ผลของโปรแกรมการปรึกษาการพัฒนาพฤติกรรมสุขภาพต่อการควบคุมระดับน้ำตาล ในเลือดและประสิทธิภาพการทำงานของไตของผู้ที่เป็นโรคเบาหวาน
คำสำคัญ:
โปรแกรมการปรึกษาการพัฒนาพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ, ระดับน้ำตาลในเลือด, อัตราการกรองของไต, โรคเบาหวานบทคัดย่อ
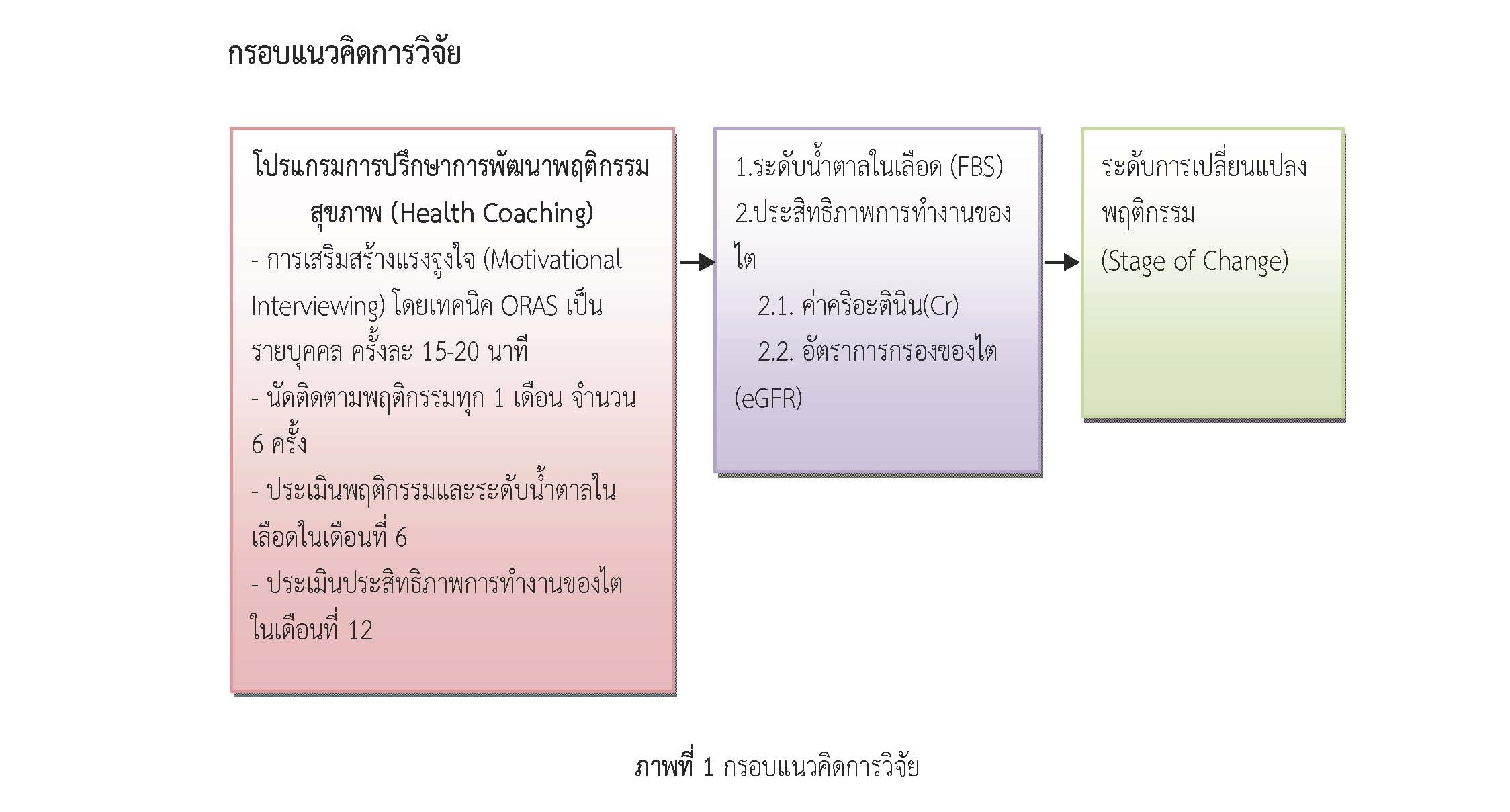
การวิจัยกึ่งทดลองนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาผลของโปรแกรมการปรึกษาการพัฒนาพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ (Health Coaching) ต่อการควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดและประสิทธิภาพการทำงานของไตของผู้ที่เป็นโรคเบาหวาน โรงพยาบาลร้องกวาง จังหวัดแพร่ ระหว่างเดือน มิถุนายน - ธันวาคม พ.ศ.2559 กลุ่มตัวอย่าง คือ ผู้ที่เป็นโรคเบาหวานที่ไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลได้ โดยมีระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดหลังงดอาหาร 8 ชั่วโมง (Fasting Blood Glucose (FBS)) มากกว่า 180 มิลลิกรัมเปอร์เซ็นต์ และมีค่าอัตราการกรองของไต (Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (e GFR)) อยู่ในช่วง 30-90 ml/min/1.73 m2 จำนวน 30 ราย เครื่องมือที่ใช้ดำเนินการวิจัย คือ โปรแกรมการปรึกษาพัฒนาพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ (Health Coaching) เป็นโปรแกรมที่ใช้ทักษะการเสริมสร้างแรงจูงใจ (Motivational Interviewing Skills (MI)) และทักษะการปรึกษา 4 ทักษะ โดยให้การปรึกษารายบุคคลครั้งละ 15-20 นาที นัดติดตามทุก 1 เดือน เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการเก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล ประกอบด้วยแบบบันทึกระดับน้ำตาลในเลือด (FBS) ระดับครีอะตินินในเลือด (Creatinine (Cr)) และอัตราการกรองของไต (eGFR) บันทึกในสมุดประจำตัวผู้ที่เป็นโรค ประเมินผลพฤติกรรมสุขภาพและระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดหลังให้การปรึกษา 6 เดือน ประเมินประสิทธิภาพการทำงานของไต 1 ปีหลังให้การปรึกษาวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลทั่วไปด้วยสถิติ ความถี่ ร้อยละ ค่าเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน เปรียบเทียบใช้ Paired T–Test. ผลการศึกษาพบว่ากลุ่มตัวอย่างหลังได้รับโปรแกรมการปรึกษาการพัฒนาพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ (Health Coaching) ค่าเฉลี่ยระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดลดลงอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ 0.05 ค่าเฉลี่ยระดับครีอะตินินในเลือดลดลงมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติระดับ 0.05 และอัตราการกรองของไตเฉลี่ยเพิ่มขึ้นอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ 0.05 ผลการวิจัยนี้แสดงให้เห็นว่า โปรแกรมการให้การปรึกษาเพื่อพัฒนาพฤติกรรมสุขภาพช่วยให้ผู้ที่เป็นโรคเบาหวานได้สำรวจตนเอง มองเห็นปัญหา เกิดแรงกระตุ้นภายใน จูงใจให้ตัดสินใจเปลี่ยนแปลงพฤติกรรมด้วยตนเอง ทำให้ผู้ที่เป็นโรคเบาหวานสามารถค้นพบวิธีการปฏิบัติตัวเพื่อให้สามารถควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลด้วยตนเอง และช่วยชะลอการเสื่อมของไตได้
เอกสารอ้างอิง
กรมควบคุมโรค. (2563). รายงานการสำรวจสุขภาพประชาชนไทยโดยการตรวจร่างกายครั้งที่ 6 พ.ศ.2562-2563. สืบค้นจากhttps://ddc.moph.go.th/dncd/ncdstrategy/public/home/media/142เมื่อวันที่ 19 ตุลาคม 2564.
งานโรคไม่ติดต่อโรงพยาบาลร้องกวาง. (2559). รายงานสถิติประจำปี. แพร่: ม.ป.ท.
จันจิรา หินขาว และ พรฤดี นิธิรัตน์. (2563). การสัมภาษณ์เพื่อสร้างแรงจูงใจแบบกลุ่มในการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรม ผู้ที่เป็นโรคเบาหวานที่ควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดไม่ได้. วารสารวิทยาลัยพยาบาลพระปกเกล้า จันทบุรี, 31(1), 205-212.
จุฑามาศ เทียนสะอาด. (2561). ผลของโปรแกรมการให้คำปรึกษาและการให้ความรู้ตามหลักการสัมภาษณ์ เพื่อเสริมสร้างแรงจูงใจต่อพฤติกรรมสุขภาพและผลลัพธ์ทางคลินิกในผู้ที่เป็นโรคโรคไตเรื้อรังก่อนได้รับการบำบัดทดแทนไต .วารสารการปฏิบัติการพยาบาลและการผดุงครรภ์ไทย, 5(2), 19-38.
ธวัชชัย วรพงศธร และ สุรีพันธ์ วรพงศธร. (2561). การคำนวณขนาดกลุ่มตัวอย่างสำหรับงานวิจัยโดยใช้โปรแกรมสำเร็จรูป G*power. Thailand Journal of Health Promotion and Environment Healthเมษายน-มิถุนายน 2561 สืบค้นจาก http://advisor.anamai.moph.go.th/download/Journal_health/2561/HEALTH41_2/HEALTH_Vol41No2_02.pdf.
ปิยะ วงษ์ไทยเจริญ. (2558). ผลการสัมภาษณ์เพื่อสร้างแรงจูงใจแบบกลุ่มต่อพฤติกรรมสุขภาพและระดับคอเรสเตอรอลของผู้ที่เป็นโรคความดันโลหิตสูง. วารสารราชพฤกษ์, 13(3), 91-102.
มุจลินท์ เรืองไพศาล และ กรแก้ว จันทภาษา. (2562). เหตุผลของความไม่ร่วมมือในการกินยาในมุมมองของผู้ที่เป็นโรคเบาหวานชนิดที่2: กรณีศึกษาโรงพยาบาลวาริชภูมิจังหวัดสกลนคร. วารสารเภสัชกรรมไทย, 12(2), 485.
วิจิตรา แพงชะ.(2559). ประสิทธิผลการดูแลผู้ที่เป็นโรคเบาหวานที่มีภาวะไตเสื่อมระยะ 2-4 ด้วยการจัดการรายกรณีเครือข่ายโรงพยาบาลน้ำหนาว อ.น้ำหนาว จ.เพชรบูรณ์. วารสารวิชาการแพทย์เขต 11, 31(3), 405-414.
สำนักโรคไม่ติดต่อ กรมควบคุมโรค. (2555). หลักสูตรการปรึกษาเพื่อปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมสุขภาพลดเสี่ยงลดโรคไม่ติดต่อ สำหรับบุคลากรสาธารณสุข. กรุงเทพฯ: ชุมนุมสหกรณ์การเกษตรแห่งประเทศไทย.
สำนักงานหลักประกันสุขภาพแห่งชาติ. (2554). แนวทางเวชปฏิบัติสำหรับโรคเบาหวาน พ.ศ.2554. กรุงเทพฯ: ศรีเมืองการพิมพ์ จำกัด.
อรวัลย์ เมฆเลื่อน. (2559). การศึกษาผลของการให้การปรึกษาแบบสร้างแรงจูงใจในการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมการสูบบุหรี่ของผู้ที่เป็นโรคโรคเรื้อรังที่ได้รับการบำบัดในคลินิกสุขภาพใจ โรงพยาบาลศรีประจันต์. วารสารวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี สุพรรณบุรี, 1(1), 38-48.
อัจฉรา ภักดีพินิจ และเมตตา คำพิบูลย์. (2554). มีเพื่อนคิดชีวิตก็เปลี่ยน(พฤติกรรม). นนทบุรี: สยามศิลป์การพิมพ์.
อนุสรณ์ พยัคฆาคม และ อัจฉรา ภักดีวิจิตร. (2555). (แปลจาก Health Change Associates, 2011). To change or not to change making a dicision one way the other. From www.healthchangeassociates.com.
Prochaska and DiClemente. (2011). Prochaska and DiClemente's Stages of Change Model for Social Workers. Retrieved from https://online.yu.edu/wurzweiler/blog/prochaska-and diclementes-stages-of-change-model-for-social-workers May 11, 2011.
Miller, W.R.& Rollnick,S. (2013). Motivational Interviewing: Helping people to change (3rd Edition) Guiford Press.
Miller&Rollniek. (1991). Motivational interviewing: Preparing people to change addictive behavior. The Guilford Press.
Retrieved from https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1991-98398-000.
Saeedi, P, Petersohn, I., Salpea, P. & Malanda, B. (2019). Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, (157), 4.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
เวอร์ชัน
- 2022-02-03 (2)
- 2022-02-03 (1)
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข







