The Effects of a Self-Management Program in Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3A to 4 Patients on Knowledge, Self- Management Behaviors, and Glomerular Filtration Rate, Sakaeo Crown Prince Hospital
Keywords:
A Self-Management Program, Knowledge, Behaviors, Slow Down Kidney Deterioration, Chronic kidney disease PatientsAbstract
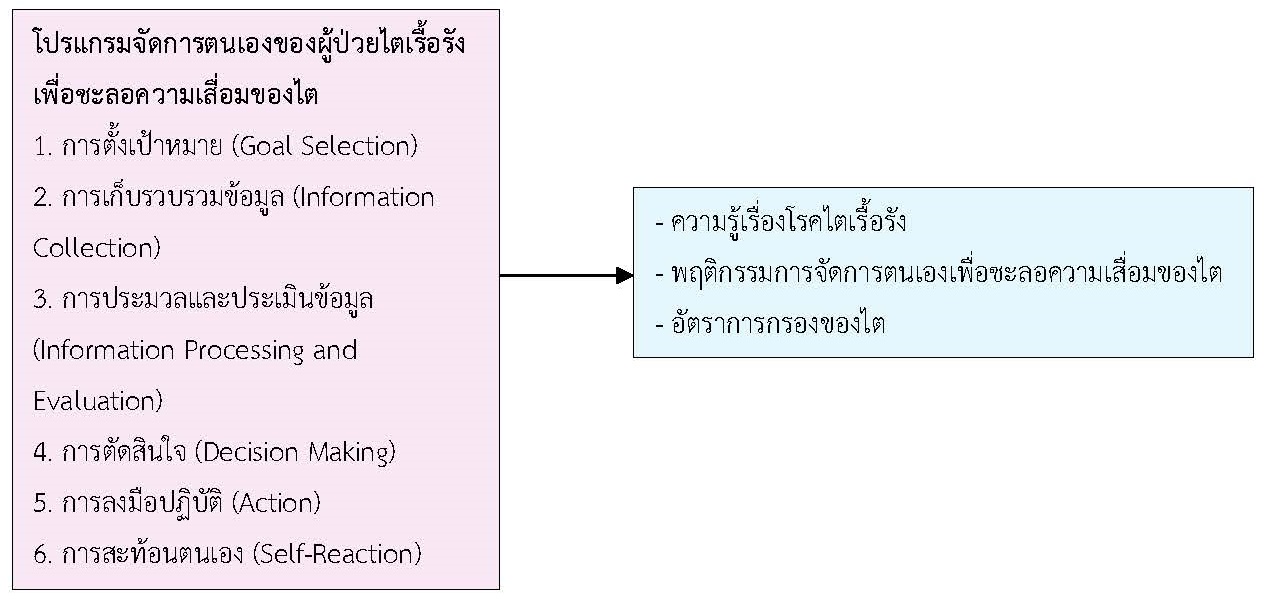
The objective of this quasi-experimental study was to examine the effects of a self-management program in chronic kidney disease stages 3a–4 patients on knowledge, self-management, and glomerular filtration rate at Sakaeo Crown Prince Hospital. Participants were 66 patients with chronic kidney disease stages 3A–4 who were selected by a random sampling technique. The study was conducted between September and November 2022. The research instrument was a self-management program, including three processes: 1) creating health knowledge; 2) developing self-management to slow down kidney deterioration; and 3) monitoring and evaluating behavioral performance in self-management to delay kidney deterioration. Data collection instruments were a demographic data questionnaire, a knowledge assessment form, a glomerular filtration rate recording form, and a self-management behavior assessment to slow down kidney deterioration. Data were analyzed using descriptive analysis to compare knowledge, self-management behavior, and the glomerular filtration rate before and after receiving the self-management program using paired t-test statistics.
The results showed that after receiving a self-management program, participants had a knowledge score about chronic kidney disease, self-management behaviors, and glomerular filtration rate that were higher than before receiving the self-management program (p-value < 0.001). It has been shown that a self-management program for patients with chronic kidney disease to slow down kidney deterioration has effectiveness. Nurses and other health providers can apply this self-management program to chronic kidney failure patients to promote knowledge, self-care behavior, and glomerular filtration rate in their own units.
References
กมลทิพย์ วิจิตรสุนทรกุล. (2565). ระบาดวิทยาและการทบทวนมาตรการป้องกันโรคไตเรื้อรัง. นนทบุรี: กองโรคไม่ติดต่อกรมควบคุมโรค.
กวิศรา สอนพูด และสัฆวี ปิยะบัณฑิตกุล. (2563). การดูแลสุขภาพเพื่อชะลอไตเสื่อมของผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวาน ความดันโลหิตสูงและประชาชนในชุมชนแห่งหนึ่ง จังหวัดศรีสะเกษ. วารสารพยาบาลสงขลานครินทร์, 40(1), 101-114.
