Development of a Nursing Practice Guideline for Patients with Ischemic and Obstructive Cerebrovascular Disease Treated with Cerebral Artery Catheterization at Udon Thani Hospital
Keywords:
Nursing Practice Guideline, Cerebral Artery Catheterization, Ischemic and Obstructive Cerebrovascular DiseaseAbstract
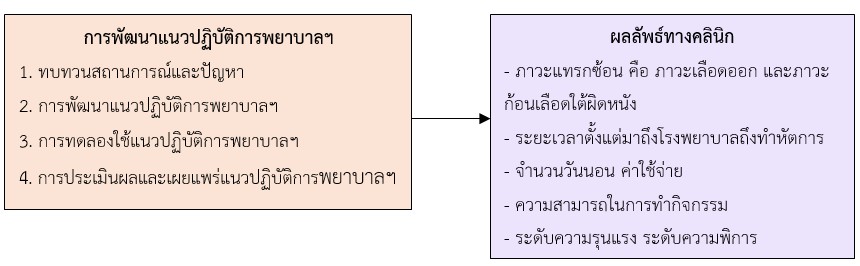
This research and development study aimed to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of nursing practice guidelines for patients with ischemic and obstructive cerebrovascular disease treated with cerebral artery catheterization at Udon Thani Hospital. The research process consisted of four phases: (1) reviewing the current situation and problems, (2) developing nursing practice guidelines, (3) implementing the guidelines, and (4) evaluating and disseminating the guidelines. The purposive sample included a guideline development team of 4 members, 30 professional nurses working in the emergency unit, stroke unit, and cerebral artery catheterization room, and 100 patients with ischemic and obstructive cerebrovascular disease treated with cerebral artery catheterization. The patients were divided into two groups: 50 in the control group and 50 in the experimental group. Research instruments included the developed nursing practice guidelines, an evaluation form for guideline implementation, and personal data recording forms for nurses and patients. Data analysis was conducted using descriptive statistics, Independent t-test, Chi-square test, and Paired t-test.
The research findings revealed that the nursing practice guidelines comprised four key components: 1) guidelines for screening patients with indications for cerebral artery catheterization; 2) nursing care before the procedure; 3) nursing care during the procedure; and 4) nursing care after the procedure. These guidelines resulted in 97.20% of nurses achieving an excellent level of performance. Clinical outcomes between the control and experimental groups showed that the experimental group had significantly fewer hospital days, reduced complications, lower levels of disability, and greater improvement in functional ability (p-value < 0.05). Therefore, these nursing practice guidelines are effective in preventing and reducing post-procedural complications in patients undergoing cerebral angiography and can be adapted for use in managing other vascular conditions at Udon Thani Hospital and its network facilities.
References
ธนบูรณ์ วรกิจธำรงชัย, ประสูตร ถาวรชัยสิทธิ์ และสุคนธา คงศีล. (2565). การวิเคราะห์ต้นทุนอรรถประโยชน์ของการรักษาผู้ป่วยโรคหลอดเลือดสมองตีบหรืออุดตันระยะเฉียบพลันด้วยสายสวนหลอดเลือดสมอง. วารสารวิจัยระบบสาธารณสุข, 16(4), 472-487.
ธนบูรณ์ วรกิจธำรงชัย. (2560). Endovascular treatment in acute ischemic stroke. วารสารสมาคมโรคหลอดเลือดสมองไทย, 16(3), 5-13.
โรงพยาบาลอุดรธานี. (2566). สถิติงานหอผู้ป่วยโรคหลอดเลือดสมอง. อุดรธานี: โรงพยาบาลอุดรธานี.
วีรยุทธ ศรีทุมสุข, ชัยยุทธ โคตะรักษ์, สุภลักษณ์ นอใส และพรชัย จูลเมตต์. (2562) บทบาทพยาบาลในการป้องกันภาวะแทรกซ้อนในผู้ป่วยโรคหลอดเลือดสมองตีบหรืออุดตันที่่ได้รับการรักษาผ่านสายสวนหลอดเลือดสมอง. วารสารพยาบาลทหารบก, 20(1), 47-55.
สถาบันประสาทวิทยา. (2558). แนวทางการพยาบาลผู้ป่วยโรคหลอดเลือดสมองสำหรับพยาบาลทั่วไป (Clinical nursing practice guideline for stroke). (ฉบับปรับปรุงครั้งที่ 4). กรุงเทพฯ. บริษัท ธนาเพลส จำกัด.
สถาบันประสาทวิิทยา. (2567). แนวทางการพยาบาลผู้ป่วยโรคหลอดเลือดสมองสำหรับพยาบาลทั่วไป (Clinical nursing practice guideline for stroke). (ฉบับปรับปรุงครั้งที่ 5). กรุงเทพฯ: บริษัท ธนาเพลส จำกัด.
สมศักดิ์ เทียมเก่า. (2566). อุบัติการณ์โรคหลอดเลือดสมองประเทศไทย. วารสารประสาทวิทยาแห่งประเทศไทย, 39(2), 39-46.
เสาวนีย์ หอมสุด. (2566). คู่มือการพยาบาลผู้ป่วยโรคหลอดเลือดสมองอุดตันเฉียบพลันที่รับการรักษาด้วยวิธีผ่านสายสวนหลอดเลือดสมองสมอง. กรุงเทพฯ: งานการพยาบาล ฝ่ายการพยาบาลโรงพยาบาลศิริราช คณะแพทยศาสตร์ศิริราชพยาบาล มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล.
อโนมา ศรีแสง. (2560). การใส่สายสวนหัวใจผ่านทางหลอดเลือดแดงที่ข้อมือ. เวชบันทึกศิริราช, 10(2), 90-96.
Calviere, L., et al. (2022). Rebleeding after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in two centers using different blood pressure management strategies. Frontiers in Neurology, 13, 836268. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2022.836268
Churojana, A. et al. (2017). Results of endovascular mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke in Siriraj Hospital. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand, 100(5), 588-597.
GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. (2021). Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet. Neurology, 20(10), 795-820. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0
He, Y., Wang, R., Dong, S., Long, S., Zhang, P., & Feng, L. (2023). Nurse-led rapid rehabilitation following mechanical thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A historical control study. Medicine, 102(28), e34232. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000034232
World Stroke Organization. (2019). Global stroke fact sheet 2019. Retrieved October 25, 2023 from http://www.world-stroke.org.
Yang, P., et al. (2022). Effect of cluster nursing on recovery effect and hospitalization time of patients with acute cerebral infarction after thrombectomy. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare, 15, 2503-2510. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S378509
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Nursing and Public Health Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใด ๆ ที่ปรากฏในวารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข ที่เป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน บรรณาธิการไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย
2. บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารวิจัยการพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุข








