Association of religious and socio-cultural factors on dental service utilization among the elderly in Narathiwat, Thailand.
Main Article Content
Abstract
Objective: The objective is to explore the association between religious and socio-cultural factors on dental service uses of elderly.
Materials and Methods: This observational study used retrospective dental treatment data from public dental health services in Narathiwat Province collected from July to December 2022 to identify eligible elderly patients. All of the elderly patients with an ADL Barthel score of 12 or higher were recruited to participate in the study. Then, face-to-face interviews were conducted using questionnaires adapted from Penchansky and Thomas's framework on health-service accessibility. The analysis included descriptive statistics and chi-square tests.
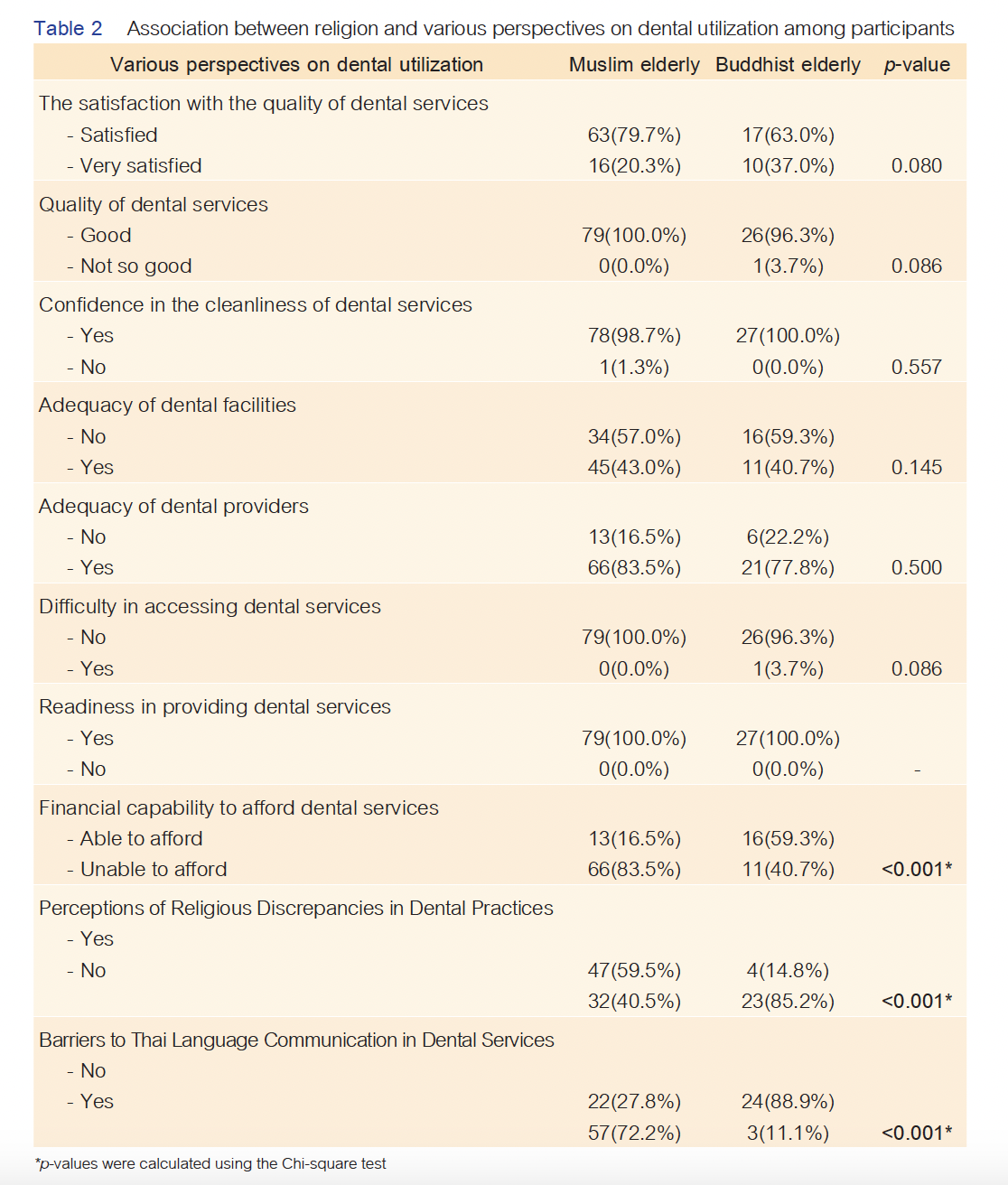
Results: A total of 106 elderly participated in the study. Most participants were female, aged 60-69, Muslims, and 47% had no formal education. Muslim-elderly-participants were more likely than Buddhists to report conflicts between dental procedures and religious principles. Additionally, 72.2% of Muslim elderly experienced difficulties in accessing services due to language barriers.
Conclusion: The study highlighted the significant association of socio-cultural factors on dental service utilization among the elderly in Thailand's southern border provinces. These findings emphasized the need for culturally sensitive public health policies, incorporating cultural awareness and language proficiency, to improve healthcare accessibility.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
ThaiPublica. When Thailand fully becomes an Aged Society, what welfare benefits do Thai elderly receive? 2024 [updated 10 February 2024; cited 2024 25 May]. Available from: https://thaipublica.org/2024/02/thailand-becomes-aged-society/.
Social Statistics Division, Office NS. The 2021 Health and Welfare Survey. Bangkok: THANA PLACE CO., LTD.; 2021.
Nitschke I, Stillhart A, Kunze J. Utilization of dental services in old age. Swiss Dent J. 2015;125(4):433-447. doi: 10.61872/sdj-2015-04-03.
Spinler K, Aarabi G, Valdez R, Kofahl C, Heydecke G, Konig HH, et al. Prevalence and determinants of dental visits among older adults: findings of a nationally representative longitudinal study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019 Aug;19(1):590. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-4427-0.
Soares GH, Ortiz-Rosa E, Alves CP, Paz D, An KS, Pereira AC, et al. Factors associated with utilisation of dental services by the elders from Sao Paulo, Brazil. Gerodontology. 2021 Jun;38(2):216-227. doi: 10.1111/ger.12519.
Wongsasauluk Y, Srithong N. Assessing Oral Health Care Utilization Patterns among Thai Seniors: a Study on Elderly Dental Services. J Health Sci Thailand. 2024 Feb;33(1):49-62.
Chiraporn Khitdee, Noppawan Pochanukul, Pattraporn Hasadisevee, Nanmanas Yaebut, Orachad Gururatana, Voramon Agrasuta, et al. Thailand 9th National Oral Health Survey. Nonthaburi: Aksorn Graphic and Design publication limited partnership 2024:p.404.
Penchansky R, Thomas JW. The concept of access: definition and relationship to consumer satisfaction. Med Care. 1981 Feb;19(2):127-40. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198102000-00001.
Ghanbari-Jahromi M, Bastani P, Jalali FS, Delavari S. Factors affecting oral and dental services; utilization among Elderly: a scoping review. BMC Oral Health. 2023 Aug;23(1):597. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03285-4.
Herkrath FJ, Vettore MV, Werneck GL. Contextual and individual factors associated with dental services utilisation by Brazilian adults: A multilevel analysis. PLoS One. 2018 Feb;13(2):e0192771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192771.
Drachev SN, Puriene A, Aleksejuniene J, Stankeviciene I, Stangvaltaite-Mouhat L. Prevalence of and factors associated with dental service utilization among early elderly in Lithuania. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Jan;22(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-07388-y.
The Bureau of Registration Administration DOPA. Monthly Population Registration Statistics 2022 [Available from: https://stat.bora.dopa.go.th/stat/statnew/statMONTH/statmonth/#/view.
Paisi M, Baines R, Burns L, Plessas A, Radford P, Shawe J, et al. Barriers and facilitators to dental care access among asylum seekers and refugees in highly developed countries: a systematic review. BMC Oral Health. 2020 Nov;20(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s12903-020-01321-1.
Prasongsuk P. Access to dental services among the elderly in Chonburi province: Burapha University; 2017.
Saengtipbovorn S. Factors associated with the utilization of dental health services by the elderly patients in Health Center No.54, Bangkok, Thailand [Pub Health - Theses]. Chulalongkorn University: Chulalongkorn University; 2011.
Subbowon U. Factors related to utilization of dental services among elderly in Nakhonchaisi Subdistrict, Nakhonchaisi District, Nakhon Pathom Province. REGION 4-5 Medical J. 2019;37(4):306-317.
General Information of Si Sakhon district 2019 [updated 01 April 2019. Available from: http://gishealth.moph.go.th/healthmap/info_history.php?maincode=11439.
Olerud E, Hagman-Gustavsson ML, Gabre P. Experience of dental care, knowledge and attitudes of older immigrants in Sweden-A qualitative study. Int J Dent Hyg. 2018 May;16(2): e103-e11. doi: 10.1111/idh.12325.
Flores G. The impact of medical interpreter services on the quality of health care: a systematic review. Med Care Res Rev. 2005 Jun;62(3):255-99. doi: 10.1177/1077558705275416.