The Effect of a Self-Management Program on Blood Pressure Control Behavior of Hypertensive Patients
Keywords:
Self-Management Program, Hypertension-Controlling Behaviors, Hypertensive PatientsAbstract
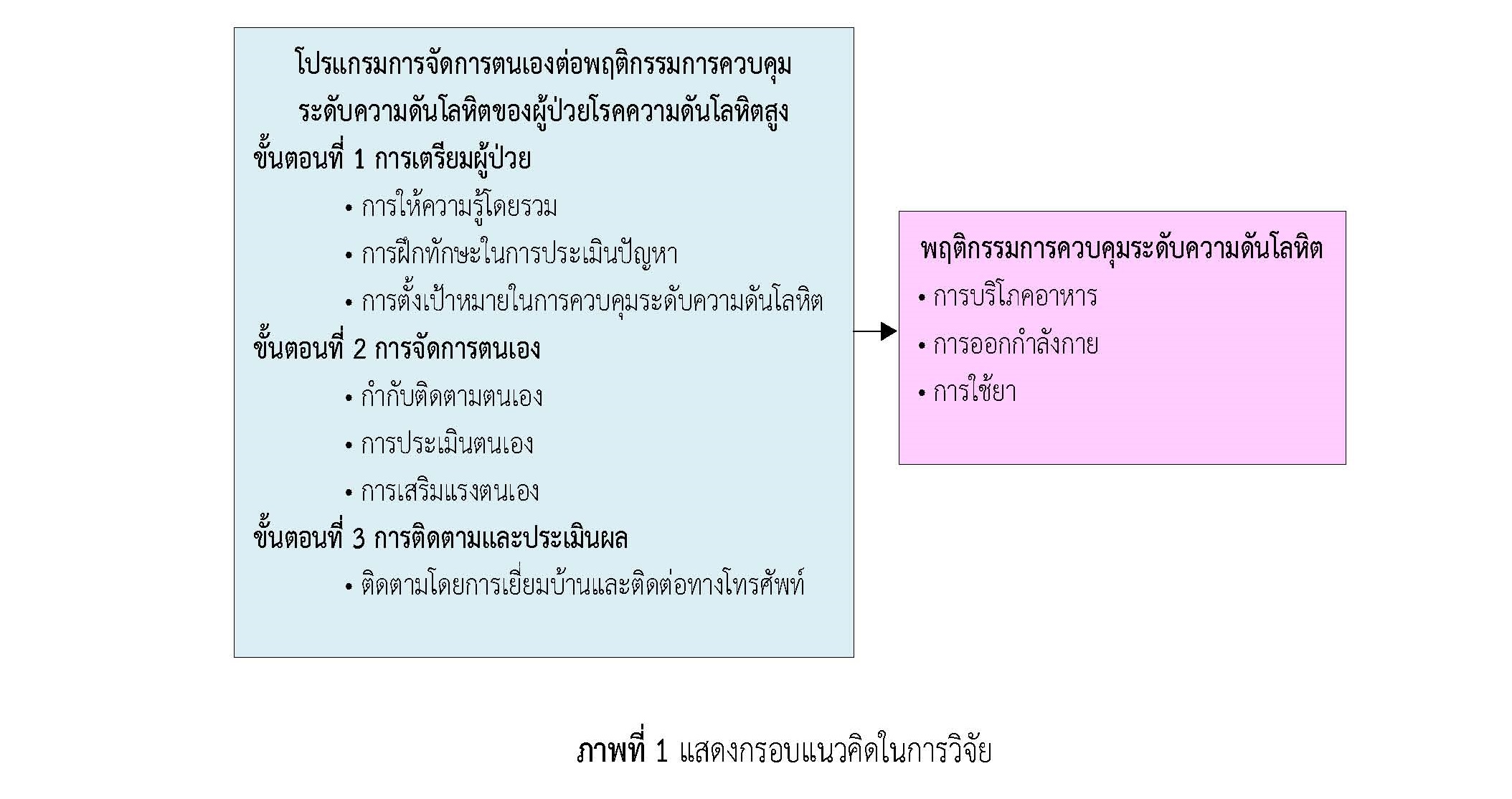
The objective of this quasi-experimental study was to examine the effect of a self-management program on blood pressure control behaviors among hypertensive patients. The self-management program proposed by the concept of (Kanfer and Gaelick-Buys, 1991). 27 participants were recruited by purposive sampling. Participants were diagnosed as hypertensive at Bang Riang Health Promotion Hospital, Khuan Niang District, Songkhla Province. The research instruments were a self-management program and the behavioral questionnaire for controlling blood pressure. The reliability of this questionnaire was 0.741. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and the Wilcoxon Sign Rank Test. The results showed that at 12-weeks after program completion, participants had significantly higher scores of hypertension-controlling behaviors (= 2.77 SD = 0.13) before enrolling in the program (
= 2.51, SD = 0.23) (z = -4.155, p-value <0.001). Our results suggested that a self-management program can be used to promote hypertensive-controlling behaviors in other areas in order to reduce the burden of hypertension and to maintain good health among hypertensive patients.
References
กรมควบคุมโรค กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. (2559).รายงานประจำปี 2559 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. [สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 มิ.ย. 2562]. เข้าถึงได้จาก http://thaincd.com/document/file/download/paper-manual/.pdf.
ธาริณี พังจุนันท์ และ นิตยา พันธุเวทย์. (2558) ประเด็นสารรณรงค์วัน ความดันโลหิตสูงโลก 2558. กรุงเทพฯ: สำนักงานโรคไม่ติดต่อ กรมควบคุมโรค กระทรวงสาธารณสุข.
เบญจมาศ ถาดแสง, ดวงฤดี ลาศุขะ, และทศพร คำผลศิริ. (2555). ผลของโปรแกรมสนับสนุนการจัดการตนเองต่อพฤติกรรมการจัดการตนเองและค่าความดันโลหิตของผู้สูงอายุที่มีโรคความดันโลหิตสูง. พยาบาลสาร, 39(4), 124-137.
ระบบคลังข้อมูลโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้อรัง จังหวัดสงขลา. (2562). รายงานจำนวนผู้ป่วยความดันโลหิตสูงที่รับบริการ. [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. [สืบค้นเมื่อ 5 ก.ค. 2562]. เข้าถึงได้จาก http://chronic.skho. moph.go.th/chronic/rep/htptvisit.php.
ศูนย์เทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศและการสื่อสาร สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข. (2561). กลุ่มรายงานมาตรฐาน. การป่วยด้วยโรคไม่ติดต่อที่สำคัญ. [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. [สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 มิ.ย. 2562]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://hdcservice.moph.go.th/hdc/main/Index pk.php.
ศิริวัฒน์ วงศ์พุทธคำ. (2551). ผลของการจัดการตนเองต่อพฤติกรรมสุขภาพและความดันโลหิตของผู้ป่วยความดันโลหิตสูง. วิทยานิพนธ์ปริญญาพยาบาลศาสตรมหาบัณฑิตสาขาวิชาการพยาบาลผู้ใหญ่, บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย, มหาวิทยาลัยเชียงใหม่.
สมพร เจือจันทึก. (2552). การประยุกต์ทฤษฎีแรงจูงใจเพื่อการป้องกันโรคและการมีส่วนร่วมของชุมชนในการป้องกันโรค ความดันโลหิตสูง อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดหนองคาย. วิทยานิพนธ์สาธารณสุขศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต มหาวิทยาลัย มหาสารคาม.
สำนักนโยบายและยุทธศาสตร์ สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข.(2562). จำนวนและอัตราผู้ป่วยในด้วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูง พ.ศ. 2556-2560 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. [สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 มิ.ย. 2562]. เข้าถึงได้จาก http://www.thaincdiof.com//information-statistic/non-communicable-disease- data.php.
สำนักโรคไม่ติดต่อ กรมควบคุมโรค. (2561). ประเด็นสารรณรงค์ วันความดันโลหิตสูงโลก ปี 2561. กรมควบคุมโรค กระทรวงสาธารณสุข [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2561 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 มิ.ย. 2562]. เข้าถึงได้จาก http://www.thai ncd.com/document/file/info/non-communi cable-disease/.pdf.
Kanfer, F. H., & Gaelick-Buys, L. (1991). Self-management methods. In F. Kanfer & A. Goldtein (Eds.), Helping people change: A text book of methods. (4th ed.). New York: Pergamonpress.
Medical Research Network of the Consortium of Thai Medical Schools. (2014). Summary of evaluation of care for patients with diabetes and hypertension 2010-2015. Retrieved from https://dmht.thaimedresnet.org/document/NHSO_DMHT_2561_OnTour1_REGIONS_7_8.pdf.
Orem, D. E.(1995). Nursing: Concept of practice (5th ed). St. Louis, MO: Mosby Year Book.
Phangjunan, T., & Phanthawet, N. (2015). Campaign issues for World Hypertension Day 2015. Retrieved from http://www.thaincd.com/media/leaflet/non-communicable-disease.php.
World Health Organization. (2015). Q & As on hypertension. Retrieved July 1, 2016. from http://www.who.int/features/qa/82/en/.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข








