การศึกษาประสิทธิผลของโปรแกรมส่งเสริมการจัดการด้วยตนเองต่อพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ ระดับความดันโลหิต ระดับน้ำตาลในเลือด และเส้นรอบเอว ของผู้สูงอายุภาวะเมตาบอลิก
คำสำคัญ:
โปรแกรมส่งเสริมการจัดการด้วยตนเอง, ผู้สูงอายุภาวะเมตาบอลิก, พฤติกรรมสุขภาพ, ความดันโลหิต, น้ำตาลในเลือดบทคัดย่อ
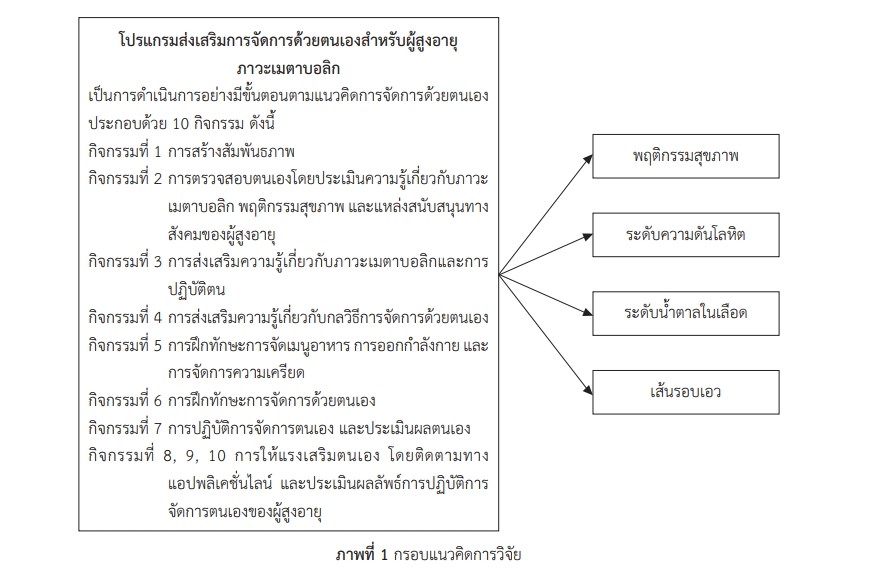
การวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาความเป็นไปได้ของโปรแกรมส่งเสริมการจัดการด้วยตนเองต่อพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ ระดับความดันโลหิต ระดับน้ำตาลในเลือด และเส้นรอบเอวของผู้สูงอายุภาวะเมตาบอลิก กลุ่มตัวอย่าง คือ ผู้สูงอายุภาวะเมตาบอลิกที่มารับบริการ ณ แผนกผู้ป่วยนอกอายุรกรรม จำนวน 10 ราย เครื่องมือการวิจัยที่ใช้ คือ แบบประเมินพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ เครื่องวัดความดันโลหิต เครื่องตรวจน้ำตาลในเลือด สายวัดรอบเอว และโปรแกรมส่งเสริมการจัดการด้วยตนเอง กลุ่มตัวอย่างได้รับโปรแกรมส่งเสริมการจัดการด้วยตนเอง จำนวน 10 กิจกรรม แบ่งเป็น 6 ครั้ง สถิติที่ใช้ในการวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลคือ การแจกแจงความถี่ หาค่าร้อยละ และสถิติ Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test
ผลการศึกษา พบว่า คะแนนเฉลี่ยพฤติกรรมสุขภาพของกลุ่มตัวอย่างในระยะหลังการทดลองมากกว่าระยะก่อนการทดลองอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (p < .01) ค่าเฉลี่ยความดันโลหิตตัวบนและค่าเฉลี่ยความดันโลหิตตัวล่างของกลุ่มตัวอย่างในระยะหลังการทดลองน้อยกว่าระยะก่อนการทดลองอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (p < .01) ค่าเฉลี่ยระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดในระยะหลังการทดลองน้อยกว่าระยะก่อนการทดลองอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (p < .05) ส่วนค่าเฉลี่ยของเส้นรอบเอว ในระยะหลังการทดลองน้อยกว่าระยะก่อนการทดลองอย่างไม่มีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ
สรุปได้ว่า โปรแกรมส่งเสริมการจัดการด้วยตนเองสามารถเพิ่มพฤติกรรมสุขภาพของผู้สูงอายุภาวะเมตาบอลิกให้ดีขึ้น และลดระดับความดันโลหิต ระดับน้ำตาลในเลือด และเส้นรอบเอว จึงมีข้อเสนอแนะว่าควรมีการนำโปรแกรมไปศึกษาประสิทธิผลของโปรแกรมเพิ่มเติมในจำนวนกลุ่มตัวอย่างที่มากขึ้น
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Aekplakorn, W., Puckcharern, H., Thaikla, K., & Satheannoppakao, W. (2014). Report of 5th Thai national health examination survey. Nonthaburi: Health Systems Research Institute (HSRI). [in Thai]
Alberti, K., Eckel, R. H., Grundy, S. M., Zimmet, P. Z., Cleeman, J. I., Donato, K. A., Jean-Charles, F., James, W. P. T., Loria, C. M., & Smith Jr, S. C. (2009). Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome a joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; National heart, lung, and blood institute; American heart association; World heart federation; International atherosclerosis society; and International association for the study of obesity. Circulation, 120(16), 1640-1645.
American Heart Association [AHA] (2021). American Heart Association [AHA]. (2021). What is
metabolic syndrome? Retrieved from https://www.heart.org/-/media/files/health-topics/
answers-by-heart/what-is-metabolic-syndrome.pdf
American Diabetes Association [ADA]. (2015). Standards of medical care in diabetes-2015. Diabetes Care, 38(Supplement1), S31-S33.
Amput, P., & Wongphon, S. (2016). Correlation between risk factors and blood sugar levels of elderly with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Srinagarind Med Journal, 31(5), 305-313. [in Thai]
Azarbad, L., & Gonder-Frederick, L. (2010). Obesity in women. Psychiatric Clinical North American, 33(2), 423-440.
Bua-ium, P., Jareinpituk, S., Siri, S., & Satitvipawee P. (2018). Prevalence and associated factors with multimorbidity among the elderly in Siprachan district, Suphanburi province. The 16th National Public Health Conference, (pp. 254-262), Bangkok: Public Health Mahidol University. [in Thai]
Chansree, N., Nateetanasombat, K., & Kasiphol, T. (2020). The effects of self-management program among uncontrolled hypertensive patients. Huachiew Chalermprakiet Science Technology Journal, 6(2), 58-67. [in Thai]
Chattakul, P. (2021). Prevalence and factors associated with metabolic syndrome at health promoting hospital, Khon Kaen. Srinagarind Med Journal, 36(3), 273-280. [in Thai]
Chuengsaman, S. (2017). Type 2 diabetes/ metabolism. Nonthaburi: PT Inter Print. [In Thai]
Chumchiang, P., Supametaporn, P., & Songthai, N. (2018). The effects of self-management support program on health behaviors and body mass index in people with pre- diabetes. Nursing Public Health and Education Journal, 19(1), 108-119. [in Thai]
Collin, C., Wade, D. T., Davies, S., & Home, V. (1988). The Barthel ADL index: A reliability study. International Disability Studies, 10(9), 61-63.
Deenan, A., & Subruang, J. (2016). Prediction of factors of body fat of metabolic syndrome persons. Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 7(2), 89-104. [in Thai]
Grundy, S. M. (2016). Metabolic syndrome update. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine, 26(4), 364-373.
International Diabetes Federation [IDF]. (2006). The IDF consensus worldwide definition of the metabolic syndrome. Retrieved from http://www.idf.org/webdata/docs/ IDF_Meta_def_final.pdf
Jitapunkul, S., Kamolratanakul, P., Chandraprasert, S., & Bunnag, S. (1994). Disability among thai elderly living in Klong Toey slum. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand, 77(5), 231-238.
