รายงานเบื้องต้น ประสิทธิภาพและผลการรักษาของการใช้เกล็ดเลือดเข้มข้น สำหรับการรักษาโรคข้อเข่าเสื่อม
คำสำคัญ:
การฉีดข้อเข่า, ข้อเข่าเสื่อม, เกล็ดเลือดเข้มข้นบทคัดย่อ
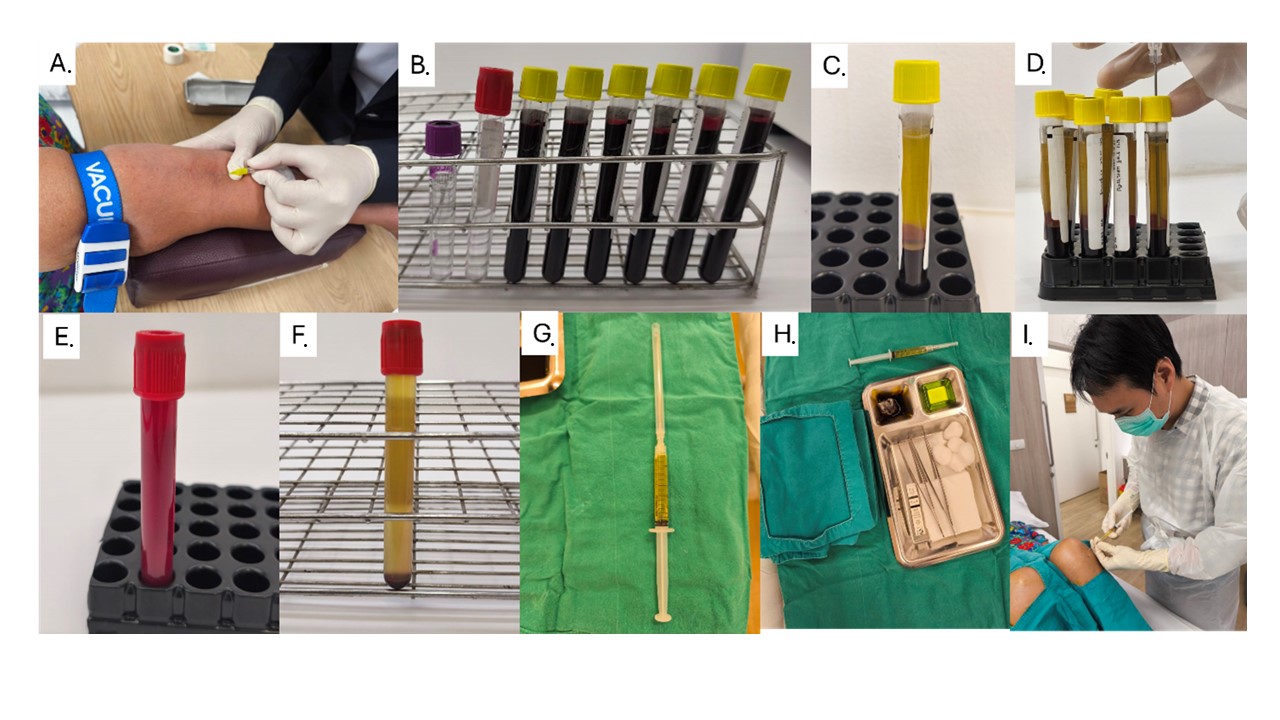
บทนำ: เกล็ดเลือดเข้มข้น (Platelet Rich Plasma: PRP) เป็นหนึ่งในทางเลือกในการรักษาโรคข้อเข่าเสื่อม (Osteoarthritis Knee: OA knee) แม้การรักษาด้วย PRP จะให้ผลดีทางคลินิก จากกลไกการลดการอักเสบและสารกระตุ้นการเจริญเติบโต (growth factors) แต่การทบทวนวรรณกรรม กลับพบข้อถกเถียงในแง่ความปลอดภัยและขั้นตอนการเตรียม รวมทั้งผลการรักษาทั้งระยะสั้นและระยะยาว วัตถุประสงค์: เพื่อควบคุมขั้นตอนกระบวนการเตรียม PRP รักษาข้อเข่าเสื่อม และรายงานผลการรักษา วิธีการศึกษา: รายงานผลลัพท์การรักษาผู้ป่วย OA Knee จำนวน 50 ราย ระหว่าง 1 ธันวาคม พ.ศ. 2564 ถึง 31 พฤศจิกายน พ.ศ. 2565 และติดตามที่ 1, 3 และ 6 เดือน โดยรายงานเป้าหมายหลักของการศึกษาคือ ค่าเกล็ดเลือดเข้มข้น ระดับความเจ็บปวด (Visual analogue score: VAS) และคะแนนแบบประเมินความเจ็บปวดข้อเข่า (WOMAC score) ผลการศึกษา: ติดตามการรักษาทั้งหมด 47 ราย อายุเฉลี่ย 64.76 ± 7.3 ปี ผู้ป่วยส่วนมากเป็นข้อเข่าเสื่อมระยะ 3-4 (41 ราย) พบค่าเกล็ดเลือด ก่อนปั่นและหลังปั่นเพิ่มขึ้นมีนัยสำคัญ 2.7 เท่า (258,562 ± 78,204, 702,621 ± 718,621 platelets/mm3) VAS ก่อนฉีดเฉลี่ย 6.7 ± 1.19 ลดลงมีนัยสำคัญที่ 1, 3 และ 6 เดือน (3.7 ± 1.38, 2.77 ± 1.20, 2.68 ± 1.2) WOMAC score ก่อนฉีดเกล็ดเลือดเข้มข้น 43.32 ± 14.91 ลดลงมีนัยสำคัญที่ 1 , 3 และ 6 เดือน (31.00 ± 16.26, 26.80 ± 15.41, 25.31 ± 13.74) บทสรุป: การกำหนดมาตรฐานการเตรียม PRP สามารถนำมาปฏิบัติได้จริงในโรงพยาบาลเป็นทางเลือกเพื่อรักษาผู้ป่วย OA Knee มีผลการรักษาที่ดีเมื่อติดตามที่ 6 เดือน โดยมีระดับความเจ็บปวด (VAS) และคะแนนแบบประเมินความเจ็บปวดข้อเข่า (WOMAC score) ลดลง
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
ราชวิทยาลัยแพทย์ออร์โธปิดิกส์แห่งประเทศไทย. แนวปฏิบัติบริการสาธารณสุข โรคข้อเข่าเสื่อม พ.ศ. 2554 ปฏิบัติทางคลินิก (clinical practice guideline).
Tang JZ, Nie MJ, Zhao JZ, Zhang GC, Zhang Q, Wang B. Platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):403. doi:10.1186/s13018-020-01919-9.
Dhurat R, Sukesh M. Principles and methods of preparation of platelet-rich plasma: A review and author’s perspective. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2014;7(4):189-197. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.150734.
Sax OC, Chen Z, Mont MA, Delanois RE. The efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis symptoms and structural changes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(11):2282-2290.e2. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2022.05.014.
Xiong Y, Gong C, Peng X, et al. Efficacy and safety of platelet-rich plasma injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1204144. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1204144
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of osteoarthritis of the knee (non-arthroplasty) Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline. https://www.aaos.org/oak3cpg. Accessed December 7, 2024.
Dório M, Pereira RMR, Luz AGB, Deveza LA, de Oliveira RM, Fuller R. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma and plasma for symptomatic treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a double-blinded placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):822. doi:10.1186/s12891-021-04706-7.
Lin MT, Wei KC, Wu CH. Effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injection in rotator cuff tendinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(4):189. doi:10.3390/diagnostics10040189.
Rathod V, Shrivastav S, Gharpinde MR. Platelet-rich plasma therapy for rotator cuff injuries: A comprehensive review of current evidence and future directions. Cureus. 2024;16(9):e70042. doi:10.7759/cureus.70042.
Costa LAV, Lenza M, Irrgang JJ, Fu FH, Ferretti M. How does platelet-rich plasma compare clinically to other therapies in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(4): 1074-1086. doi:10.1177/03635465211062243.
Mitra S, Seenappa H, Madhavan P. A clinical evaluation study of single spin vs double spin intra-articular PRP injection in patients with bilateral early OA knee: A novel technique. Int J Orthop Sci. 2021;7(3):01-06. doi:10.22271/ortho.2021.v7.i3a.2718.
Machado ES, Leite R, Dos Santos CC, et al. Turn down - turn up: a simple and low-cost protocol for preparing platelet-rich plasma. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019;74(e1132):e1132. doi:10.6061/clinics/2019/e1132.
Machado ES, Soares FP, Yamaguchi RS, et al. A simple double-spin closed method for preparing platelet-rich plasma. Cureus. 2022;14(1):e20899. doi:10.7759/cureus.20899.
Kohn MD, Sassoon AA, Fernando ND. Classifications in brief: Kellgren-Lawrence classification of osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(8):1886-1893. doi:10.1007/s11999-016-4732-4.
Pietrzak J, Maharaj Z, Mokete L, Sikhauli N, van der Jagt DR. Total hip arthroplasty in obesity: separating 'fat' from fiction. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2019;80(6):325-330. doi:10.12968/hmed.2019.80.6.325.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence NICE. Platelet-rich plasma injections for knee osteoarthritis: interventional procedures guidance [IPG637]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg637. Accessed December 7, 2024.
Subramanyam K, Alguvelly R, Mundargi A, Khanchandani P. Single versus multi-dose intra-articular injection of platelet rich plasma in early stages of osteoarthritis of the knee: A single-blind, randomized, superiority trial. Arch Rheumatol. 2021;36(3):326-334. doi:10.46497/ArchRheumatol.2021.8408.
Parmanantham M, Seenappa H, Das S, Shanthappa AH. Comparison of functional outcome of single versus multiple intra-articular platelet-rich plasma injection for early Osteoarthritis knee. Cureus. 2023;15(5):e38513. doi:10.7759/cureus.38513.
Szwedowski D, Mobasheri A, Moniuszko A, Zabrzynski J, Jeka S. Intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma is more effective than hyaluronic acid or steroid injection in the treatment of mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis: A prospective, randomized, triple-parallel clinical trial. Biomedicines. 2022;10(5):991. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10050991.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2025 ราชวิทยาลัยจุฬาภรณ์

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของราชวิทยาลัยจุฬาภรณ์
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับราชวิทยาลัยจุฬาภรณ์ และคณาจารย์ท่านอื่น ในราชวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว


