Case report: Dual Cutaneous Atypical Mycobacterium Infection After Tattooing
Keywords:
Atypical mycobacterium, Skin and soft tissue infection, Non-tuberculous mycobacteria, Skin infectionAbstract
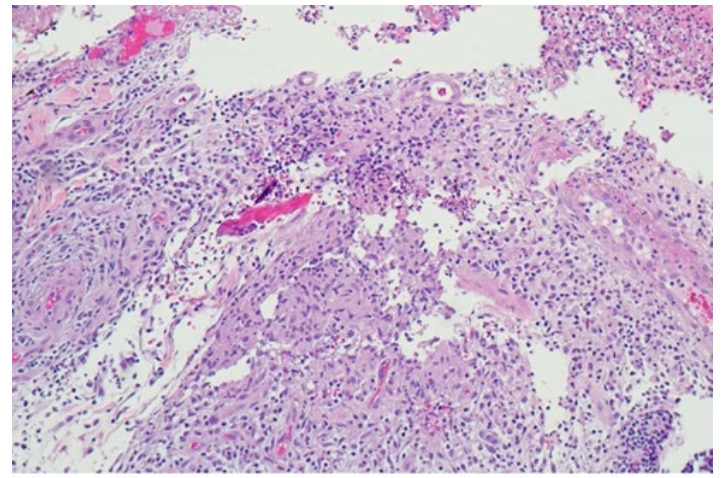
A cutaneous atypical mycobacterium or non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) infection commonly found in contaminated medical and cosmetic procedures such as amateur tattoos1. The main route of infection is caused by the direct inoculation of Mycobacterium spp. during the procedure. The clinical presentations of this infection have many patterns which could lead to a misdiagnosis. Microbaterial studies such as tissue culture and drug susceptibility are essential clues for both definite diagnosis and treatment. Multi-antimicrobial agents are required to treat this infection with a long period of treatment to be cured. We report an unusual dual NTMs infection in an otherwise healthy person who had tattoos.
Downloads
References
Falsey RR, Kinzer MH, Hurst S, Kalus A, Pottinger PS, Duchin JS, Zhang J, Noble-Wang J, Shinohara MM. Cutaneous inoculation of nontuberculous mycobacteria during professional tattooing: a case series and epidemiologic study. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57: e143-e147.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Tattoo-associated nontuberculous mycobacterial skin infections--multiple states, 2011-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012; 61:653-6.
Drage LA, Ecker PM, Orenstein R, Phillips PK, Edson RS. An outbreak of Mycobacterium chelonae infections in tattoos. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010; 62:501-506.
Safranek TJ, Jarvis WR, Carson LA, Cusick LB, Bland LA, Swenson JM, Silcox VA. Mycobacterium chelonae wound infections after plastic surgery employing contaminated gentian violet skin-marking solution. N Engl J Med. 1987; 317:197-201.
Kim YN, Kim KM, Choi HN, Lee JH, Park HS, Jang KY, Moon WS, Kang MJ, Lee DG, Chung MJ. Clinical Usefulness of PCR for Differential Diagnosis of Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infection in Paraffin-Embedded Lung Tissues. J Mol Diagn. 2015; 17:597-604.
Hsiao Ch, Tsai TF, Hsueh PR. Characteristics of skin and soft tissue infection caused by non-tuberculous mycobacteria in Taiwan. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2011; 15:811-817.
Dodiuk-Gad R, Dyachenko P, Ziv M, Shani-Adir A, Oren Y, Mendelovici S, Shafer J, Chazan B, Raz R, Keness Y, Rozenman D. Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections of the skin: A retrospective study of 25 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007; 57:413-420.
Uslan DZ, Kowalski TJ, Wengenack NL, Virk A, Wilson JW. Skin and soft tissue infections due to rapidly growing mycobacteria: comparison of clinical features, treatment, and susceptibility. Arch Dermatol. 2006; 142:1287-1292.
Kasperbauer S, Huitt G. Management of extrapulmonary nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 34:143-150.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Chulabhorn Royal Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright and Disclaimer
Articles published in this journal are the copyright of Chulabhorn Royal Academy.
The opinions expressed in each article are those of the individual authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of Chulabhorn Royal Academy or any other faculty members of the Academy. The authors are fully responsible for all content in their respective articles. In the event of any errors or inaccuracies, the responsibility lies solely with the individual authors.