Kanfer, F. H., & Gaelick, L. (1991). Self-management method. In F. H. Kanfer & A. Goldstein (Eds.), Helping people change: A textbook of methods (4th ed., pp. 305-360). New York: Pergamon Press.
Khamchata, L., Wattana, C., & Harnirattisai, T. (2017). The effects of a self-management program on self-management behaviors, waist circumference, blood sugar level, and cardiovascular disease risk among persons with metabolic syndrome. Nursing Journal, 44(3), 65-76. [in Thai]
Munsrakeat, K., Rawiworrakul, T., & Lagampan, S. (2019). Effects of a self-management program for glycemic control among insulin dependent type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. The Journal of Baromarajonani College of Nusing, Nakhonratchasima, 25(2), 87-103. [in Thai]
Pondongnok, S., Rattanachaiwong,. S, Wichai, J., & Thonrach, T. (2015). Metabolic syndrome. Khonkan: Health Promotion Unit Srinagarind Hospital. [in Thai]
Pradubpoth, K., Noonil, N., Aekwarangkoon, S., & Phonphet, Ch. (2019). Older adults with metabolic syndrome: The effects of swing arms walking exercise on blood sugar level, blood pressure, and waist circumference. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 6(1), 154-166. [in Thai]
Ranasinghe, P., Mathangasinghe, Y., Jayawardena, R., Hills, A., & Misra, A. (2017). Prevalence and trends of metabolic syndrome among adults in the Asia-pacific region: A systematic review. Biomed Central Public Health, 17(1), 1-9.
Saklayen, M. G. (2018). The global epidemic of the metabolic syndrome. Current Hypertension Reports, 20(2), 1-8.
Sararuk, M., Nganchamung, T., & Krasuaythong, N. (2020). Health status and health behaviors among elderly in Kham Kwang sub-district, Warin Chamrap district, Ubon Ratchathani province. Srinagarind Med Journal, 35(3), 304-310. [in Thai]
Statistics Report of Burapha University Hospital. (2020). Registration and statistics: Top 10 OPD patients aged 60 and over, 2013. Chonburi: Burapha University Hospital.
Sindhu, S., Limruangrong, P., & Tankumpuan, T. (2016). Nurse led in overweigth management. Bangkok: Wattana printing. [in Thai]
Suwankruhasn, N., Pothiban, L., Panuthai, S., & Boonchuang, P. (2013). Effects of a self-management support program for Thai people diagnosed with metabolic syndrome. Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research, 17(4), 371-383.
Tipkanjanaraykha, K., Kangchai, W., Hengudomsub, P., & Schneider, J. K. (2016). A metabolic syndrome self-management program for older adults: A randomized controlled trail. Journal of Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Bangkok, 32(2), 12-26.
Thongcharoen, W. (2015). Science and art of geriatric nursing (2nd ed.). Bangkok: NPS. [in Thai]
Trongsakul, S., Lambert, R., Clark, A., Wongpakaran, N., & Cross, J. (2015). Development of the Thai version of Mini-Cog, a brief cognitive screening test. Geriatrics & gerontology international, 15(5), 594-600.
Whitehead, A. L., Julious, S. A., Cooper, C. L., & Campbell, M. J. (2016). Estimating the sample size for a pilot randomised trial to minimise the overall trial sample size for the external pilot and main trial for a continuous outcome variable. Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 25(3), 1057-1073.
Wongchan, W. (2018). Metabolic syndrome in adult: Self-management. Journal of The Royal Thai Army Nurses, 19(Supplement), 16-24. [in Thai]
Wongpakaran, N., & Wongpakaran, T. (2012). Prevalence of major depressive disorders and suicidein long-term care facilities: A report from northern Thailand. Psychogeriatrics, 12(1), 11-17.
Yuenyongchaiwat, K., Pipatsitipon, D., & Sangprasert, P. (2017). The prevalence and risk factors of metabolic syndrome a suburban community in Pathum Thani province Thailand. Songklanakarin Journal of Science and Technology, 39(6), 787-792.
Zafar, U. (2020). Metabolic Syndrome Update. In J. Faintuch & S. Faintuch (Eds.), Obesity and Diabetes (pp. 305-320). Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.




