Effects of 40% hydrogen peroxide on the surface roughness and biofilm formation of three different types of resin composites
Main Article Content
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the effects of hydrogen peroxide on three different resin composites (Z250: microhybrid, Z250XT: nanohybrid, and Z350XT: nanocomposite) in terms of surface roughness alteration and biofilm formation.
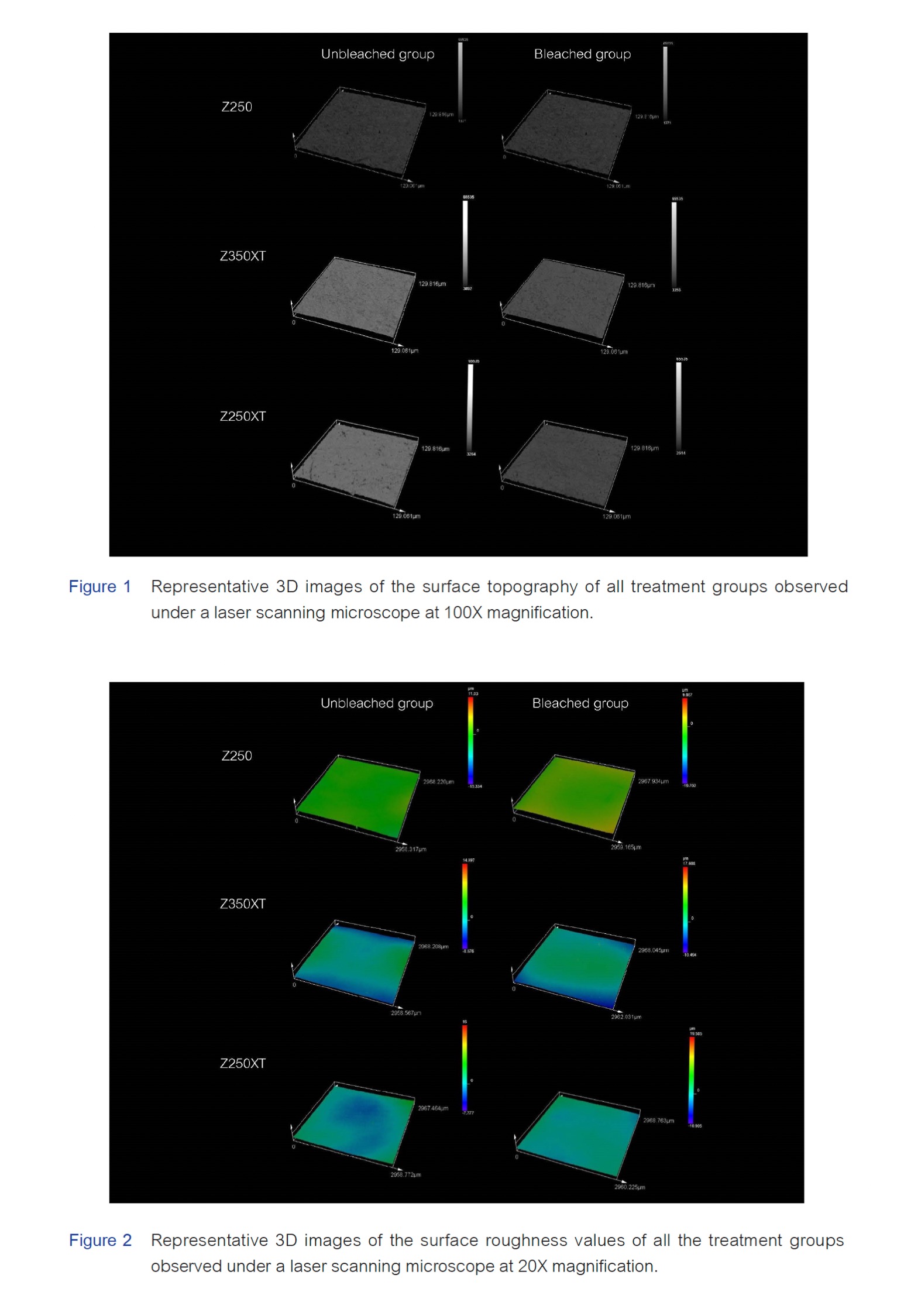
Materials and Methods: Forty-two samples were prepared from each material and then randomly divided into two groups for investigation. In total, 20 samples were used to determine the surface roughness, and the remaining 22 samples were used to determine biofilm formation. Finally, the samples were divided into two subgroups: the bleached group and the nonbleached group. In the bleached group, the samples were bleached with 40% hydrogen peroxide (opalescence boost). The bleaching procedures were conducted following the manufacturer’s instructions. The surface roughness was assessed using an arithmetical mean height of an area (Sa) by a laser scanning microscope. For biofilm measurement, S. mutans was cultured on each sample coated with the acquired pellicle and stained with a Live/Dead Bac LightTM Bacterial Viability Kit. Biofilm formation was measured under a confocal laser scanning microscope.
Results: The surface roughness significantly differed among the three groups of materials without bleaching (p=0.000) and with bleaching (p=0.000). The roughness of Z250 was significantly greater than that of the other two samples, while no significant difference between Z350XT and Z250XT was observed. Compared with that of the samples without bleaching, the surface roughness of the three types of resin composites was significantly different (p<0.05). For biofilm formation, no significant differences among the groups were observed.
Conclusions: Bleaching affected the Sa of three different types of resin composites, but the change in Sa had no effect on the average volume of colonies at the substratum of S. mutans biofilms. The resin-based materials Z250, Z350XT and Z250XT represent potentially suitable materials for aesthetic restoration, and the 40% hydrogen peroxide bleaching agent had no adverse effects.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Kielbassa AM. Tooth bleaching--increasing patients' dental awareness. Quintessence Int. 2006 Oct;37(9):673.
Baldissera RA, Corrêa MB, Schuch HS, Collares K, Nascimento GG, Jardim PS, et al. Are there universal restorative composites for anterior and posterior teeth? J Dent. 2013 Nov;41(11):1027-1035. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2013.08.016.
Attin T, Paqué F, Ajam F, Lennon AM. Review of the current status of tooth whitening with the walking bleach technique. Int Endod J. 2003 May;36(5):313-329. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2591.2003.00667.x.
Wongpraparatana I, Matangkasombut O, Thanyasrisung P, Panich M. Effect of vital tooth bleaching on surface roughness and streptococcal biofilm formation on direct tooth-colored restorative materials. Oper Dent. 2018 Jan/Feb;43(1):51-59. doi: 10.2341/16-366-L.
Angerame D, De Biasi M. Do nanofilled/nanohybrid composites allow for better clinical performance of direct restorations than traditional microhybrid composites? a systematic review. Oper Dent. 2018 Jul/Aug;43(4):E191-E209. doi: 10.2341/17-212-L.
Mitra SB, Wu D, Holmes BN. An application of nanotechnology in advanced dental materials. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003 Oct;134(10):1382-1390. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2003.0054.
Nedeljkovic I, Teughels W, De Munck J, Van Meerbeek B, Van Landuyt KL. Is secondary caries with composites a material-based problem? Dent Mater. 2015 Nov;31(11):e247-277. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2015.09.001.
Wattanapayungkul P, Yap AU, Chooi KW, Lee MF, Selamat RS, Zhou RD. The effect of home bleaching agents on the surface roughness of tooth-colored restoratives with time. Oper Dent. 2004 Jul-Aug;29(4):398-403.
Turker SB, Biskin T. Effect of three bleaching agents on the surface properties of three different esthetic restorative materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2003 May;89(5):466-473. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3913(03)00105-7.
Komalsingsakul A, Srisatjaluk RL, Senawongse P. Effect of brushing on surface roughness, fluoride release, and biofilm formation with different tooth-colored materials. J Dent Sci. 2022 Jan;17(1):389-398. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.08.013.
Bahari M, Ebrahimi Chaharom ME, Daneshpooy M, Gholizadeh S, Pashayi H. Effect of bleaching protocols on surface roughness and biofilm formation on silorane-based composite resin. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2019 Jul-Aug;16(4):264-270.
Kaya S, Bektas O. Effect of in-office bleaching on the surface roughness of different composite resins. Cumhuriyet Dental Journal. 2022;25:78-82. doi: 10.7126/cumudj.1030957.
Jefferies SR. The art and science of abrasive finishing and polishing in restorative dentistry. Dent Clin North Am. 1998 Oct;42(4):613-627. PMID: 9891644.
Komalsingsakul A, Klaophimai A, Srisatjaluk RL, Senawongse P. Effect of the surface roughness of composite resins on the water contact angle and biofilm formation. Mahidol Dent J 2019;39(2):75-84.
Senawongse P, Pongprueksa P. Surface roughness of nanofill and nanohybrid resin composites after polishing and brushing. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2007;19(5):265-273; discussion 274-275. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8240.2007.00116.x.
Da Silva EM, Giannini M, Ambrosano GM, Price RB. Polishing effect on the surface roughness of nanofill and nanohybrid composites. Oper Dent. 2008;33(6):642-7.
Turssi CP, Ferracane JL, Serra MC. Abrasive wear of resin composites as related to finishing and polishing procedures. Dent Mater. 2005 Jul;21(7):641-648. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2004.10.011.
Bollen CM, Lambrechts P, Quirynen M. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: a review of the literature. Dent Mater. 1997 Jul;13(4):258-269. doi: 10.1016/s0109-5641(97)80038-3.
Teughels W, Van Assche N, Sliepen I, Quirynen M. Effect of material characteristics and/or surface topography on biofilm development. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006 Oct;17 Suppl 2:68-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2006.01353.x.
Bailey SJ, Swift EJ Jr. Effects of home bleaching products on composite resins. Quintessence Int. 1992 Jul;23(7):489-494.
Wattanapayungkul P, Yap AU. Effects of in-office bleaching products on surface finish of tooth-colored restorations. Oper Dent. 2003 Jan-Feb;28(1):15-19.
Durner J, Stojanovic M, Urcan E, Spahl W, Haertel U, Hickel R, et al. Effect of hydrogen peroxide on the three-dimensional polymer network in composites. Dent Mater. 2011 Jun;27(6):573-580. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2011.02.013.
Söderholm KJ, Zigan M, Ragan M, Fischlschweiger W, Bergman M. Hydrolytic degradation of dental composites. J Dent Res. 1984 Oct;63(10):1248-1254. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630101701.
Vishwakarma P, Karale R, Srirekha A, Hegde J, Savitha B, Srinivasan A. The effect of home bleaching agents on the surface roughness and fracture toughness of composite resin materials. Dentistry. 2014;4(7). doi: 10.4172/2161-1122.1000246.
Gladys S, Van Meerbeek B, Braem M, Lambrechts P, Vanherle G. Comparative physico-mechanical characterization of new hybrid restorative materials with conventional glass-ionomer and resin composite restorative materials. J Dent Res. 1997 Apr;76(4):883-894. doi: 10.1177/00220345970760041001.
Attin T, Hannig C, Wiegand A, Attin R. Effect of bleaching on restorative materials and restorations--a systematic review. Dent Mater. 2004 Nov;20(9):852-861. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2004.04.002.
Ryba TM, Dunn WJ, Murchison DF. Surface roughness of various packable composites. Oper Dent. 2002 May-Jun;27(3):243-247.
Ikeda M, Matin K, Nikaido T, Foxton RM, Tagami J. Effect of surface characteristics on adherence of S. mutans biofilms to indirect resin composites. Dent Mater J. 2007 Nov;26(6):915-923. doi: 10.4012/dmj.26.915.
Kantorski KZ, Scotti R, Valandro LF, Bottino MA, Koga-Ito CY, Jorge AO. Surface roughness and bacterial adherence to resin composites and ceramics. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2009;7(1):29-32.
Kimyai S, Lotfipour F, Pourabbas R, Sadr A, Nikazar S, Milani M. Effect of two prophylaxis methods on adherence of Streptococcus mutans to microfilled composite resin and giomer surfaces. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011 Jul ;16(4):e561-567. doi: 10.4317/medoral.16.e561.
Mohammadi N, Kimyai S, Abed-Kahnamoii M, Ebrahimi-Chaharom ME, Sadr A, Daneshi M. Effect of 15% carbamide peroxide bleaching gel on color stability of giomer and microfilled composite resin: an in vitro comparison. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012 Nov ;17(6):e1082-1088. doi: 10.4317/medoral.17916.
Hosoya N, Honda K, Iino F, Arai T. Changes in enamel surface roughness and adhesion of Streptococcus mutans to enamel after vital bleaching. J Dent. 2003 Nov;31(8):543-548. doi: 10.1016/s0300-5712(03)00109-x.
Rosentritt M, Hahnel S, Gröger G, Mühlfriedel B, Bürgers R, Handel G. Adhesion of Streptococcus mutans to various dental materials in a laminar flow chamber system. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008 Jul;86(1):36-44. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.30985.
Mitra SB, Sakaguchi RL. Chapter 9 - Restorative Materials—Composites and polymers. In: Sakaguchi RL, Powers JM, editors. Craig's Restorative Dental Materials (Thirteenth Edition). Saint Louis: Mosby; 2012. p. 161-198. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-08108-5.10009-X.