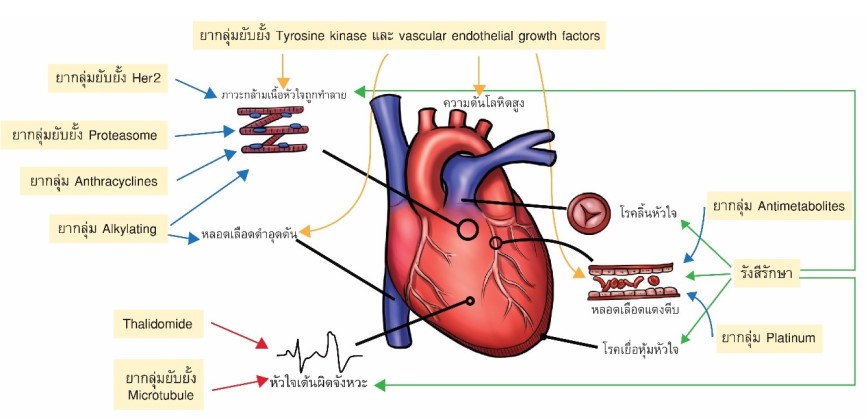
Introduction to cardio-oncology: Anthracyclines induced cardiotoxicity
Keywords:
Cardio-oncology, Chemotherapy induced cardiotoxicity, AnthracyclineAbstract
Cancer is known to be the leading cause of death among Thai people. New advanced technology has brought about many novel effective treatments which lead to an impressive increase in cancer survivors over the past decade. Parallelly, the number of morbidity and mortality due to treatment side effects also grows. Cardiovascular diseases are one of the most frequent side effects. Evidence founds that cancer treatment with chemotherapy has an adverse impact on the cardiovascular system. This article will discuss the burden, risk factors, and how to recognize and prevent chemotherapy induce cardiotoxicity especially from Anthracyclines. Since Anthracycline is highly used in treating cancer and is notorious for causing cardiotoxicity.
Downloads
References
Boer RA, Meijers WC, Meer P, Veldhuisen DJ. Cancer and heart disease: associations and relations. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21(12):1515-1525. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejhf.1539
Zamorano JL, Lancellotti P, Rodriguez Muñoz D, et al. 2016 ESC Position Paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(36):2768-2801. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehw211
Komuro I. Harmonization of Cardiovascular and Oncology and the Blossoming of Cardio-Oncology in Japan. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccao.2020.11.011
Lenneman CG, Sawyer DB. Cardio-oncology: An update on cardiotoxicity of cancer-related treatment. Circ Res. 2016;118(6):1008-1020. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.303633
Oeffinger KC, Mertens AC, Sklar CA, et al. Chronic Health Conditions in Adult Survivors of Childhood Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(15):1572-1582. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmsa060185
Limat S, Daguindau E, Cahn J-Y, et al. Incidence and risk-factors of CHOP/R-CHOP-related cardiotoxicity in patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014;39(2):168-174. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpt.12124
Hall PS, Harshman LC, Srinivas S, Witteles RM. The frequency and severity of cardiovascular toxicity from targeted therapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma patients. JACC Heart Fail. 2013;1(1):72-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchf.2012.09.001
Swain SM, Whaley FS, Gerber MC, et al. Cardioprotection With Dexrazoxane for Doxorubicin-Containing Therapy in Advanced Breast Cancer. Vol 15.; 1997.
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G, et al. Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulation. 2015;131(22):1981-1988. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013777
Plana JC, Galderisi M, Barac A, et al. Expert consensus for multimodality imaging evaluation of adult patients during and after cancer therapy: A report from the American society of echocardiography and the European association of cardiovascular imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014;27(9):911-939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2014.07.012
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright and Disclaimer
Articles published in this journal are the copyright of Chulabhorn Royal Academy.
The opinions expressed in each article are those of the individual authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of Chulabhorn Royal Academy or any other faculty members of the Academy. The authors are fully responsible for all content in their respective articles. In the event of any errors or inaccuracies, the responsibility lies solely with the individual authors.


