The Effects of Developing a Self-Management Model in Patients with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes, Banthi Hospital, Lamphun Province
Keywords:
Self-Management Model, Patients with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes, Uncontrolled Glycemic LevelsAbstract
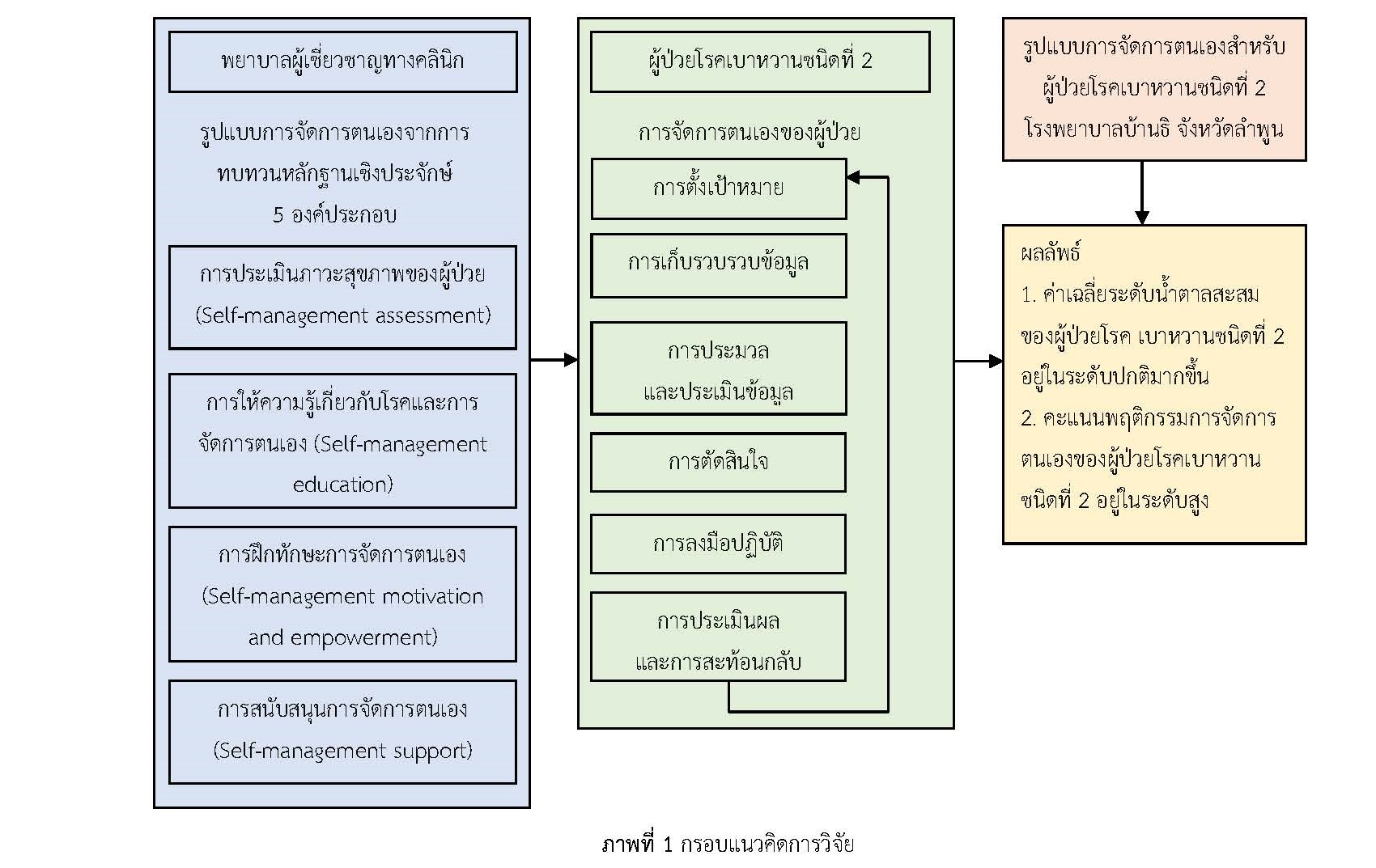
The objectives of this research and development study were to develop a self-management model in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes and compare the mean scores for self-management behavior and the mean cumulative glycemic scores of patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes before and after attending the program in Banthi Hospital, Lamphun Province. The self-management model was developed based on the self-management concepts of Sucup (2000) and Creer (2000). Participants were professional nurses in an Outpatient Department and 290 patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes. The research instrument was a Self-Management Model. Data collection instruments were a general record form, an assessment efficiency form of the self-management model, a diabetes knowledge questionnaire, and a self-management behavior assessment form. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and a paired t-test.
The results showed that a self-management model was highly effective in treating patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes (Mean = 66.80, S.D. = 25.09). After attending the program, the mean scores of self-management behaviors in terms of exercise and stress reduction statistically significantly increased more than before attending the program (p-value < 0.001). The mean cumulative glucose levels of the samples after attending the program statistically significantly decreased more than before enrolling in the program (p-value < 0.001). Based on the results of this study, nurses in a diabetes clinic could apply this self-management model to help patients act in a healthy way and keep their blood sugar levels under control.
References
กัลยกร ลักษณะเลขา, สมสมัย รัตนกรีฑากุล และสุวรรณา จันทร์ประเสริฐ. (2560). ผลของการชี้แนะต่อพฤติกรรมการจัดการตนเองและระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้เป็นเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ฉีดอินซูลิน. วารสารพยาบาลศาสตร์ จุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย, 29(1), 67- 89.
ญาณิสรา ปินตานา และนิทรา กิจธีระวุฒิวงษ์. (2561). ผลของโปรแกรมการจัดการตนเองต่อพฤติกรรมการจัดการตนเองของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2. วารสารพยาบาลศาสตร์และสุขภาพ, 12(1),72-83.
ดารารัตน์ อุ่มบางตลาด และศตกมล ประสงค์วัฒนา. (2560). ผลของโปรแกรมการดูแลผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 แบบเข้ม ต่อความรู้ พฤติกรรมการจัดการตนเองและระดับน้ำตาล ในเลือด ของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานใน PCU อำเภอบางปะอิน จังหวัดพระนครศรีอยุธยา. วารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและสุขภาพ, 18(1), 11-23.
ธัสมน นามวงษ์, รัชชนก กลิ่นชาติ, สุมาลี ราชนิยม, พนัชกร ค้าผล และนฤมล ทองภักดี. (2562). การพัฒนารูปแบบการส่งเสริมการจัดการตนเอง ผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานที่ควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลไม่ได้. วารสารพยาบาลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข, 29(3), 179-193.
พิกุล นันทชัยพันธ์. (2550). การประเมินคุณภาพด้านการนำไปใช้ของแนวปฏิบัติทางคลินิก: เอกสารประกอบการบรรยายการอบรม เรื่อง การปฏิบัติตามหลักฐานเชิงประจักษ์. กรุงเทพฯ: ศูนย์บริการพยาบาล คณะพยาบาลศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยเชียงใหม่.
เพ็ญบุญญา สัตยสมบูรณ์, สุวรรณี สร้อยสงค์, ภัณฑิรชา เฟื่องทอง และคุณญา แก้วทันคํา. (2563). ผลของโปรแกรมการจัดการตนเองต่อระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2. วารสารบัณฑิตศึกษา ปริทรรศน์ มจร วิทยาเขตแพร่, 6(1), 32-47.
ศูนย์ข้อมูลโรงพยาบาลบ้านธิ จังหวัดลำพูน. (2564). ข้อมูลโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้อรัง. ม.ป.ท.
สลิดา รันนันท์ และพาพร เหล่าสีนาท. (2562). พัฒนาแนวปฏิบัติทางการพยาบาลเพื่อส่งเสริมการจัดการตนเองของผู้ป่วยเบาหวาน ชนิดที่ 2 ที่ควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดไม่ได้ โรงพยาบาลกันทรวิชัย จังหวัดมหาสารคาม. วารสารโรงพยาบาลมหาสารคาม, 16(3), 138-148.
สหพันธ์เบาหวานนานาชาติ. (2564). สถิติโรคเบาหวาน. สืบค้นเมื่อ 27 มีนาคม 2565 จาก https://www.pptvhd36.com/health/news/2298
สำนักโรคไม่ติดต่อ กรมควบคุมโรค. (2565). ข้อมูลโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้อรัง. สืบค้นเมื่อ 27 มีนาคม 2565 จาก https://pr.moph.go.th/ url=pr/detail/2/02/181256
Banday, M. Z., Sameer, A. S., & Nissar, S. (2020). Pathophysiology of diabetes: An overview. Avicenna Journal of Medicine, 10(4), 174–188. https://doi.org/10.4103/ajm.ajm_53_20
Creer, L.T. (2000). Self-management of chronic illness. In: Boekaerts M, Pintrich PR, & Zeidner M, (eds). Handbook of self-regulation. California: Academic Press.
Papatheodorou, K., Banach, M., Bekiari, E., Rizzo, M., & Edmonds, M. (2018). Complications of Diabetes 2017. Journal of Diabetes Research, 3086167. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3086167
Soukup, S. M. (2000). Evidence-based Practice Model Promoting the Scholarship of Practice. In SM Soukup & CF Beason Eds. Nursing Clinic of North America. Philadelphia: WB Saunders.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Nursing and Public Health Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข








