Prehospital intubation performed by Emergency Physicians in severe traumatic brain injury patients
Keywords:
Prehospital intubation, Traumatic brain injury, Emergency physiciansAbstract
Background: Airway management is the first essential step for caring traumatic brain injury (TBI). Recent studies failed to demonstrate survival benefit from prehospital Intubation (PHI) that was done by paramedics. However, there is lack of study about PHI that was done by emergency physicians (EP) who have more experience for intubation than paramedics.
Objective: To study the effect of PHI that was done by EP for survival to discharge rate in TBI patients.
Methods: Retrospective study was conducted from 1 October 2015 to 30 September 2017. Adult severe TBI patients who were GCS score less than 9 and were treated at scene by EP from Emergency medical service were included to the study. The patients were divided to PHI group and in-hospital intubation group. Survival rate was demonstrated by Odds ratio and control influenced factor by multivariate analysis. The significant level was 0.05 and all data were analyzed by STATA version 14.
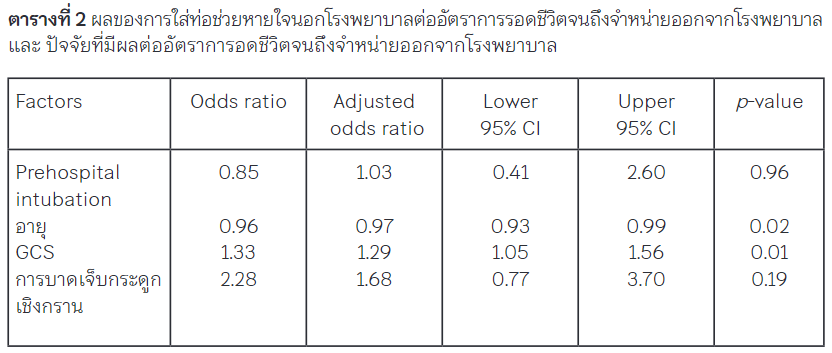
Results: From 121 patients, most of them were middle-aged men and 5 points in GCS score. The major cause of accident was motorcycle accident and overall survival rate was 47.1%. The PHI group had adjusted odds ratio 1.03 (p-value 0.96). Independent factor for survival rate were age and GCS score and odds ratio were 0.96 and 1.33 respectively.
Conclusion: There is no statistic significant for survival to discharge in severe TBI patients who were done PHI by EP.
Downloads
References
American College of Surgeons. Advanced Traumatic Life Support (ATLS). 10th edition. Chicago: American College of Surgeons; 2018.
National Association of Emergency Medical Technicians. Prehospital Trauma Life Support (PHTLS). 9th edition. Miami: Jones & Bartlett learning; 2020
Wang HE. AIRWAY SAFETY PEARLS. Strategies for safer prehospital intubation. JEMS. 2015;40(8): 34-39.
Fevang E, Perkins Z, Lockey D, Jeppesen E, Lossius HM. A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing mortality in pre-hospital tracheal intubation to emergency department intubation in trauma patients. Crit Care. 2017;21(1):192. Published 2017 Jul 31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-017-1787-x PMid:28756778 PMCid:PMC5535283
Bossers SM, Schwarte LA, Loer SA, Twisk JW, Boer C, Schober P. Experience in Prehospital Endotracheal Intubation Significantly Influences Mortality of Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0141034. Published 2015 Oct 23. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141034 PMid:26496440 PMCid:PMC4619807
Jensen JL, Cheung KW, Tallon JM, Travers AH. Comparison of tracheal intubation and alternative airway techniques performed in the prehospital setting by paramedics: a systematic review. CJEM. 2010;12(2):135-140. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1481803500012161 PMid:20219161
Jung E, Cho YS, Ryu SJ, Kim DK, Lee JH, Han JH. The impact of prehospital endotracheal intubation on mortality in traumatic brain injury.Am J Emerg Med. 2022;55:152-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2022.02.001 PMid:35325789
Bossers SM, Verheul R, van Zwet EW, et al. Prehospital Intubation of Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Dutch Nationwide Trauma Registry Analysis [published online ahead of print, 2022 Sep 12]. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2022;1-7. https://doi.org/10.1080/10903127.2022.2119494 PMid:36074561
Bochicchio GV, Ilahi O, Joshi M, Bochicchio K, Scalea TM. Endotracheal intubation in the field does not improve outcome in trauma patients who present without an acutely lethal traumatic brain injury. J Trauma.2003;54(2):307-311. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.TA.0000046252.97590.BE PMid:12579056
Pepe PE, Roppolo LP, Fowler RL. Prehospital endotracheal intubation: elemental or detrimental?. Crit Care. 2015;19:121. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-015-0808-x PMid:25887350 PMCid:PMC4440604
Bossers SM, Schwarte LA, Loer SA, Twisk JW, Boer C, Schober P. Experience in Prehospital Endotracheal Intubation Significantly Influences Mortality of Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0141034. Published 2015 Oct 23. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141034 PMid:26496440 PMCid:PMC4619807
Rubenson Wahlin R, Nelson DW, Bellander BM, Svensson M, Helmy A, Thelin EP. Prehospital Intubation and Outcome in Traumatic Brain Injury-Assessing Intervention Efficacy in a Modern Trauma Cohort. Front Neurol. 2018;9:194. Published 2018 Apr 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00194 PMid:29692755 PMCid:PMC5903008
Tuma M, El-Menyar A, Abdelrahman H, et al. Prehospital intubation in patients with isolated severe traumatic brain injury: a 4-year observational study. Crit Care Res Pract. 2014;2014:135986. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/135986 PMid:24527211 PMCid:PMC3914516
Choffat C, Delhumeau C, Fournier N, Schoettker P. Effect of Pre-Hospital Intubation in Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury on Outcome: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Clin Med. 2019;8(4):470. Published 2019 Apr 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040470 PMid:30959868 PMCid:PMC6517889
Anderson J, Ebeid A, Stallwood-Hall C. Pre-hospital tracheal intubation in severe traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2022;129(6):977-984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2022.07.033 PMid:36088135
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Chulabhorn Royal Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright and Disclaimer
Articles published in this journal are the copyright of Chulabhorn Royal Academy.
The opinions expressed in each article are those of the individual authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of Chulabhorn Royal Academy or any other faculty members of the Academy. The authors are fully responsible for all content in their respective articles. In the event of any errors or inaccuracies, the responsibility lies solely with the individual authors.


