การทบทวนวรรณกรรม: การตรวจจับคลื่นสมองประเภท Sleep spindles แบบอัตโนมัติ
คำสำคัญ:
การตรวจวัดคลื่นไฟฟ้าสมอง, การประมวลผลสัญญาณ, การเรียนรู้ของเครื่อง, คลื่นสมอง Sleep spindle, วิธีการตรวจจับแบบอัตโนมัติบทคัดย่อ
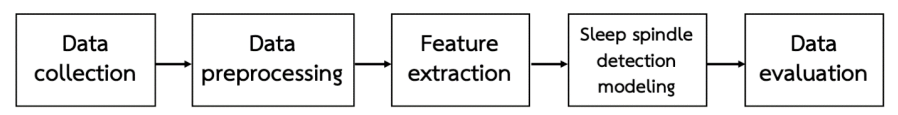
Sleep spindle เป็นคลื่นสมองรูปแบบหนึ่งที่เกิดขึ้นในช่วงระยะที่ 2 ของการนอนหลับแบบ NREM (Non-rapid eye movement) โดยมีหลักฐานบ่งชี้ว่าคลื่นสมองประเภทนี้มีบทบาทสำาคัญในหลากหลายด้าน อาทิ มีความสำคัญ ในกระบวนการเปลี่ยนความทรงจำระยะสั้นเป็นความทรงจำระยะยาวของสมอง และอาจมีความสัมพันธ์กับความเสื่อม ของระบบประสาท เช่น โรคอัลไซเมอร์ โรคนอนไม่หลับ เป็นต้น การตรวจจับคลื่นดังกล่าวในทางปฏิบัติทำได้โดย การประเมินจากแพทย์หรือผู้เชี่ยวชาญ ซึ่งใช้ระยะเวลานาน อีกทั้งมีโอกาสเกิดข้อผิดพลาดสูงจากความแปรปรวน ของหลายปัจจัย ไม่ว่าจะเป็นความชำานาญของผู้ประเมินหรือลักษณะของคลื่น Sleep spindle ในปัจจุบันมีการศึกษาการใช้ประโยชน์จากการเรียนรู้ของเครื่อง (Machine learning) ในการตรวจจับคลื่นสมองประเภท Sleep spindle แบบอัตโนมัติ โดยคาดหวังให้สามารถทำงานได้เทียบเท่ากับการประเมินของผู้เชี่ยวชาญ และสามารถแก้ปัญหาข้างต้นได้ ทั้งนี้ การทบทวนบทความที่เกี่ยวข้องยังคงมีจำนวนไม่มากนัก บทความนี้ศึกษาและเปรียบเทียบวิธีการที่นำมาใช้ใน การตรวจจับคลื่นสมองประเภท Sleep spindle แบบอัตโนมัติ โดยสรุปขั้นตอนการทำางานของการศึกษาได้เป็น การรวบรวมข้อมูล การจัดการกับข้อมูลคลื่นสมอง การเลือกคุณลักษณะ การสร้างโมเดล และการประเมินประสิทธิภาพของโมเดล โดยพบว่าการเรียนรู้ของเครื่อง (Machine learning) ถูกนำมาใช้อย่างหลากหลาย และการศึกษาที่ใช้โมเดลในกลุ่มที่เรียนรู้แบบมีผู้สอนโดยส่วนใหญ่สามารถตรวจจับ Sleep spindle ได้ตรงกับที่ผู้เชี่ยวชาญระบุ แต่ยังต้องมีการปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพของโมเดลให้เหมาะกับข้อมูลที่หลากหลายมากยิ่งขึ้น นอกจากนี้ในบทวิจารณ์ยังประกอบ ด้วยข้อเสนอแนะและความเป็นไปได้ในการศึกษาเพื่อพัฒนาต่อยอดต่อไปอีกด้วย
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
What are Sleep Deprivation and Deficiency? [Internet]. NHLBI, NIH. [cited 2022 Nov 11]. Available from: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/sleep-deprivation-anddeficiency
Memar P, Faradji F. A Novel Multi-Class EEGBased Sleep Stage Classification System. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering. 2018;26(1):84-95. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2017.2776149 PMid:29324406
In Recognition of World Sleep Day, Philips Presents Its Annual Global Sleep Survey Results [Internet]. Philips. 2019 [cited 2022 Nov 11]. Available from: https://www.philips. com/a-w/about/news/archive/standard/news/press/2019/20190307-in-recognitionof-world-sleep-day-philips-presents-itsannual-global-sleep-survey-results.html
Klem GH, Lüders HO, Jasper HH, Elger C. The Ten-twenty Electrode System of the International Federation. The International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl. 1999;52:3-6.