ธิดารัตน์ อภิญญา. (2559). คู่มือปฏิบัติการเพื่อดำเนินงานลดโรคไตเรื้อรัง (CKD) ในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานและความดันโลหิตสูง. นนทบุรี: สำนักงานกิจการโรงพิมพ์ องค์กรสงเคราะห์ทหารผ่านศึก ในพระบรมราชูปถัมภ์.
เบญจวรรณ กล้าถิ่นภู, นงนุช โอบะ และสุภาพร แนวบุตร. (2563). ผลของโปรแกรมการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรม ต่อการควบคุมภาวะแทรกซ้อน ของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานที่มีภาวะแทรกซ้อนไตเรื้อรัง. วารสารสุขภาพและการศึกษาพยาบาล, 26(1), 58-70.
ปิยะดา ด้วงพิบูลย์. (2565). การพัฒนารูปแบบการเสริมสร้างทักษะในการจัดการตนเอง ด้านพฤติกรรมการรับประทานอาหารเพื่อการชะลอไตเสื่อมในผู้ป่วยไตเรื้อรัง คลินิกชะลอไตเสื่อม โรงพยาบาลวัดเพลง.วารสารวิจัยเพื่อการส่งเสริมสุขภาพและคุณภาพชีวิต, 2(3), 13-24.
ปุญญิศา วัจฉละอนันท์. (2562). การพัฒนาระบบการดูแลผู้ป่วยโรคไตเรื้อรังระยะ 3-4 โรงพยาบาลโนนสูง.วารสารอนามัยสิ่งแวดล้อมและสุขภาพชุมชน, 4(3), 15-25.
ระบบคลังข้อมูลด้านการแพทย์และสุขภาพ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. (2564). ข้อมูลผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานและโรคความดันโลหิตสูง โรงพยาบาลสมเด็จพระยุพราชสระแก้ว. สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 กันยายน 2565 จาก https://hdcservice.moph.go.th/hdc/main/index_pk.php)
รุ้งลาวัลย์ ยี่สุ่นแก้ว, สุรชาติ ณ หนองคาย, ชัยรัตน์ ฉายากุล และดุสิต สุจิรารัตน์. (2559). คุณภาพชีวิตของผู้ป่วยไตเรื้อรังระยะสุดท้ายที่ได้รับการฟอกเลือดด้วยเครื่องไตเทียมตามสิทธิที่กฎหมายกำหนด กรณีศึกษาโรงพยาบาลเอกชนแห่งหนึ่ง. วารสารวิชรสารการพยาบาล, 18(1), 79-88.
ลดาวัลย์ มาลัยเจริญ. (2564). ผลของโปรแกรมสนับสนุนการจัดการตนเองโดยใช้แถบสีสื่อสาร ต่อความรู้ เจตคติและการปฏิบัติตัวในผู้ป่วยไตเรื้อรังระยะ 1-3a. วารสารวิทยาลัยพยาบาลพระจอมเกล้า จังหวัดเพชรบุรี, 4(3), 109-121.
ศิริลักษณ์ ถุงทอง. (2560). การชะลอไตเสื่อมในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดได้. วารสารพยาบาลทหารบก, 18(พิเศษ), 17-24.
สุนิสา สีผม. (2556). การจัดการตนเองในผู้ป่วยไตเรื้อรัง. วารสารพยาบาลสภากาชาดไทย, 6(1), 12-18.
อัมพร จันทชาติ, มาลี มีแป้น และเพ็ญศรี จาบประไพ. (2560). การพัฒนารูปแบบการพยาบาลผู้ป่วยเบาหวานที่มีภาวะไตเรื้อรังระยะที่ 3 โดยใช้แนวคิดการจัดการตนเอง. วารสารสมาคมเวชศาสตร์ ป้องกันแห่งประเทศไทย, 7(3), 280-291.
Creer, L. T. (2000). Self-management of chronic illness. In Boekaerts, M., Printrich, P. R., & Zeidner, M. (Eds.). Handbook of self-regulation. pp. 601-629. San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A.-G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39, 175-191. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03193146
GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. (2020). Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet, 395(10225), 709-733. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30045-3
Herrington, W. G., et al. (2017). Body-mass index and risk of advanced chronic kidney disease: Prospective analyses from a primary care cohort of 1.4 million adults in England. PLoS One, 12(3), e0173515. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173515
Hill, N. R., et al. (2016). Global prevalence of chronic kidney disease: A Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 11(7), e0158765. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158765
Kobo, O., et al. (2023). CKD-associated cardiovascular mortality in the United States: Temporal trends from 1999 to 2020. Kidney Medicine, 5(3), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xkme.2022.100597
Xie, Y., et al. (2018). Analysis of the global burden of disease study highlights the global, regional, and national trends of chronic kidney disease epidemiology from 1990 to 2016. Kidney International, 94(3), 567-581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2018.04.011
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Nursing and Public Health Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข








