Epidemiology of Frailty, Sarcopenia, Dementia among Community - Dwelling Older Persons in Lak Si District, Bangkok
Keywords:
Frailty, Sarcopenia, Dementia, Older personsAbstract
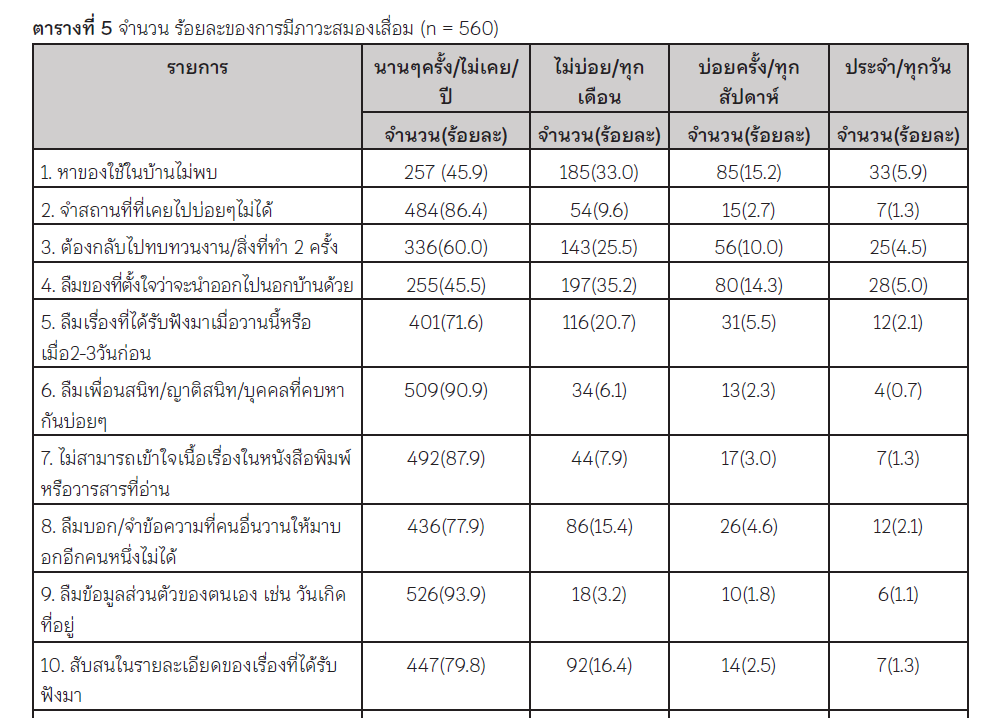
Introduction: Older persons are at higher risks for frailty, sarcopenia and dementia. These are major health problems among Thai older persons. The Research in Thailand is quite limited. Objective: The aims to explore the epidemiology on frailty, sarcopenia and dementia among community - dwelling older persons in Lak Si District, Bangkok. Methods: Use descriptive study among 560 older people in their community-dwelling. Interviews and self-reports were conducted for data collection. Interviews included demographic, The Tilburg Frailty Indicator (TFI) part B Components for frailty, SARC-F test for sarcopenia and dementia test. All data was analyzed by descriptive statistics. Results: The study found that the average age of the sample was 69.3 with 1) prevalence of frailty (21.07%); reduced eye vision, fatigue, body unbalancing, and walking difficulty including walking upstairs 2) prevalence of sarcopenia (15.18%); holding and lifting difficulties (36.1%), and falling during the year (31.1%) and3)dementia(4.83%) ;memory and cognitive system problems. Conclusion: From the study, it is suggested that health personnel should concern and manage about frailty, sarcopenia and dementia in the older persons and help the clients in every dimension; health promotion, prevention, caring, rehabilitation and referring system for their good quality of life.
Downloads
References
World Health Organization. WHO/ Health topics: Ageing. https://www.who.int/health-topics/ ageing#tab=tab_1. Accessed November 1, 2022
สำนักงานสถิติแห่งชาติ. ระบบคลังข้อมูลสถิติ สำนักงานสถิติแห่งชาติ. จาก https://nsodw.nso.go.th/ dwportal/It em.aspx?p=+gsaDgQv4TQFrLJCEbyvEQ==. เมื่อวันที่ 12 ตุลาคม 2565.
กองยุทธศาสตร์สาธารณสุขและสิ่งแวดล้อม สำนักยุทธศาสตร์และประเมินผล กรุงเทพมหานคร.สรุปฐานข้อมุลผู้สูงอายุระดับเขตของกรุงเทพมหานคร. กองยุทธศาสตร์สาธารณสุขและสิ่งแวดล้อม.จาก https://webportal.bangkok.go.th/hesd/page/main/1686/. เมื่อวันที่ 1 ตุลาคม 2565.
Fried L, Walston J. Frailty and failure to thrive. In: Hazzard WR, Blass JP, Ettinger WH Jr, Halter JB, Ouslander JG. Principles of geriatric medicine and gerontology, fourth edition. NY: Mc Graw Hill; 1998: 1387–1402.
Welstead M, Jenkins ND, Russ TC, Luciano M, Muniz-Terrera G. A Systematic Review of Frailty Trajectories: Their Shape and Influencing Factors. Gerontologist. 2021;61(8):e463-e475. doi:10.1093/geront/gnaa061
American Psychiatric Association, Force DSMT. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders : DSM V 2013. American Psychiatric Association. http://dsm.psychiatry online.org/book.aspx?bookid=556. Accessed November 1, 2022
Fogg C, Fraser SDS, Roderick P, et al. The dynamics of frailty development and progression in older adults in primary care in England (2006-2017): a retrospective cohort profile. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22(1):30. Accessed January 6, 2022. doi:10.1186/ s12877-021-02684-y
Sanford AM, Morley JE, Berg-Weger M, Lundy J, Little MO, Leonard K, Malmstrom TK. High prevalence of geriatric syndromes in older adults. PLoS One. 2020; 15(6):e0233857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233857.
O'Caoimh R, Galluzzo L, Rodríguez-Laso Á, et al. Prevalence of frailty at population level in European ADVANTAGE Joint Action Member States: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2018;54(3):226-238. doi:10.4415/ANN_18_03_10
สัณหวัช โสประทุม, พัฒน์ศรี ศรีสุวรรณ, ทนงสรรค์ เทียนถาวร, สุภัชฌา เก่งพานิช. ความชุกและปัจจัยเสี่ยงที่สัมพันธ์กับภาวะเปราะบางของผู้สูงอายุที่เข้ารับการบริการในห้องตรวจโรคผู้ป่วยนอก โรงพยาบาลพระมงกุฏเกล้า : การศึกษาเชิงผสมผสาน. วารสารพฤฒาวิทยาและเวชศาสตร์ผู้สูงอายุ. 2565; 21(1-2). 1-11.
Kulthanit W, Weerasak M, Vilai K, Chalobol C, Apiwan N. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Frailty and Cognitive Frailty among Community-Dwelling Elderly with Knee Osteoarthritis. J COMMUN HEALTH. 2019; 44: 587-595. doi.org/10.1007/s10900-018-00614-5.
ณัฐกฤตา บริบูรณ์, พีระศักดิ์ เลิศตระการนนท์, เพ็ญประภา ศิวิโรจน์. ความชุกและปัจจัยที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภาวะเปราะบางของผู้สูงอายุในชุมชน : กรณีศึกษาในอำเภอเสริมงาม จังหวัดลำปาง.วารสารการแพทย์และวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ. 2560; 24(1). 45-54.
สุพรรณี ใจดี, ศิริพันธุ์ สาสัตย์. การศึกษาภาวะเปราะบางของผู้สูงอายุในชุมชน กรุงเทพมหานคร.วารสารแพทย์นาวี. 2560; 44(3): 117-135.
Zodpey SP. Sample size and power analysis in medical research. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2004; 70(2): 123–128. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17642587. Accessed February 2, 2020.
Gobbens RJ, Schols JM, van Assen MA. Exploring the efficiency of the Tilburg Frailty Indicator: a review. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:1739-1752. Accessed October 19, 2017. doi:10.2147/CIA.S130686
Woo J, Leung J, Morley JE. Validating the SARC-F: a suitable community screening tool for sarcopenia?. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15(9):630-634. doi:10.1016/j.jamda. 2014.04.021
สถาบันเวชศาสตร์สมเด็จพระสังฆราชญาณสังวรเพื่อผู้สูงอายุ กรมการแพทย์. แนวทางการจัดการดูแลผู้สูงอายุภาวะ สมองเสื่อมแบบครบวงจร. กรุงเทพฯ: บริษัท ไซเบอร์พริ้นท์กรุ๊ป จำกัด; 2562. จาก http://agingthai.dms.go.th/agingthai/manual-guideline/manual-guideline-table. เมื่อวันที่ 12 ตุลาคม 2565
Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, et al. Frailty in Older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001; 56(3): M 146-156. doi:10.1093/gerona/56.3.m146.
Delbari A, Zanjari N, Momtaz YA, Rahim F, Saeidimehr S. Prevalence of frailty and associated socio-demographic factors among community-dwelling older people in southwestern Iran: a cross-sectional study. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021;20(1):601-610. Accessed March 31, 2021. doi:10.1007/s40200-021-00787-2.
Cheung SL, Krijnen WP, van der Schans CP, Hobbelen JSM. Frailty, Quality of Life, and Loneliness of Aging in Native and Diasporic Chinese Adults. J Frailty Aging. 2022; 3: 1-10. doi.org/10.14283/jfa.2022.27.
Rachel AM, Edword HI, Qiang Z, Robert MB, Peggy MC, Anne BN, t al. Transition to Sarcopenia & Determinants of Transitions in Older Adults : A Population – Based Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014; 69(6): 751-758. doi.10.1093/gerona/glt131.
Malmstrom TK, Miller DK, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, Morley JE. SARC-F: a symptom score to predict persons with sarcopenia at risk for poor functional outcomes.
J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2016;7(1):28-36. doi:10.1002/jcsm.12048
Shige Q, Peng Y, Han Z, Qingjun Z, Yize X, Ying D, et al. Prevalence of Dementia in China in 2015: A Nationwide Community – Based Study. Front Public Health. 2021; 2(9): 1-11. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.733314.
Kala MM, Gwen WY. Systematic review of dementia prevalence and incidence in United States race/ethnic populations. Alzheimer Dement. 2017; 13(1): 72-83. doi: 10.1016/ j.jalz.2016.06.2360.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Chulabhorn Royal Academy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright and Disclaimer
Articles published in this journal are the copyright of Chulabhorn Royal Academy.
The opinions expressed in each article are those of the individual authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of Chulabhorn Royal Academy or any other faculty members of the Academy. The authors are fully responsible for all content in their respective articles. In the event of any errors or inaccuracies, the responsibility lies solely with the individual authors.


