Bullous Erysipeloid: An Atypical Manifestation in an Immunocompromised Patient – A Case Report
Keywords:
Erysipeloid, Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, Immunocompromised host, localized infection, Zoonotic pathogenAbstract
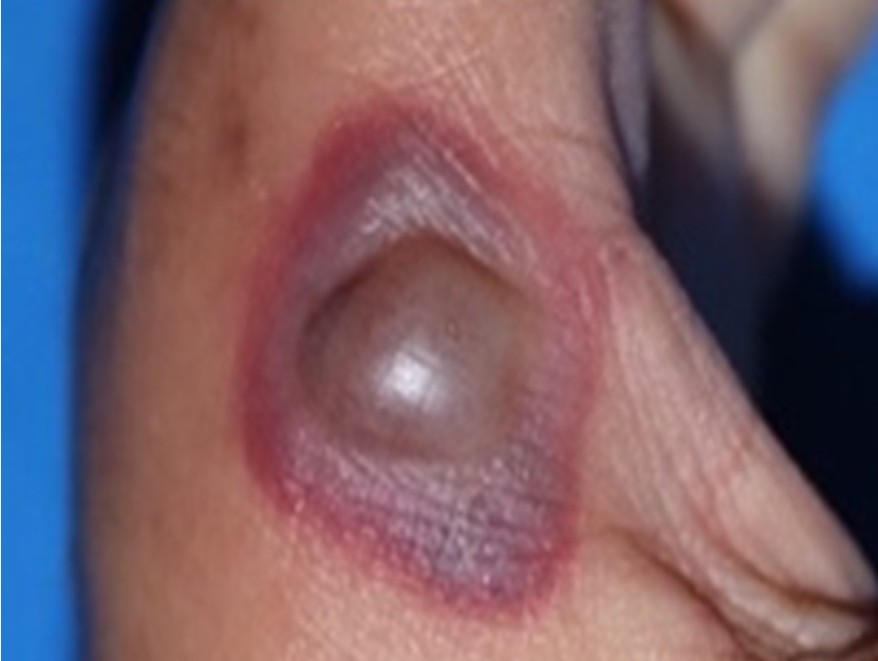
Erysipeloid is a rare infection caused by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. We report the case of a 58-year-old woman with HIV and spondylarthritis on immunosuppressants, who had a history of direct contact fish and shrimp, who presented with a progressive, painful plaque with central bullae on her left index finger. At her initial visit, she was diagnosed with bullous cellulitis and was treated with oral clindamycin (300 mg three times daily) and intravenous levofloxacin 750 mg once daily. Despite treatment, her condition worsened, necessitating hospitalization and surgical debridement. Microbiological culture from skin lesion confirmed the presence of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, leading to the diagnosis of erysipeloid. Following a 14-day course of penicillin V, the patient showed significant clinical improvement. Atypical presentations of erysipeloid, as bullous lesions, can occur, particularly in immunocompromised host.
References
Veraldi S, Girgenti V, Dassoni F, Gianotti R. Erysipeloid: a review. Clin Exp Dermatol 2009;34:859-62.
Wang Q, Chang BJ, Riley TV. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Vet Microbiol 2010;140:405-17.
Rostamian M, Rahmati D, Akya A. Clinical manifestations, associated diseases, diagnosis, and treatment of human infections caused by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: a systematic review. Germs 2022;12:16-31.
Clark AE. The Occupational Opportunist: an Update on Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Infection, Disease Pathogenesis, and Microbiology. Clinical Microbiology Newsletter 2015;37:143-51.
Boyd AS, Ritchie C, Fenton JS. Cutaneous Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae (erysipeloid) infection in an immunocompromised child. Pediatr Dermatol 2014;31:232-5.
Winston LG, Winkler ML, Kheterpal A, Villalba JA. Case 36-2021: A 22-Year-Old Man with Pain and Erythema of the Left Hand. N Engl J Med 2021;385:2078-86.
Jean S, Lainhart W, Yarbrough ML. The Brief Case: Erysipelothrix Bacteremia and Endocarditis in a 59-Year-Old Immunocompromised Male on Chronic High-Dose Steroids. J Clin Microbiol 2019;57.
Bîrlutiu V. Sepsis due to Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia associated with bronchopneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli: A case report. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol 2015;26:108-10.
Reboli AC, Farrar WE. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: an occupational pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 1989;2:354-9.
Gorby GL, Peacock JE Jr. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae endocarditis: microbiologic, epidemiologic, and clinical features of an occupational disease. Rev Infect Dis 1988;10:317-25.
Meric M, Keceli Ozcan S. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae pneumonia in an immunocompetent patient. J Med Microbiol 2012;61:450-1.
Fidalgo SG, Longbottom CJ, Rjley TV. Susceptibility of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae to antimicrobial agents and home disinfectants. Pathology 2002;34:462-5.
Dec M, Łagowski D, Nowak T, Pietras-Ożga D, Herman K. Serotypes, Antibiotic Susceptibility, Genotypic Virulence Profiles and SpaA Variants of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strains Isolated from Pigs in Poland. Pathogens 2023;12:409.
Bobrek K, Gaweł A. Antimicrobial Resistance of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strains Isolated from Geese to Antimicrobials Widely Used in Veterinary Medicine. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023;12:1339.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Thai Journal of Dermatology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใดๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารโรคผิวหนัง ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารฯ หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใดๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักอักษรจากบรรณาธิการวารสารโรคผิวหนังก่อนเท่านั้น


