Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Management of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Preliminary Study
Keywords:
Intraarticular knee injection, Osteoarthritis knee, Platelet rich plasmaAbstract
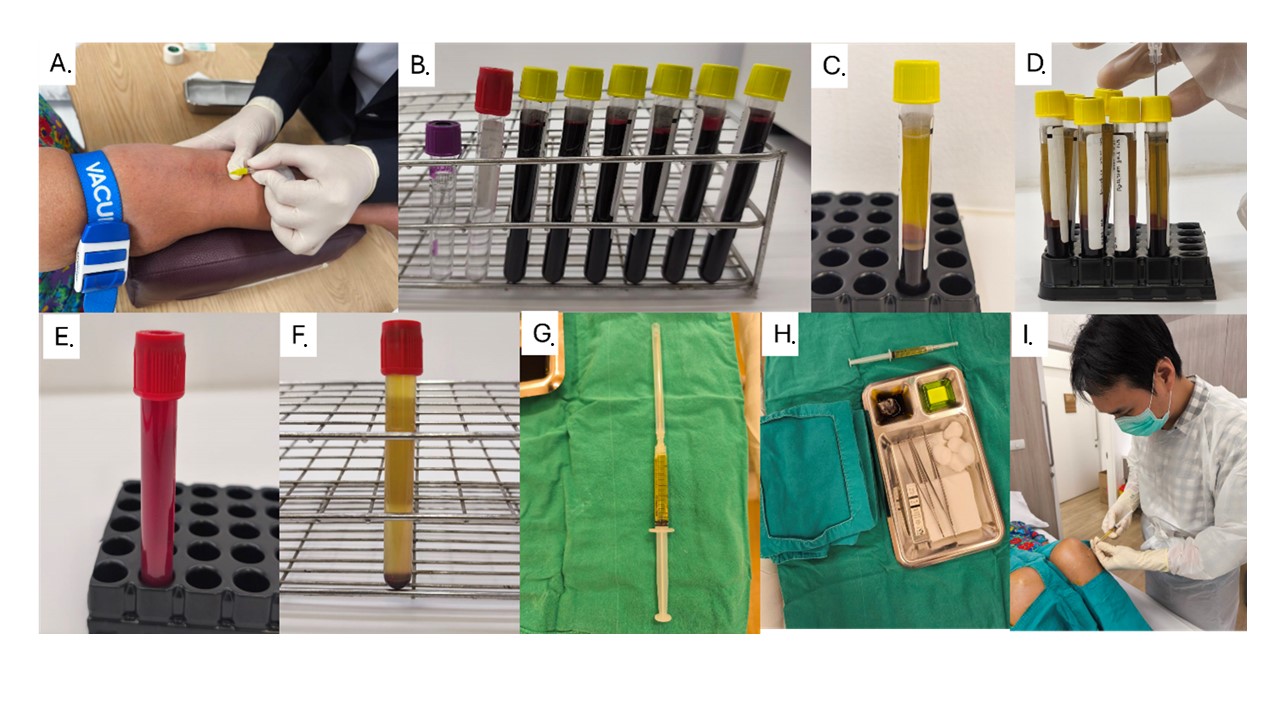
Introduction: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is an alternative treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee (OA Knee). While PRP treatment has shown promising clinical outcomes through its anti-inflammatory mechanisms and growth factors, literature reviews reveal debates regarding its short- and long-term efficacy, as well as safety concerns and the complexity of the preparation process, which may hinder its therapeutic outcomes. Objective: To standardize the PRP preparation process for treating OA Knee and evaluate the treatment outcomes. Methods: The study was conducted on 50 patients with OA Knee from December 1, 2021, to November 30, 2022. PRP was prepared according to standardized protocols, and the outcomes at 1, 3, and 6 months post-treatment. The primary outcomes included platelet concentration in the PRP, pain intensity measured by Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), and functional improvement assessed by the WOMAC score. Results: A total of 47 patients completed follow-up, with a mean age of 64.76 ± 7.3 years. The majority had advanced OA (stage 3-4; 41 patients). Platelet concentration in PRP significantly increased by 2.7 times after centrifugation compared to baseline (258,562 ± 78,204 vs. 702,621 ± 718,621 platelets/mm³). Pain levels measured by the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) significantly decreased from a baseline of 6.7 ± 1.19 to 3.7 ± 1.38, 2.77 ± 1.20, and 2.68 ± 1.2 at 1, 3, and 6 months, respectively. Knee function and quality of life, as assessed by the WOMAC score, also showed significant improvement. The baseline score of 43.32 ± 14.91 decreased to 31.00 ± 16.26, 26.80 ± 15.41, and 25.31 ± 13.74 at the same time intervals. Conclusion: Standardizing the PRP preparation process is feasible in hospital settings and offers an effective treatment option for OA Knee. The treatment demonstrated significant pain reduction and improved knee quality of life (WOMAC score) for up to 6 months post-treatment.
Downloads
References
ราชวิทยาลัยแพทย์ออร์โธปิดิกส์แห่งประเทศไทย. แนวปฏิบัติบริการสาธารณสุข โรคข้อเข่าเสื่อม พ.ศ. 2554 ปฏิบัติทางคลินิก (clinical practice guideline).
Tang JZ, Nie MJ, Zhao JZ, Zhang GC, Zhang Q, Wang B. Platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):403. doi:10.1186/s13018-020-01919-9.
Dhurat R, Sukesh M. Principles and methods of preparation of platelet-rich plasma: A review and author’s perspective. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2014;7(4):189-197. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.150734.
Sax OC, Chen Z, Mont MA, Delanois RE. The efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis symptoms and structural changes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(11):2282-2290.e2. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2022.05.014.
Xiong Y, Gong C, Peng X, et al. Efficacy and safety of platelet-rich plasma injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1204144. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1204144
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of osteoarthritis of the knee (non-arthroplasty) Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline. https://www.aaos.org/oak3cpg. Accessed December 7, 2024.
Dório M, Pereira RMR, Luz AGB, Deveza LA, de Oliveira RM, Fuller R. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma and plasma for symptomatic treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a double-blinded placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):822. doi:10.1186/s12891-021-04706-7.
Lin MT, Wei KC, Wu CH. Effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injection in rotator cuff tendinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(4):189. doi:10.3390/diagnostics10040189.
Rathod V, Shrivastav S, Gharpinde MR. Platelet-rich plasma therapy for rotator cuff injuries: A comprehensive review of current evidence and future directions. Cureus. 2024;16(9):e70042. doi:10.7759/cureus.70042.
Costa LAV, Lenza M, Irrgang JJ, Fu FH, Ferretti M. How does platelet-rich plasma compare clinically to other therapies in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(4): 1074-1086. doi:10.1177/03635465211062243.
Mitra S, Seenappa H, Madhavan P. A clinical evaluation study of single spin vs double spin intra-articular PRP injection in patients with bilateral early OA knee: A novel technique. Int J Orthop Sci. 2021;7(3):01-06. doi:10.22271/ortho.2021.v7.i3a.2718.
Machado ES, Leite R, Dos Santos CC, et al. Turn down - turn up: a simple and low-cost protocol for preparing platelet-rich plasma. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019;74(e1132):e1132. doi:10.6061/clinics/2019/e1132.
Machado ES, Soares FP, Yamaguchi RS, et al. A simple double-spin closed method for preparing platelet-rich plasma. Cureus. 2022;14(1):e20899. doi:10.7759/cureus.20899.
Kohn MD, Sassoon AA, Fernando ND. Classifications in brief: Kellgren-Lawrence classification of osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(8):1886-1893. doi:10.1007/s11999-016-4732-4.
Pietrzak J, Maharaj Z, Mokete L, Sikhauli N, van der Jagt DR. Total hip arthroplasty in obesity: separating 'fat' from fiction. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2019;80(6):325-330. doi:10.12968/hmed.2019.80.6.325.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence NICE. Platelet-rich plasma injections for knee osteoarthritis: interventional procedures guidance [IPG637]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg637. Accessed December 7, 2024.
Subramanyam K, Alguvelly R, Mundargi A, Khanchandani P. Single versus multi-dose intra-articular injection of platelet rich plasma in early stages of osteoarthritis of the knee: A single-blind, randomized, superiority trial. Arch Rheumatol. 2021;36(3):326-334. doi:10.46497/ArchRheumatol.2021.8408.
Parmanantham M, Seenappa H, Das S, Shanthappa AH. Comparison of functional outcome of single versus multiple intra-articular platelet-rich plasma injection for early Osteoarthritis knee. Cureus. 2023;15(5):e38513. doi:10.7759/cureus.38513.
Szwedowski D, Mobasheri A, Moniuszko A, Zabrzynski J, Jeka S. Intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma is more effective than hyaluronic acid or steroid injection in the treatment of mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis: A prospective, randomized, triple-parallel clinical trial. Biomedicines. 2022;10(5):991. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10050991.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Chulabhorn Royal Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright and Disclaimer
Articles published in this journal are the copyright of Chulabhorn Royal Academy.
The opinions expressed in each article are those of the individual authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of Chulabhorn Royal Academy or any other faculty members of the Academy. The authors are fully responsible for all content in their respective articles. In the event of any errors or inaccuracies, the responsibility lies solely with the individual authors.