Born J, Wilhelm I. System consolidation of memory during sleep. Psychological Research. 2012;76(2):192-203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-011-0335-6 PMid:21541757 PMCid:PMC3278619
Astori S, Wimmer RD, Lüthi A. Manipulating sleep spindles - expanding views on sleep, memory, and disease. Trends in Neurosciences. 2013;36(12):738-748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2013.10.001 PMid:24210901
Gorgoni M, Lauri G, Truglia I, et al. Parietal Fast Sleep Spindle Density Decrease in Alzheimer's Disease and Amnesic Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neural Plasticity. 2016; 2016:e8376108 . https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8376108
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson AL, Quan S. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications. Westchester, IL: American Academy of Sleep Medicine. Published online January 1, 2007.
Danker-Hopfe H, Kunz D, Gruber G, et al. Interrater reliability between scorers from eight European sleep laboratories in subjects with different sleep disorders. Journal of Sleep Research. 2004;13(1):63-69. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2869.2003.00375.x PMid:14996037
Wendt SL, Welinder P, Sorensen HBD, et al. Inter-expert and intra-expert reliability in sleep spindle scoring. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2015;126(8):1548-1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2014.10.158 PMid:25434753 PMCid:PMC4426257
Güneş S, Dursun M, Polat K, Yosunkaya Ş. Sleep spindles recognition system based on time and frequency domain features. Expert Systems with Applications. 2011;38(3):2455- 2461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.08.034
Loomis Alfred L., Harvey E. Newton, Hobart Garret. Potential Rhythms of the Cerebral Cortex During Sleep. Science.1935;81(2111): 597-598. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.81.2111.597 PMid:17739875
De Gennaro L, Ferrara M. Sleep spindles: an overview. Sleep Medicine Reviews. 2003; 7(5):423-440. https://doi.org/10.1053/smrv.2002.0252 PMid:14573378
Berry RB, Wagner MH. Sleep Medicine Pearls E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2014.
Schönauer M, Pöhlchen D. Sleep spindles. Current Biology. 2018;28(19):R1129-R1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.07.035 PMid:30300592
Devuyst S, Dutoit T, Kerkhofs M. The DREAMS databases and assessment algorithm. Zenodo, Genève. Published online 2005.
Purcell SM, Manoach DS, Demanuele C, et al. Characterizing sleep spindles in 11,630 individuals from the National Sleep Research Resource. Nature Communications. 2017;8(1): 15930. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15930 PMid:28649997 PMCid:PMC5490197
Sitnikova E, Grubov V, Hramov AE. Slow-wave activity preceding the onset of 10-15-Hz sleep spindles and 5-9-Hz oscillations in electroencephalograms in rats with and without absence seizures. Journal of Sleep Research. 2020;29(6):e12927. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12927 PMid:31578791
Keenan S, Hirshkowitz M. Chapter 161 - Sleep Stage Scoring. In: Kryger M, Roth T, Dement WC, eds. Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine (Sixth Edition). Elsevier; 2017:1567-1575.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-24288-2.00161-6
Koubeissi MZ. Niedermeyer's Electroencephalography, Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and Related Fields, 6th ed. Archives of Neurology. 2011;68(11):1481-1481. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2011.251
Warby SC, Wendt SL, Welinder P, et al. Sleep-spindle detection: crowdsourcing and evaluating performance of experts, non-experts and automated methods. Nature Methods. 2014;11(4):385-392. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2855 PMid:24562424 PMCid:PMC3972193
Werth E, Achermann P, Dijk DJ, Borbély AA. Spindle frequency activity in the sleep EEG: individual differences and topographical distribution. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology. 1997;103(5):535-542. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4694(97)00070-9 PMid:9402884
Coppieters 't Wallant D, Maquet P, Phillips C. Sleep Spindles as an Electrographic Element: Description and Automatic Detection Methods. Timofeev I, ed. Neural Plasticity. 2016; 2016:6783812. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6783812 PMid:27478649 PMCid:PMC4958487
Parekh A, Selesnick IW, Osorio RS, Varga AW, Rapoport DM, Ayappa I. Multichannel sleepspindle detection using sparse low-rank optimization. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 2017;288:1-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2017.06.004 PMid:28600157
Nonclercq A, Urbain C, Verheulpen D, Decaestecker C, Van Bogaert P, Peigneux P. Sleep spindle detection through amplitude- frequency normal modelling. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 2013;214(2):192-203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.01.015 PMid:23370313
LaRocco J, Franaszczuk PJ, Kerick S, Robbins K. Spindler: a framework for parametric analysis and detection of spindles in EEG with application to sleep spindles. Journal of Neural Engineering. 2018;15(6):066015. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/aadc1c PMid:30132445
Patti CR, Penzel T, Cvetkovic D. Sleep spindle detection using multivariate Gaussian mixture models. Journal of Sleep Research. 2018; 27(4):e12614. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12614 PMid:29034521
Mei N, Grossberg MD, Ng K, Navarro KT, Ellmore TM. Identifying sleep spindles with multichannel EEG and classification optimization. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2017;89:441-453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.08.030 PMid:28886481 PMCid:PMC5650544
O'Reilly C, Gosselin N, Carrier J, Nielsen T. Montreal Archive of Sleep Studies: an open-access resource for instrument benchmarking and exploratory research. Journal of Sleep Research. 2014;23(6):628-635. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12169 PMid:24909981
Kulkarni PM, Xiao Z, Robinson EJ, et al. A deep learning approach for real-time detection of sleep spindles. Journal of Neural Engineering. 2019;16(3):036004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ab0933 PMid:30790769 PMCid:PMC6527330
T. Penzel, M. Glos, C. Garcia, C. Schoebel, I. Fietze. The SIESTA database and the SIESTA sleep analyzer. In: 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. ; 2011:8323-8326. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2011.6092052 PMid:22256276
Adamczyk M, Genzel L, Dresler M, Steiger A, Friess E. Automatic Sleep Spindle Detection and Genetic Influence Estimation Using Continuous Wavelet Transform. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 2015;9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00624 PMid:26635577 PMCid:PMC4652604
Peppard PE, Young T, Barnet JH, Palta M, Hagen EW, Hla KM. Increased Prevalence of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Adults. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2013; 177(9):1006-1014. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kws342 PMid:23589584 PMCid:PMC3639722
Lacourse K, Delfrate J, Beaudry J, Peppard P, Warby SC. A sleep spindle detection algorithm that emulates human expert spindle scoring. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 2019;316:3-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.08.014 PMid:30107208 PMCid:PMC6415669
Duman F, Erdamar A, Erogul O, Telatar Z, Yetkin S. Efficient sleep spindle detection algorithm with decision tree. Expert Systems with Applications. 2009;36(6):9980-9985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.01.061
Huupponen E, Gómez-Herrero G, Saastamoinen A, Värri A, Hasan J, Himanen SL. Development and comparison of four sleep spindle detection methods. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. 2007;40(3):157-170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2007.04.003 PMid:17555950
B. Babadi, S. M. McKinney, V. Tarokh, J. M. Ellenbogen. DiBa: A Data-Driven Bayesian Algorithm for Sleep Spindle Detection. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering.2012;59(2):483-493. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2011.2175225 PMid:22084041
T. Shimada, T. Shiina, Y. Saito. Detection of characteristic waves of sleep EEG by neural network analysis. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. 2000;47(3):369-379. https://doi.org/10.1109/10.827301 PMid:10743779
Darien, IL. Standard polysomnography. American Association of Sleep Technologists. 2012.
L. Wei, S. Ventura, M. Lowery, et al. Random Forest-based Algorithm for Sleep Spindle Detection in Infant EEG. In: 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). ; 2020:58-61. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9176339
Görür D, Halici U, Aydin H, Ongun G, Ozgen F, Leblebicioglu K. Sleep spindles detection using autoregressive modeling. In: ; 2003: 26-29.
Jung T-P, Makeig S, Humphries C, Lee T-W, McKeown MJ, Iragui V, et al. Removing Electroencephalographic Artifacts by Blind Source Separation. Psychophysiology. 2000; 37(2):163-78. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-8986.3720163
Jung TP, Makeig S, Westerfield M, Townsend J, Courchesne E, Sejnowski TJ. Removal of eye activity artifacts from visual eventrelated potentials in normal and clinical subjects. Clin Neurophysiol. 2000;111(10): 1745-1758. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-2457(00)00386-2 PMid:11018488
Danasingh AAGS, Subramanian A alias B, Epiphany JL. Identifying redundant features using unsupervised learning for highdimensional data. SN Applied Sciences. 2020;2(8):1367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-3157-6
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2022 ราชวิทยาลัยจุฬาภรณ์

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของราชวิทยาลัยจุฬาภรณ์
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับราชวิทยาลัยจุฬาภรณ์ และคณาจารย์ท่านอื่น ในราชวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว


