The Effect of Health Literacy Program According to the 3E 2S Principle on Health Literacy, Preventive Behaviors, and Blood Pressure Levels among People in Hypertensive Risk Group
Keywords:
Health Promotion Model, 3E 2S, Health Literacy, Healthy Behaviors, Hypertensive Risk GroupAbstract
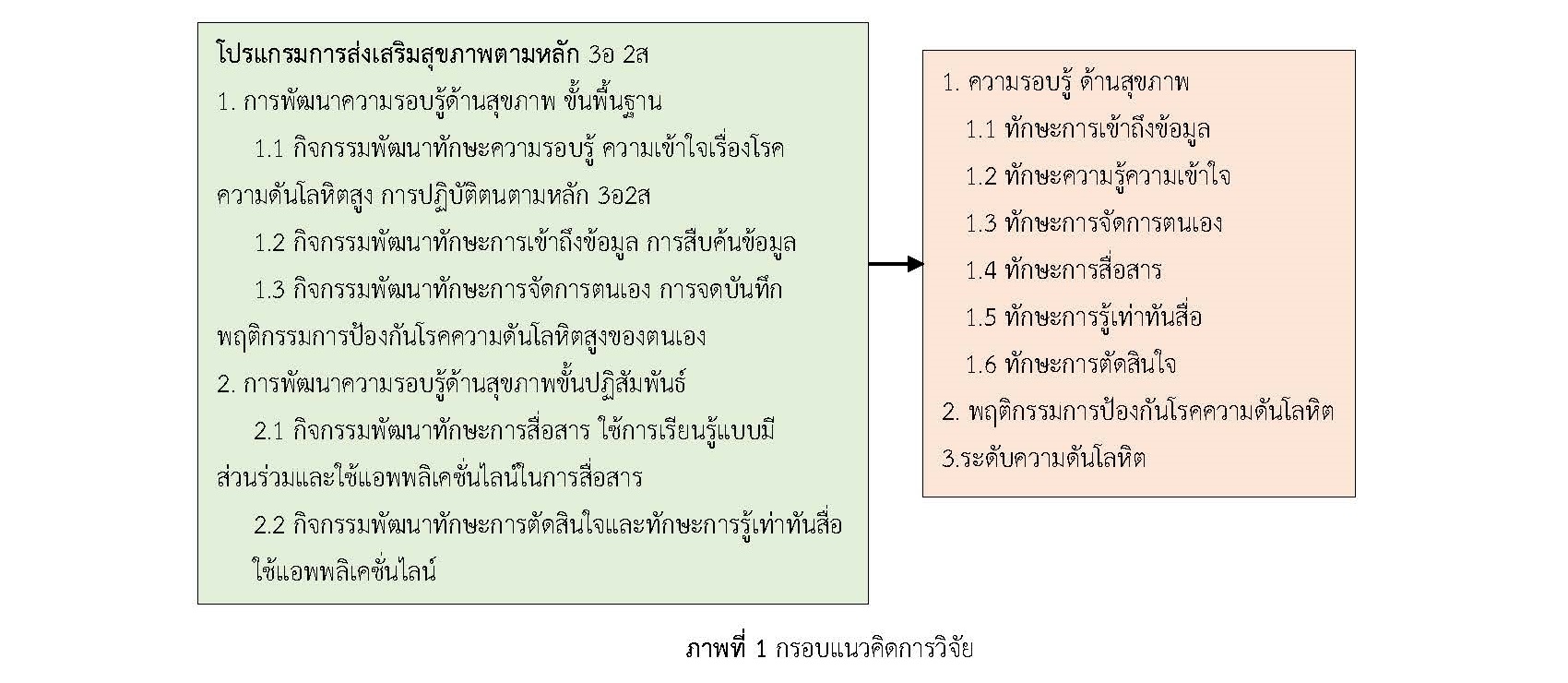
The objectives of this quasi-experimental research with a one-group pretest-posttest design were to compare the average scores of health literacy, preventive behaviors for high blood pressure, and blood pressure levels in people at risk of hypertension before and after attending a health literacy promotion program according to the 3E 2S principle. Participants were 42 people in the hypertension risk group in 2020, selected using a purposive sampling technique. Research instruments were a health literacy promotion program according to the 3E 2S principle, the health literacy assessment form with a confidence value of KR20 of 0.75, the access to information and health service assessment form, health communication, self-management, media literacy, the correct discrimination decision form according to the 3E 2S principle, and the behavioral assessment for preventing hypertension according to the 3E 2S principle with a confidence of 0.90, 0.83, respectively. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and a dependent t-test.
The results showed that after attending the program, participants in a hypertensive risk group had an average score on health literacy and behaviors in preventing hypertension that was statistically significantly higher than before receiving the program (p-value < 0.001). Also, systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels in participants in a hypertensive risk group were statistically significantly lower than before attending the program (p-value < 0.001). Therefore, health provider teams should apply this program as a guideline for promoting health literacy for people with hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or other chronic conditions in order to improve the patient's health behavior.
References
ทรัพย์ทวี หิรัญเกิด, พร้อมจิตร ห่อนบุญเหิม และสุรชาติ สิทธิปกรณ์. (2556). ผลของโปรแกรมปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมต่อความรอบรู้ พฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเอง และระดับความดันโลหิตของกลุ่มเสี่ยงโรคความดันโลหิตสูง. วารสารสมาคมพยาบาลฯ สาขาภาคตะวันออกเฉียงเหนือ, 31(4), 100-101.
นุชนาถ สำนัก, มาเรียม แอกูยิ, ตั้ม บุญรอด และกำไล สมรักษ์. (2554). ประสิทธิผลของโปรแกรมการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมสุขภาพของประชาชนกลุ่มเสี่ยงต่อโรคความดันโลหิตสูงในชุมชนหลักกิโลสาม ตำบลปากพนัง ฝั่งตะวันออก อำเภอปากพนัง จังหวัดนครศรีธรรมราช. วารสารการวิจัยสาธารณสุขศาสตร์มหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น, 4(2), 25-26.
นุสบา สันหละ. (2564). ผลของโปรแกรมการจัดการตนเองต่อพฤติกรรมการควบคุมระดับความดันโลหิตของผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูง. วารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข, 1(1), 37.
เนติยา แจ่มทิม และสินีพร ยืนยง. (2562). การใช้สื่อออนไลน์ และการรู้เท่าทันสื่อสารสนเทศสุขภาพออนไลน์ของผู้สูงอายุ จังหวัดสุพรรณบุรี. วารสารสุขภาพและการศึกษาพยาบาล, 25(2), 180.
ประภาศรี ภูมิถาวร, นงพิมล นิมิตรอานันท์ และศศิธร รุจนเวช. (2560). ผลของโปรแกรมการส่งเสริมความฉลาดทางสุขภาพสำหรับนักเรียนระดับ ประถมศึกษาที่มีภาวะน้ำหนักตัวเกิน. วารสาร โรงพยาบาลชลบุรี, 42(2), 169-178.
ยุภาพร นาคกลิ้ง และปราณี ทัดศรี. (2560). ผลของโปรแกรมการสร้างเสริมการรับรู้ความสามารถตนเองต่อพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ ของผู้สูงอายุโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่ควบคุมระดับความดันโลหิตไม่ได้. วารสารวิชาการสมาคมสถาบันอุดมศึกษาเอกชนแห่งประเทศไทย ในพระราชูปถัมภ์สมเด็จพระเทพรัตนราชสุดาฯ สยามบรมราชกุมารี ฉบับมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์, 6(1), 27-35.
รุ่งนภา อาระหัง. (2561). ผลของโปรแกรมการส่งเสริมความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพต่อพฤติกรรมการป้องกันโรคความดันโลหิตสูงสำหรับกลุ่มเสี่ยงโรคความดันโลหิตสูง ที่ชุมชนแห่งหนึ่งในจังหวัดนครปฐม. วิทยานิพนธ์ปริญญามหาบัณฑิต สาขาการพยาบาลเวชปฏิบัติชุมชน คณะพยาบาลศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยคริสเตียน.
ศรีรัตน์ อินถา และกิริยา คำนาน. (2566). ผลของโปรแกรมการสัมภาษณ์เพื่อสร้างแรงจูงใจร่วมกับการใช้โค้ชด้านสุขภาพของผู้ที่เป็นโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่มีโรคไตเรื้อรังระยะที่ 3 ต่อการบริโภคโซเดียมระดับความดันโลหิตและอัตราการกรองไต. วารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข, 3(1), 73-74.
สำนักงานสาธารณสุขจังหวัดสงขลา. (2563). กลุ่มรายงานมาตรฐาน การป่วยด้วยโรคไม่ติดต่อที่สำคัญ. สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 พฤศจิกายน 2563 จาก https://ska.hdc.moph.go.th/hdc/reports/report.php source=pformated/format1.php&cat_id=6a1fdf282fd28180eed7d1cfe0155e11&id=29 eec762c9591d1f8092da14c7462361
สำนักโรคไม่ติดต่อ กรมควบคุมโรค.(2563). ข้อมูลโรคไม่ติดต่อจำนวนอัตราป่วยตาย ปี 2559-2562. สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 พฤศจิกายน 2563 จาก http://www.thaincd.com/2016/mission/documentsdetail.php?id=13684&tid=32&gid=1-020.
สำนักโรคไม่ติดต่อ กรมควบคุมโรค.(2563). จำนวนและอัตราผู้ป่วยในโรคไม่ติดต่อ ปี 2558. สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 พฤศจิกายน 2563 จาก http://www.thaincd.com/2016/mission/documents.php?tid=32&gid=1-020&searchText=&pn=2.
สุภาพ พุทธปัญโญ, นิจฉรา ทูลธรรม และนันทิพัฒน์ พัฒนโชติ. (2559). ประสิทธิผลของโปรแกรมพัฒนาพฤติกรรมสุขภาพต่อความฉลาดทางสุขภาพ พฤติกรรมการลดน้ำหนัก และน้ำหนักของบุคลากรที่มีภาวะโภชนาการเกินในโรงพยาบาลร้อยเอ็ด อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดร้อยเอ็ด. วารสารการพยาบาลและการศึกษา, 9(4), 42-59.
อัมภรณ์รัตน์ มากแก้ว, สุทธีพร มูลศาสตร์ และมนตรี บุญเรืองเศษ. (2561). ประสิทธิผลของโปรแกรมเสริมแรงจูงใจผ่านการสื่อสารทางอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ในการป้องกันโรคความดันโลหิตสูงในกลุ่มเสี่ยง. วารสารพยาบาลสาธารณสุข, 32(3), 146.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. (2nd). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175-191.
Joint National Committee. (2003). The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood pressure. N.P.
Mackert, M., Mabry-Flynn, A., Champlin, S., Donovan, E. E., &Pounders, K. (2016). Health literacy and health information technology adoption: The potential for a new digital divide. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 18(10), e264. Doi:10.2196/jmir.6349
Nutbeam, D. (2000). Health literacy as a public health goal: a challenge for contemporary health education and community strategies into the 21st century. Health Promotion International, 15(3), 259-267.
Nutbeam, D. (2008). The evolving concept of health literacy. Social Science and Medicine, 67(12), 2072-2078.
Taggart, J et al., (2012). A systematic review of interventions in primary care to improve health literacy for chronic disease behavioral risk factors. BMC Family Practice, 13, 49.
Wu, S.L. et al. (2012). Prevalence of prehypertension and associated cardiovascular risk: two years follow up results. Zhonghua Xin Xua Guan Bing Za Zhi, 38(5), 415-419.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Nursing and Public Health Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข








