Edward Island, Canada. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 40, 100856.
Tennent-Brown, B., Nielsen, M.K., Jabbar, A., 2019. A systematic review of gastrointestinal nematodes of horses from Australia. Parasite. Vectors. 12 (1), 188.
Tirtasari, K., Atma, C.D., Kholik., 2021. Prevalence and degree of gastrointestinal nematode infection of horses (Equus caballus) used as public transport in Mataram city, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 712.
Ulutaş Esatgil, M., Efil, İ., 2012. A coprological study of helminth infections of horses in Istanbul, Turkey. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 18, A1–A6.
Umur, Ş., Açici, M., 2009. A survey on helminth infections of equines in the Central Black Sea region, Turkey. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 33, 373–378.
Uslu, U., 2007. Prevalence of endoparasites in horses and donkeys in Turkey. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy. 51, 237-240.
Xiao, Y., Watson, M., 2019. Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 39, 93–112.