Influences of calcium silicate cement modified in glass ionomer cement on human pulp tissue using tooth culture model
Main Article Content
Abstract
Objectives: To study the influence of experimental bioactive material-modified in glass ionomer cements on dentin mineralization and pulpal morphology in the tooth culture model.
Materials and Methods: Two experimental calcium silicate cement (Biodentine and MTA) modified in glass ionomer cement, glass ionomer cement (Fuji IXTM GP), and Biodentine were evaluated using a tooth culture model. The teeth were cultured for 28 days, then the histology procedure was performed and evaluated. The data was statistically analyzed using Fisher exact test analysis (α<0.05).
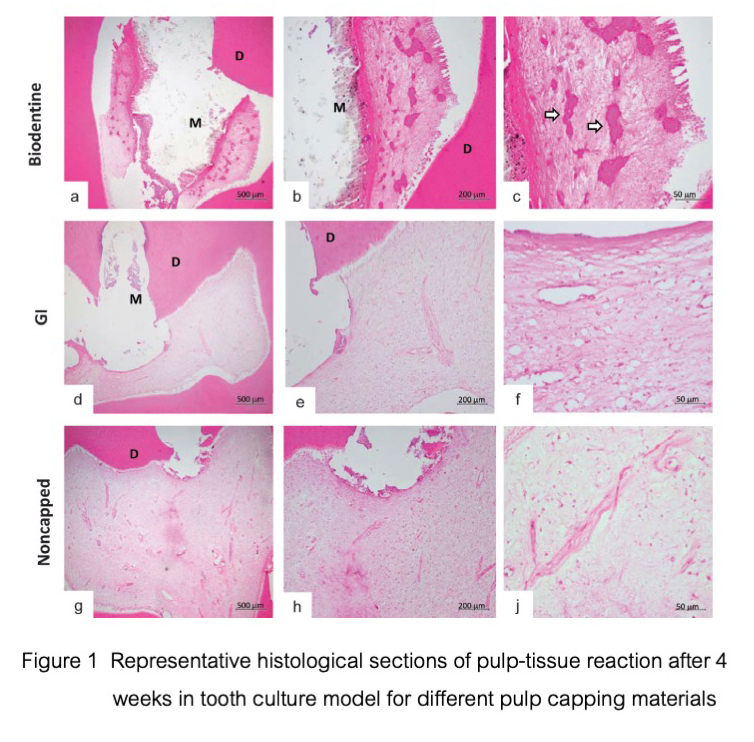
Results: Biodentine showed significantly higher mineralization nodules at 28 days among others. Whereas two experimental calcium silicate cement (Biodentine and MTA) modified in glass ionomer cement did not show mineralization potential. Besides, all experimental materials showed pulpal biocompatibility and promoted pulpal inflammatory healing.
Conclusions: Glass ionomer cement and the experimental calcium silicate cement modified glass ionomer cement were biocompatibility and promoted inflammation in the human pulp cell. However, the mineralization potential of these modified glass ionomer and glass ionomer cement was absent in this short period.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Stanley HR. Pulp capping: conserving the dental pulp--can it be done? Is it worth it? Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1989 Nov;68(5):628-639. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(89)90252-1.
AAE position statement on vital pulp therapy. J Endod. 2021 Sep;47(9):1340-1344. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2021.07.015.
Morotomi T, Washio A, Kitamura C. Current and future options for dental pulp therapy. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2019 Nov;55(1):5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2018.09.001.
Arandi NZ. Calcium hydroxide liners: a literature review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2017 Jul;9:67-72. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S141381.
Kunert M, Lukomska-Szymanska M. Bio-inductive materials in direct and indirect pulp capping-A review article. Materials (Basel). 2020 Mar;13(5):1204. doi: 10.3390/ma13051204.
de Souza Costa CA, Hebling J, Garcia-Godoy F, Hanks CT. In vitro cytotoxicity of five glass-ionomer cements. Biomaterials. 2003 Sep;24(21):3853-3858. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(03)00253-9.
Felton DA, Cox CF, Odom M, Kanoy BE. Pulpal response to chemically cured and experimental light-cured glass ionomer cavity liners. J Prosthet Dent. 1991 May;65(5):704-712. doi: 10.1016/0022-3913(91)90210-n.
Téclès O, Laurent P, Aubut V, About I. Human tooth culture: a study model for reparative dentinogenesis and direct pulp capping materials biocompatibility. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008 Apr;85(1):180-187. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.30933.
Pedano MS, Li X, Jeanneau C, Ghosh M, Yoshihara K, Van Landuyt K, et al. Survival of human dental pulp cells after 4-week culture in human tooth model. J Dent. 2019 Jul;86:33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2019.05.023.
Sangsuwan P, Tannukit S, Chotigeat W, Kedjarune-Leggat U. Biological activities of glass ionomer cement supplemented with fortilin on human dental pulp stem cells. J Funct Biomater. 2022 Aug;13(3):132. doi: 10.3390/jfb13030132.
Camilleri J, Laurent P, About I. Hydration of biodentine, Theracal LC, and a prototype tricalcium silicate-based dentin replacement material after pulp capping in entire tooth cultures. J Endod. 2014 Nov;40(11):1846-1854. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2014.06.018.
Chumpraman A, Tannukit S, Chotigeat W, Kedjarune-Leggat U. Biocompatibility and mineralization activity of modified glass ionomer cement in human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Sci. 2023 Jul;18(3):1055-1061. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2022.11.024.
da Silva JG, Babb R, Salzlechner C, Sharpe PT, Brauer DS, Gentleman E. Optimisation of lithium-substituted bioactive glasses to tailor cell response for hard tissue repair. J Mater Sci. 2017;52(15):8832-8844. doi: 10.1007/s10853-017-0838-7.
Jeong YN, Yang SY, Park BJ, Park YJ, Hwang YC, Hwang IN, et al. Physical and chemical properties of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2010;35(5):344-352. doi:10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.344.
Hilton TJ. Keys to clinical success with pulp capping: a review of the literature. Oper Dent. 2009 Sep-Oct;34(5):615-625. doi: 10.2341/09-132-0.
Pedano MS, Li X, Yoshihara K, Landuyt KV, Van Meerbeek B. Cytotoxicity and bioactivity of dental pulp-capping agents towards human tooth-pulp Cells: A Systematic review of in-vitro studies and meta-analysis of randomized and controlled clinical trials. Materials (Basel). 2020 Jun;13(12):2670. doi: 10.3390/ma13122670.
Tran ATL, Sukajintanakarn C, Senawongse P, Sritanaudomchai H, Ruangsawasdi N, Lapthanasupkul P, et al. Influence of Lithium- and Zinc-containing bioactive glasses on pulpal regeneration. Eur J Dent. 2023 Feb.. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1758789.