Development of the Information System Program for Data Management among Patients with Cerebrovascular Diseases Hod Hospital, Chiang Mai Province
Keywords:
Cerebrovascular Disease, Information System Program, Data Management, Feasibility, SatisfactionAbstract
The objectives of this research and development were to develop and to evaluate the effectiveness of the information system program for data management of patients with cerebrovascular diseases. There were three phases in the research procedure: the situation analysis phase, the operational phase, and the evaluation phase. These phases were evaluated using the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC). Participants were recruited by purposive sampling. Five participants were recruited for the situation analysis and the operational phases. Six participants were recruited for the evaluation phase. The research instruments were a structured interview and questionnaires about the efficiency and effectiveness of the program. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics.
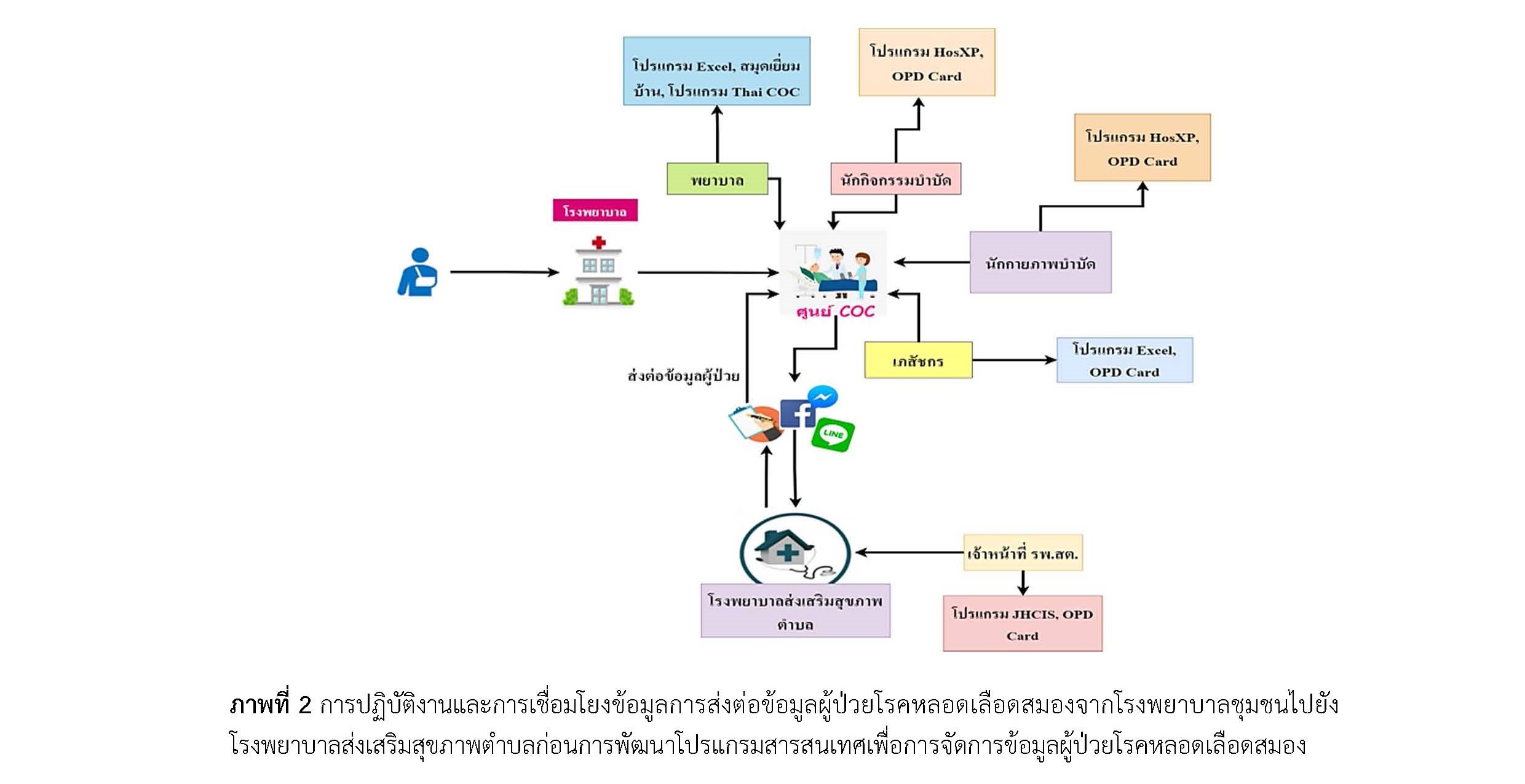
The results from the situation analysis phase established that follow up contact guidelines regarding when to initiate and when to terminate post discharge contact with cerebrovascular patients were established. The follow up process was based on patient symptom severity. Patient care management was negatively affected by problems in sharing patient information due to incomplete, unclear, or missing important data via application line, messenger, or Facebook. This research showed that there were four steps in using the Information System Program: 1) accessing to the system, 2) displaying patient information, 3) receiving home care information, and 4) reporting the outcomes. The results from the evaluation phase indicated that the program was user friendly highly accessible and useful because it reduces the time to transfer information by linking the patient database to provide accurate and complete patient information.
References
Bangkok Medical Software. (2561). BMS - HOSxP. สืบค้น 5 กันยายน 2564, จาก http://hosxp.net/joomla25.
กรมควบคุมโรค สำนักโรคไม่ติดต่อ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. (2563). วันที่สืบค้นข้อมูล 1 มิถุนายน 2563, เข้าถึงได้จาก https://ddc.moph.go.th/index.php.
คณะกรรมการพัฒนาระบบบริการที่ตอบสนองต่อปัญหาสุขภาพที่สำคัญสาขาโรคไม่ติดต่อ. (2562). แนวทางพัฒนาระบบบริการสุขภาพ สาขาโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้อรัง (NCD). กรุงเทพฯ: โรงพิมพ์ชุมนุมสหกรณ์การเกษตรแห่งประเทศไทย จำกัด.
ชูหงส์ มหรรทัศนพงศ์ (2561).ความสำเร็จโดยการเพิ่มขึ้นของอัตราการตอบกลับเยี่ยมบ้านจากการใช้โปรแกรมสารสนเทศ เพื่อสนับสนุนการดูแลต่อเนื่องในชุมชน. วารสารศูนย์การศึกษาแพทยศาสตร์คลินิก โรงพยาบาลพระปกเกล้า. 1(1), 355-362.
ธีรินทร์ เกตุวิชิต และสุรศักดิ์ มังสิงห์. (2558). การพัฒนาตัวแบบระบบการจัดการ-สารสนเทศเพื่อการส่งต่อผู้ป่วยด้วยโปรแกรมไทยรีเฟอร์. วารสารสมาคมเวช-สารสนเทศไทย, 1(1), 51-58.
ระวิวรรณ เติมศิริกุล, ประเสริฐ เก็มประโคน, อนันต์ กนกศิลป์ และกิตติ โล่สุวรรณรักษ์. (2558). การพัฒนาคลังข้อมูลสุขภาพระดับจังหวัดแบบบูรณาการ จังหวัดบุรีรัมย์. วารสารวิชาการสาธารณสุข, 24 (3), 530 - 541.
ศูนย์ความเป็นเลิศทางการแพทย์ด้านโรคหลอดเลือดสมองแบบครบวงจร สภากาชาดไทย. (2558). โรคหลอดเลือดสมอง. กรุงเทพฯ: อมรินทร์เฮลท์ อมรินทร์พริ้นติ้งแอนด์พับลิชชิ่ง.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข








